Tratamiento axilar para el cáncer de mama primario operable
Resumen
Antecedentes
La intervención quirúrgica axilar es una parte establecida del tratamiento del cáncer de mama primario. Proporciona la información del estadiaje para guiar el tratamiento adyuvante y, potencialmente, el control local de la enfermedad axilar. Se dispone de varios abordajes alternativos para la intervención quirúrgica axilar, y la mayoría están orientados a evitarle a un grupo de pacientes la morbilidad de la disección axilar completa.
Objetivos
Evaluar los efectos beneficiosos y perjudiciales de los enfoques alternativos a la intervención quirúrgica axilar (incluida la omisión de la intervención quirúrgica) en cuanto a la supervivencia general; las recidivas locales, regionales y distantes; y eventos adversos.
Métodos de búsqueda
Se hicieron búsquedas en el registro especializado del Grupo Cochrane de Cáncer de Mama (Cochrane Breast Cancer Group Specialised Register), MEDLINE, Pre‐MEDLINE, Embase, CENTRAL, la World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform y en ClinicalTrials.gov el 12 marzo 2015 sin restricciones de idioma. También se contactó con los autores de los estudios y se verificaron las listas de referencias.
Criterios de selección
Ensayos controlados aleatorios (ECA) en pacientes con cáncer de mama primario operable, definido clínicamente, realizados para comparar la disección de ganglios linfáticos axilares (DGLA) con ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar, el muestreo axilar o la biopsia de ganglios linfáticos centinela (BGLC); ECA que compararan el muestreo axilar con la BGLC o ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar; ECA que compararan la BGLC con ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar; y ECA que compararan la DGLA con o sin radioterapia (RT) versus RT sola.
Obtención y análisis de los datos
Dos autores de la revisión evaluaron independientemente cada ensayo potencialmente relevante para su inclusión. Se extrajeron de forma independiente los datos de resultado, los datos sobre el riesgo de sesgo y las características de los estudios de todos los ensayos incluidos. Se agruparon los datos según las intervenciones de los ensayos, y se usaron los cocientes de riesgos instantáneos (CRI) para los resultados del tiempo transcurrido hasta el evento y los odds ratios (OR) para los resultados binarios.
Resultados principales
Se incluyeron 26 ECA en esta revisión. Los estudios presentaban un riesgo de sesgo bajo o incierto. No hubo cegamiento, aunque este hecho sólo fue considerado una fuente de sesgo para los resultados con posibilidad de subjetividad en las mediciones. No se encontró ningún ECA de muestreo axilar versus BGLC, muestreo axilar versus ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar o BGLC versus ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar.
Ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar versus DGLA
Diez ensayos con 3849 participantes no compararon ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar versus DGLA. Las pruebas de calidad moderada no mostraron ninguna diferencia importante entre la supervivencia general de las pacientes de los dos grupos (CRI 1,06; intervalo de confianza [IC] del 95%: 0,96 a 1,17; 3849 participantes; 10 estudios), aunque con ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar aumentó el riesgo de recidiva locorregional (CRI que varió de 1,10 a 3,06; 20 863 personas‐años de seguimiento; cuatro estudios). Era incierto si ninguna intervención quirúrgica aumentó el riesgo de metástasis distante en comparación con la DGLA (CRI 1,06; IC del 95%: 0,87 a 1,30; 946 participantes; dos estudios). Las pruebas de baja calidad indicaron que ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar disminuyó el riesgo de linfedema en comparación con la DGLA (OR 0,31; IC del 95%: 0,23 a 0,43; 1714 participantes; cuatro estudios).
Muestreo axilar versus DGLA
Seis ensayos con 1559 participantes compararon el muestreo axilar versus la DGLA. Las pruebas de baja calidad indicaron una efectividad similar del muestreo axilar en comparación con la DGLA en cuanto a la supervivencia general (CRI 0,94; IC del 95%: 0,73 a 1,21; La efectividad relativa del muestreo axilar y la DGLA para la recidiva locorregional (CRI 0,74; IC del 95%: 0,46 a 1,20; 406 participantes; un estudio) y la metástasis distante fue incierta (CRI 1,05; IC del 95%: 0,74 a 1,49; 406 participantes; un estudio). El linfedema fue menos probable después del muestreo axilar que después de la DGLA (OR 0,32; IC del 95%: 0,13 a 0,81; 80 participantes; un estudio).
SLNB versus ALND
Siete ensayos con 9426 pacientes compararon la BGLC con la DGLA. Las pruebas de calidad moderada mostraron una supervivencia general similar después de la BGLC en comparación con la DGLA (CRI 1,05; IC del 95%: 0,89 a 1,25; 6352 participantes; tres estudios; pruebas de calidad moderada). Las diferencias en la recidiva local (CRI 0,94; IC del 95%: 0,24 a 3,77; 516 participantes; un estudio), la recidiva locorregional (CRI 0,96; IC del 95%: 0,74 a 1,24; 5611 participantes; un estudio) y la metástasis distante (CRI 0,80; IC del 95%: 0,42 a 1,53; 516 participantes; un estudio) fueron inciertas. Sin embargo, los estudios revelaron escasa diferencia absoluta en los resultados mencionados anteriormente. El linfedema fue menos probable después de la BGLC que de la DGLA (el OR varió de 0,04 a 0,60; tres estudios; 1965 participantes; pruebas de baja calidad). Tres estudios con 1755 participantes informaron la calidad de vida: Los investigadores de dos estudios encontraron una mejor calidad de vida después de la BGLC que de la DGLA, y no se observaron diferencias en el otro estudio.
RT versus DGLA
Cuatro ensayos con 2585 participantes compararon la RT sola con la DGLA (con o sin RT). Las pruebas de alta calidad indicaron que la supervivencia general se redujo en las pacientes tratadas con radioterapia sola en comparación con las sometidas a DGLA (CRI 1,10; IC del 95%: 1,00 a 1,21; 2469 participantes; cuatro estudios), y la recidiva local fue menos probable en las pacientes tratadas con radioterapia que en las sometidas a DGLA (CRI 0,80; IC del 95%: 0,64 a 0,99; 22 256 personas‐años de seguimiento; cuatro estudios). El riesgo de metástasis distante fue similar para la radioterapia sola en cuanto a la DGLA (CRI 1,07; IC del 95%: 0,93 a 1,25; 1313 participantes; un estudio) y si fue menos probable el linfedema después de la RT sola que la DGLA siguió siendo incierto (OR 0,47; IC del 95%: 0,16 a 1,44; 200 participantes; un estudio).
Intervención quirúrgica menor versus DGLA
Cuando se combinaron los resultados de todos los ensayos, el tratamiento que incluía la intervención quirúrgica menor se asoció con una menor supervivencia general en comparación con la DGLA (CRI 1,08; IC del 95%: 1,01 a 1,16; 12 864 participantes; 19 estudios). Fue incierto si la recidiva local se redujo con la intervención quirúrgica axilar menor en comparación con la DGLA (CRI 0,90; IC del 95%: 0,75 a 1,09; 24 176 participantes‐años de seguimiento; ocho estudios). La recidiva locorregional fue más probable con la intervención quirúrgica menor que con la DGLA (CRI 1,53; IC del 95%: 1,31 a 1,78; 26 880 participantes‐años de seguimiento; siete estudios). Fue incierto si el riesgo de metástasis distante aumentó después de la intervención quirúrgica menos axilar en comparación con la DGLA (CRI 1,07; IC del 95%: 0,95 a 1,20; 2665 participantes; 5 estudios). El linfedema fue menos probable después de menos cirugía axilar que después de la DGLA (OR 0,37; IC del 95%: 0,29 a 0,46; 3964 participantes; nueve estudios).
Ningún estudio informó el control de la enfermedad en la axila.
Conclusiones de los autores
Esta revisión confirma el beneficio de la BGLC y el muestreo axilar como opciones a la DGLA para el estadiaje axilar, lo que apoya el criterio de que la DGLA de la axila sin compromiso radiológico ni clínico ya no es práctica aceptable en las pacientes con cáncer de mama.
PICOs
Resumen en términos sencillos
Extracción quirúrgica de los ganglios linfáticos axilares en el cáncer de mama
Pregunta de la revisión
Esta revisión procuró comparar los efectos beneficiosos de la extracción quirúrgica de los ganglios linfáticos axilares con los efectos perjudiciales potenciales asociados a este procedimiento quirúrgico. El objetivo de la revisión también fue saber si la extracción completa de todos los ganglios axilares podría reemplazarse por los procedimientos que eliminan sólo un número reducido de ganglios linfáticos.
Antecedentes
La extracción quirúrgica de los ganglios linfáticos axilares con frecuencia es parte del tratamiento quirúrgico inicial para las pacientes con cáncer de mama operable. Si el cáncer se ha diseminado a estos ganglios linfáticos, se les recomienda a las pacientes recibir tratamientos adicionales, como la quimioterapia o la radioterapia, para ayudar al tratamiento de la enfermedad. Si el cáncer no se ha diseminado a estos ganglios linfáticos, se evitan tratamientos adicionales a las pacientes (que implican más efectos secundarios). La extracción quirúrgica de los ganglios linfáticos puede llevar a complicaciones quirúrgicas a corto plazo (como la infección y problemas de cicatrización de la herida) y consecuencias a largo plazo (como la rigidez de hombro, dolor e hinchazón del brazo [linfedema]), cuando la acumulación de líquido restringe la funcionalidad y causa malestar.
Las estrategias modernas usan un enfoque por etapas, por el que primero se extrae un número pequeño de ganglios, y el resto sólo si se detecta el cáncer en el primer estadio. Este primer estadio puede consistir en un muestreo axilar "aleatorio", por el que el cirujano extrae un número pequeño de ganglios (por lo general, cuatro) palpables. Otra posibilidad es que los cirujanos usen las técnicas del ganglio centinela para identificar los ganglios que más probablemente incluyan células cancerosas, lo que lleva a la extracción del número más bajo posible de ganglios. Para las pacientes con cáncer en los ganglios centinela (o la muestra), habitualmente se recomienda la extracción completa de todos los ganglios linfáticos axilares (disección de ganglios linfáticos axilares); sin embargo, la radioterapia axilar también puede usarse para obliterar las células cancerosas en los ganglios linfáticos. En algunos estudios se han explorado enfoques alternativos, como ningún tratamiento quirúrgico a los ganglios axilares.
Características de los estudios
Las pruebas están actualizadas hasta marzo 2015. La revisión identificó 26 ensayos controlados aleatorios, que compararon la disección de ganglios linfáticos axilares (DGLA) con enfoques alternativos, como la intervención quirúrgica axilar menor. Las pacientes de estos ensayos tenían un cáncer de mama primario operable, y algunos ensayos incorporaron a pacientes con ganglios linfáticos axilares aumentados de tamaño a la palpación Diez ensayos con 3849 pacientes compararon la DGLA con ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar. Seis ensayos con 1559 pacientes compararon la DGLA con el muestreo axilar. Siete ensayos con 9426 pacientes compararon la DGLA con la biopsia de ganglios linfáticos centinela (BGLC). Cuatro ensayos con 2585 pacientes compararon la DGLA (con o sin radioterapia) con la radioterapia sola.
Resultados clave
Las pruebas de calidad moderada indican que las pacientes tratadas con enfoques que incluyen la intervención quirúrgica axilar menor (como el muestreo axilar o la BGLC) no tienen menos perspectivas de supervivencia en comparación con las sometidas a DGLA. Las pruebas de calidad moderada indican que la supervivencia general se reduce levemente en las pacientes sometidas a radioterapia (pero ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar) en comparación con la DGLA. Si se asume una supervivencia de un 81% a cinco años después de la intervención quirúrgica con DGLA, entonces las pruebas indican que sería de entre 77% y 81% después de la radioterapia sola.
Las pruebas de calidad moderada indican que las pacientes a quienes no se les reseca ningún ganglio linfático axilar presentan un riesgo mayor de recidiva locorregional (resurgimiento del cáncer, en la mama, área de la cicatriz de mastectomía o ganglios axilares). Si se asume que un 86% de las pacientes sometidas a DGLA estarán libres de recidiva locorregional cinco años después de la intervención quirúrgica, las pruebas indican que la cifra correspondiente para las pacientes sin extracción de ganglios linfáticos sería de entre un 66% y un 76%. Para las pacientes tratadas con muestreo axilar, las pruebas de baja calidad indican que entre un 73% y 87% estaría libre de recidiva locorregional a cinco años.
Las tasas de recidiva axilar se informaron solamente en los ensayos de BGLC versus DGLA, y los investigadores siguen sin poder precisar el mejor tratamiento para este resultado porque las tasas fueron muy bajas (menos del 1% de las pacientes).
Las pruebas de baja calidad indican que las pacientes sometidas a DGLA presentan un mayor riesgo de linfedema en comparación con las sometidas a BGLC o ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar. Sobre la base de estas pruebas, se esperaría que 132 de cada 1000 pacientes sometidas a DGLA presentarían linfedema un año después de la intervención quirúrgica, en comparación con entre 22 y 115 de las sometidas a BGLC. Otros efectos perjudiciales a largo plazo como el dolor, el deterioro del movimiento de brazos y el adormecimiento fueron también más probables con la DGLA que con la BGLC.
Conclusiones de los autores
Summary of findings
| No axillary surgery compared with full axillary surgery for operable primary breast cancer | |||||
| Patient or population: women with operable primary breast cancer | |||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | Number of participants | Quality of the evidence | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | ||||
| Full axillary surgery | No axillary surgery | ||||
| All‐cause mortality | 92% overall survival at 5 yearsa | 92% overall survival at 5 years | HR 1.06 | 3849 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ |
| Locoregional recurrence | 86% locoregional recurrence‐free survival at 5 yearsc | 71% locoregional recurrence‐free survival at 5 years | HR 2.35 | 20,863d | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ |
| Lymphoedema | 236 per 1000 | 87 per 1000 | OR 0.31 | 1714 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Arm or shoulder movement impairment | 91 per 1000 | 67 per 1000 | OR 0.72 | 1495 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | |||||
| aAssumed risk is taken from full axillary surgery arm of Institut Curie. | |||||
| Axillary sampling compared with full axillary surgery for operable primary breast cancer | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with operable primary breast cancer | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | Number of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Full axillary surgery | Axillary sampling | |||||
| All‐cause mortality | 82% overall survival at 5 yearsa | 83% overall survival at 5 years | HR 0.94 | 967 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | |
| Local recurrence | 85% local recurrence‐free survival at 5 yearsd | 80% local recurrence free survival at 5 years | HR 1.41 (0.94 to 2.12) | 1404 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence. | ||||||
| aAssumed risk is taken from full axillary surgery arm of E'dburgh Sample/Clear. | ||||||
| Sentinel node biopsy compared with full axillary surgery for operable primary breast cancer | |||||
| Patient or population: women with operable primary breast cancer | |||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | Number of participants | Quality of the evidence | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | ||||
| Full axillary surgery | Sentinel node biopsy | ||||
| All‐cause mortality | 96% overall survival at 5 yearsa | 96% overall survival at 5 years | HR 1.05 | 6352 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ |
| Lymphoedema | 132 per 1000 | 48 per 1000 | OR 0.33 | 815 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Subjective arm movement impairment | 100 per 1000 | 40 per 1000 | OR 0.38 | 877 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ |
| Paraesthesia | 776 per 1000 | 343 per 1000 | OR 0.15 | 495 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Pain | 177 per 1000 | 86 per 1000 | OR 0.44 | 877 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Numbness | 346 per 1000 | 185 per 1000 | OR 0.43 | 1799 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence. | |||||
| aAssumed risk taken from the full axillary surgery arm of Milan. | |||||
| Radiotherapy alone compared with full axillary surgery for operable primary breast cancer | |||||
| Patient or population: women with operable primary breast cancer | |||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | Number of participants | Quality of the evidence | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | ||||
| Full axillary surgery | Radiotherapy alone | ||||
| All‐cause mortality | 81% overall survival at 5 yearsa | 79% overall survival at 5 years | HR 1.1 | 2469 | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ |
| Local recurrence | 90% local recurrence‐free survival at 5 yearsb | 92% local recurrence‐free survival at 5 yearsa | HR 0.8 | 22,256c | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence. | |||||
| aAssumed risk from full axillary surgery arm of NSABP B‐04 using mean 5‐year overall survival in combined N+ and N‐ groups. | |||||
Antecedentes
Descripción de la afección
El cáncer de mama invasivo ocurre cuando un crecimiento y una división celular sin control y anormal en los lobulillos o los conductos de la mama se diseminan al tejido circundante. El sistema de estadiaje de la Union Internationale Contre le Cancer (UICC 1987) para el cáncer de mama representa cómo, sin tratar, las células cancerosas pueden difundirse localmente al tejido mamario y los ganglios linfáticos de la axila (estadios I a III) y por el torrente sanguíneo y el sistema linfático a otras partes del organismo (estadio IV).
Descripción de la intervención
La extracción de ganglios linfáticos regionales para intentar una escisión curativa del tratamiento de la mayoría de los cánceres tiene una larga historia (Halsted 1895). El objetivo consiste tanto en el control local de la enfermedad axilar como la determinación del estadio para permitir un tratamiento adyuvante apropiado. La intervención quirúrgica axilar es un componente clave del tratamiento del cáncer de mama, y en guías clínicas del Reino Unido se especifica que la intervención quirúrgica mínima (preferentemente, la biopsia de ganglios linfáticos centinela [BGLC]) debe realizarse para establecer el estadio de la axila en las pacientes con cáncer de mama temprano invasivo y ganglios linfáticos axilares clínicamente negativos (NICE 2009).
Pueden usarse varios enfoques alternativos a la intervención quirúrgica axilar.
-
Anteriormente, el vaciamiento axilar (extracción de todo el tejido ganglionar en la axila mediante disección hasta el nivel de la vena axilar) (Craig 1998) fue la práctica estándar en muchas unidades. El vaciamiento axilar total acarrea una mayor morbilidad en comparación con la cirugía de mama sola, con una incidencia de un 10% a un 15% de linfedema crónica del brazo (Kissin 1986), 9% de seroma tardío, 2,2% de la tasa de infección, 12% de edema de la mama y 0,3% de riesgo de daño al nervio torácico largo (Senofski 1991). Otros problemas incluyen rigidez del hombro ("hombro congelado"), que puede ser grave (Kissin 1986). El vaciamiento inmediato de los ganglios axilares no se considera apropiado ya que faltan pruebas de la diseminación del cáncer por la biopsia antes de la intervención quirúrgica.
-
El muestreo de ganglios axilares (extracción de cuatro o cinco ganglios axilares de la axila inferior) (Craig 1998) comprende la extracción de ganglios individuales, dejando grasa axilar y la mayoría de los ganglios y el sistema linfático intacto. Como resultado, prácticamente ninguna de las complicaciones enumeradas para el vaciamiento axilar se asocia con este procedimiento. Las pacientes cuyos ganglios axilares muestreados contienen células cancerosas pueden necesitar un vaciamiento axilar o radioterapia posterior. Este enfoque, anteriormente popular, se consideraba apropiado.
-
La biopsia de ganglios linfáticos centinela (Kelley 1998) (un procedimiento en que se busca la vía linfática de la región con cáncer de mama a través de la administración de un radioisótopo o colorante linfático azul) permite la biopsia del/de los primer/os ganglio/s linfático/s (ganglio centinela). Los ganglios centinela tienen grandes probabilidades de incluir la propagación del cáncer, y este enfoque permite la evaluación exacta de la diseminación del cáncer junto con la extracción de un número pequeño de ganglios (habitualmente tres o menos).
-
En algunas pacientes que no son candidatas para los tratamientos adyuvantes, los cirujanos pueden omitir por completo la intervención quirúrgica axilar para evitar la morbilidad adicional (EBCTCG 1998, Walsh 1989). Esta situación ha llevado a algunos cirujanos a evitar someter a algunas mujeres con cáncer de mama débiles al estadiaje de la axila sin compromiso clínico por medio de la biopsia del ganglio centinela o el vaciamiento total (Yancik 1989).
De qué manera podría funcionar la intervención
La extracción de los ganglios axilares puede mejorar el control local de la enfermedad axilar al mismo tiempo que se brinda información sobre el estadio del cáncer, que puede usarse para guiar el tratamiento adyuvante.
Por qué es importante realizar esta revisión
Los argumentos a favor y en contra de cada uno de estos procedimientos son complicados y, como resultado, hay variación en la práctica. La síntesis estadística de los resultados para estos procedimientos ofrecerá a los cirujanos y las pacientes una base de pruebas más fiable, a partir de las cuales se podrá tomar decisiones difíciles en cuanto al tratamiento.
Objetivos
Evaluar los efectos beneficiosos y perjudiciales de los enfoques alternativos a la intervención quirúrgica axilar (incluida la omisión de la intervención quirúrgica) en cuanto a la supervivencia general; las recidivas locales, regionales y distantes; y eventos adversos.
Métodos
Criterios de inclusión de estudios para esta revisión
Tipos de estudios
Ensayos controlados aleatorios.
Tipos de participantes
Las pacientes con cáncer de mama primario operable definido clínicamente, es decir, cuando el tumor primario no está fijado a las estructuras subyacentes (incluye las clasificaciones del tumor‐ganglio‐metástasis [TNM, por sus siglas en inglés]) T1‐3 y T4b con compromiso sólo menor de la piel, N0‐1 y M0) ni a los ganglios linfáticos móviles (UICC 1987).
Tipos de intervenciones
-
Disección de ganglios linfáticos axilares (DGLA) versus ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar en el momento de la intervención quirúrgica primaria
-
Con los siguientes subgrupos para ambos brazos:
-
Radioterapia
-
No radioterapia
-
-
-
DGLA versus muestreo axilar en el momento de la intervención quirúrgica primaria
-
Con los siguientes subgrupos para ambos brazos:
-
Radioterapia
-
No radioterapia
-
-
Y los siguientes subgrupos para el brazo de estadiaje axilar limitado:
-
Tratamiento adicional para los casos de ganglios histológicamente positivos
-
Ningún tratamiento adicional para los casos de ganglios histológicamente positivos
-
-
-
DGLA versus BGLC en el momento de la intervención quirúrgica primaria
-
Con los siguientes subgrupos para ambos brazos:
-
Radioterapia
-
No radioterapia
-
-
Y los siguientes subgrupos para el brazo de estadiaje axilar limitado:
-
Tratamiento adicional para los casos de ganglios histológicamente positivos
-
Ningún tratamiento adicional para los casos de ganglios histológicamente positivos
-
-
-
Muestreo axilar versus biopsia del ganglio centinela en el momento de la intervención quirúrgica primaria
-
Con los siguientes subgrupos para ambos brazos:
-
Radioterapia
-
No radioterapia
-
-
Y los siguientes subgrupos para ambos brazos:
-
Tratamiento adicional para los casos de ganglios histológicamente positivos
-
Ningún tratamiento adicional para los casos de ganglios histológicamente positivos
-
-
-
Muestreo axilar versus ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar en el momento de la intervención quirúrgica primaria
-
Con los siguientes subgrupos para ambos brazos:
-
Radioterapia
-
No radioterapia
-
-
Y los siguientes subgrupos para el brazo de estadiaje axilar limitado:
-
Tratamiento adicional para los casos de ganglios histológicamente positivos
-
Ningún tratamiento adicional para los casos de ganglios histológicamente positivos
-
-
-
BGLC versus ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar en el momento de la intervención quirúrgica primaria
-
Con los siguientes subgrupos para ambos brazos
-
Radioterapia
-
No radioterapia
-
-
Y los siguientes subgrupos para el brazo de estadiaje axilar limitado:
-
Tratamiento adicional para los casos de ganglios histológicamente positivos
-
Ningún tratamiento adicional para los casos de ganglios histológicamente positivos
-
-
-
DGLA sin radioterapia versus ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar con radioterapia
-
Sin subgrupos
-
Para todos los estudios que incluyen la intervención quirúrgica axilar total o el muestreo axilar, se registró el número de ganglios extraídos y el método de análisis de ganglios usado cuando estaban disponibles, para indicar si se había realizado un muestreo o un vaciamiento adecuados.
Tipos de medida de resultado
Resultados primarios
-
Supervivencia ‐ general (intervalo entre el comienzo del tratamiento o la asignación al azar y la muerte)
-
Control de la enfermedad en la axila (intervalo entre el comienzo de tratamiento y la necesidad de tratamiento de segunda línea, tratamiento paliativo o recidiva regional en la axila)
-
Recidiva del cáncer de mama, localmente dentro de la mama (recidiva local) o a distancia, como enfermedad metastásica (recidiva distante), con registro del tiempo hasta la recidiva y lugar de la recidiva
-
Eventos adversos (complicaciones quirúrgicas), incluidas las complicaciones quirúrgicas locales agudas, como el hematoma, la infección, la dehiscencia de la herida o el seroma, y complicaciones sistémicas agudas, como la infección torácica, la trombosis venosa profunda, la embolia pulmonar, la insuficiencia cardíaca, la isquemia cardíaca y el accidente cerebrovascular
-
Complicaciones a largo plazo, incluido el linfedema, la rigidez del hombro, la parestesia, el dolor, la pérdida de la capacidad funcional, el aleteo de la escápula y la contractura o cicatrización de la herida
Resultados secundarios
-
Calidad de vida (medida con una escala validada)
-
Variables psicológicas y psicosociales (medidas en escalas validadas)
Métodos de búsqueda para la identificación de los estudios
Búsquedas electrónicas
The Trials Search Co‐ordinator for the Cochrane Breast Cancer Review Group searched the Specialised Register of the Group on 16 March 2015. Details of sources and search strategies used to populate this register are provided in the Group module in the Cochrane Library (http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/o/cochrane/clabout/articles/BREASTCA/frame.html) . We have extracted for consideration studies coded as "AXILLARY NODE(S)", "EARLY BREAST CANCER", "LOCALLY ADVANCED BREAST CANCER", "PSYCHOSOCIAL" or "SURGERY" on the Specialised Register.
We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL; Issue 2) in the Cochrane Library on 16 March 2015. See Appendix 1 for the search strategy used.
In addition, an information specialist searched the following databases while using the search terms and strategy identified in Appendix 2: MEDLINE via OvidSP (2007 to 12 March 2015), PreMEDLINE via OvidSP (12 March 2015) and Embase via OvidSP (2002 to 12 March 2015). We used a validated filter to identify reports of RCTs in our initial search of MEDLINE (Lefebvre 2001), and for updated searches, we used the revised filter (Lefebvre 2011). We used the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network RCT filter in our search of Embase (http://www.sign.ac.uk/methodology/filters.html).
We also searched on 16 March 2015 the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Portal (WHO ICTRP) (Appendix 3) and ClinicalTrials.gov (Appendix 4), for prospectively registered and ongoing trials.
Búsqueda de otros recursos
We searched (on 12 March 2015) conference proceedings from the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) 41st to 50th Annual Meetings (2005 to 2014) via Journal of Clinical Oncology (http://jco.ascopubs.org/site/meetings). We also searched (on 12 March 2015) conference proceedings from the San Antonio Breast Cancer (SABCS) 29th to 37th Annual Symposium Meetings (2006 to 2014) via the Cancer Research website (http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/).
We contacted the authors of included and ongoing trials by email and asked them if they knew of any relevant studies. This yielded no additional studies. We also checked the reference lists of included studies and published reviews to look for relevant studies.
Obtención y análisis de los datos
Selección de los estudios
Two review authors (NB, MSH or MA) screened the titles and abstracts of references identified by electronic searches to identify publications of potentially eligible trials. We obtained a copy of the full‐text article for each reference reporting a potentially eligible trial, and we applied the review selection criteria to each trial. We reported all exclusions of potentially eligible trials in the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta‐Analyses) diagram (Figure 1) and, in some cases, in the Characteristics of excluded studies table. We used trial publications to assess each trial's eligibility, and for unpublished trials, we obtained information from the trial protocol or the next best available resource. When necessary and possible, we sought additional information from the principal investigator. Two review authors (NB, MSH or MA) independently assessed each potentially eligible trial for inclusion in the review and resolved discrepancies in eligibility judgements by discussion.
Extracción y manejo de los datos
We extracted data from published trial reports and entered them onto an electronic form (using Microsoft Word). Two review authors (NB, MSH or MA) independently extracted data from each trial and resolved disagreements regarding data extraction by discussion. The Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (Clarke 2005) has published a meta‐analysis based on individual participant data for many of the included trials. We used this meta‐analysis as an additional source of outcome data for trials included in this review.
We contacted the authors of included and ongoing trials by email and asked them to share unpublished data from their trials and to clarify details about their trial that were unclear or missing from the published reports.
Evaluación del riesgo de sesgo de los estudios incluidos
We assessed the risk of bias of included studies by applying standard Cochrane methods for randomised trials as outlined in Higgins 2011. We assessed selection bias (random sequence generation, allocation concealment; two items) and reporting bias (selective reporting; one item) at study level, and detection bias (blinding of outcome assessment; one item) and attrition bias (incomplete outcome data; one item) at outcome level. We did not assess detection bias for the outcome of survival because this in an objective outcome, and we did not assess performance bias (one item) because blinding of healthcare personnel and participants is not possible for the interventions considered in this review.
Medidas del efecto del tratamiento
For dichotomous data, we used odds ratio (OR) as the measure of treatment effect. For continuous data, we used the standardised mean difference (SMD). For time‐to‐event (survival) data, we used the hazard ratio (HR). For our meta‐analysis of time‐to‐event outcomes in Review Manager 5.3 (RevMan), we used 'O‐E' (observed minus expected) and 'V' (variance) statistics or hazard ratios for each trial. If these values were not reported for a given trial, we calculated them from available statistics, if possible, using the methods described in Tierney 2007.
Cuestiones relativas a la unidad de análisis
Some trials performed serial measurements of arm volume and/or function over the first months and years after surgery. For our analysis, we used the measurement at one year post operation (or at the nearest time point after one year for trials not reporting data at the one‐year time point). One trial (NSABP B‐04) included three treatment comparison groups. This presented an issue only for analysis of less versus more axillary surgery (Analysis 5.1); to avoid double‐counting of the ALND group, we omitted the comparison of radiotherapy versus ALND in clinically node negative study participants.
Manejo de los datos faltantes
We analysed only data available in trial reports or obtained through contact with trial authors. We did not attempt data imputation.
Evaluación de la heterogeneidad
We assessed statistical heterogeneity (variability in intervention effects) in meta‐analyses by using the I2 statistic, which we interpreted alongside magnitude and direction of effects. We regarded an I2 value of 30% to 60% as indicating potentially important heterogeneity and downgraded the overall quality of evidence for that outcome (owing to inconsistency) in the summary of findings tables. If heterogeneity was greater than 50%, we did not pool effect estimates but instead used the range of effects reported by individual studies.
Evaluación de los sesgos de notificación
We checked reporting bias by using funnel plots and checked that outcomes measured in individual trials were reported in trial publications. If we suspected reporting bias for a given outcome, we downgraded the overall quality of the evidence in the summary of findings table owing to reporting/publication bias.
Síntesis de los datos
We statistically synthesised time‐to‐event outcomes that were entered into RevMan as ‘O–E' and 'Variance’ outcomes by using a fixed‐effect model (the random‐effects model is not an option for this analysis in RevMan). We analysed dichotomous outcomes by using fixed‐effect (Mantel‐Haenszel method) and random‐effects (DerSimonian and Laird) models (Sensitivity analysis).
For summary of findings tables (Summary of findings table 1; Summary of findings table 2; Summary of findings table 3; Summary of findings table 4), we used the GRADE approach to assign an overall assessment of the quality of the evidence. In addition to the risk of bias assessment, the GRADE quality rating includes assessments of inconsistency, indirectness and imprecision of results, and of the likelihood of publication bias. We prioritised Primary outcomes for inclusion in summary of findings tables and organised them according to Types of interventions.
Análisis de subgrupos e investigación de la heterogeneidad
We planned the following subgroup analyses.
-
Radiotherapy versus no radiotherapy.
-
Further treatment versus no further treatment for histologically node‐positive participants.
-
Age groups (18 to 49 years; 50 to 69 years; 70 to 79 years; 80 years and older).
We were not able to analyse results by age group. When evidence suggested potentially important between‐study statistical heterogeneity (I2 value of 30% to 60%), we compared fixed‐effect and random‐effects estimates to check whether the intervention effect was sensitive to the type of model used, although it should be noted that such comparisons were not possible for analyses of time‐to‐event outcomes, as already outlined in the Data synthesis section.
Análisis de sensibilidad
To examine the robustness of our results, we performed sensitivity analyses that included only studies with low risk of bias for allocation concealment. Moreover, we planned to undertake sensitivity analyses to examine short‐term and long‐term morbidity outcomes only for studies with low risk of bias for blinded assessment of these outcomes. However, we considered none of the studies to be at low risk of bias for these items, so we could not perform these analyses.
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
In total, we screened 7436 references for inclusion in this review (Figure 1). We retrieved full‐text articles for 163 references to potentially relevant publications to check inclusion eligibility. Of these,13 full‐text articles reported on eight trials that appeared relevant but did not meet all of the inclusion criteria (AATRM‐048‐13‐2000; ACOSOG Z0011; Buenos Aires; Copenhagen; Edinburgh SES; IBCSG‐23‐01; IPO‐P; OTOASOR). See Excluded studies section.
We identified six articles reporting on eight possibly eligible ongoing trials (AMAROS; GF‐GS 01; KiSS; NCT01717131; NCT02167490; NCT02271828; SNAC2; SOUND). Two studies (ISRCTN88463711; Semiglazov 2003) await classification. We excluded 45 other full‐text articles for the following reasons: 23 used ineligible Types of interventions, four included ineligible Types of participants and 18 were the wrong Types of studies.
The remaining 97 articles were reports of 26 eligible RCTs included in this review. We contacted the authors of included studies by email to ask about other relevant trials for inclusion in the review, but this yielded no additional studies.
Included studies
This review includes 26 studies that performed 27 treatment comparisons.
Full axillary surgery versus no axillary surgery
Ten studies compared axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) versus no axillary surgery (N = 3849; Addenbrookes; Guy's; Hammersmith; IBCSG‐10‐93; Institut Curie; Institut Bergonie; Malmo; Milan 2; Milan 3; NSABP B‐04).
The Malmo trial compared ALND plus radiotherapy (RT) versus no ALND and no RT. In one trial (IBCSG‐10‐93), only those treated with conservative breast surgery received RT. In Addenbrookes; Guy's; Hammersmith; Institut Curie; Institut Bergonie; Milan 2; and Milan 3, all study participants received RT. NSABP B‐04 reported a three‐group comparison of ALND, no ANLD plus RT and no ALND for patients with clinically negative axillary nodes. Patients in the ALND arm received limited RT to the chest wall. We included the ALND and no ALND arms of NSABP B‐04 for this comparison.
Five studies excluded patients with clinically involved lymph nodes (Institut Bergonie; Institut Curie; Malmo; Milan 2; Milan 3), whereas the remaining five studies included these patients only when clinically involved nodes were mobile and were not fixed to underlying structures (Addenbrookes; Guy's; Hammersmith; IBCSG‐10‐93; NSABP B‐04).
Seven studies (Addenbrookes; Guy's; Hammersmith; IBCSG‐10‐93; Malmo; Milan 2; NSABP B‐04) did not provide extra treatment for participants with histologically positive axillary lymph nodes. In Institut Curie, Institut Bergonie and Milan 3, such individuals could receive chemotherapy or hormone therapy.
Full axillary surgery versus axillary sampling
Six trials compared ALND versus axillary sampling (N = 1559; Cape Town; Cardiff; E'dburgh Sample/Clear; Edinburgh 1; Ostersund; Xu 2003). Of these trials, only Cape Town did not provide RT as part of the randomised treatment.
In Cardiff, E'dburgh Sample/Clear, Edinburgh 1 and Ostersund, participants with histologically positive sampled axillary lymph nodes received additional RT. In Xu 2003, RT was provided only for participants with more than three positive axillary lymph nodes and for those with a primary tumour in the central quadrant. In Cape Town, participants with histologically positive sampled nodes did not receive additional treatment.
Four trials (Cape Town; Cardiff; E'dburgh Sample/Clear; Edinburgh 1) included patients with clinically involved axillary nodes, provided such nodes were mobile. In the Ostersund and Xu 2003 trials, inclusion criteria were unclear.
Full axillary surgery versus sentinel node biopsy
Seven trials compared ALND versus sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) (N = 9426; Addenbrookes 2; ALMANAC; Genoa; GIVOM Sentinella; Milan; NSABP B‐32; SNAC).
In three studies (Genoa; GIVOM Sentinella;Milan), only participants treated with breast‐conserving surgery received RT, which meant that some of the participants in Genoa and GIVOM Sentinella did not receive RT. In the remaining trials (Addenbrookes 2; ALMANAC; NSABP B‐32; SNAC), participants received RT according to local treatment protocols, which meant that in practice, most participants received RT.
In all of these trials, participants with histologically positive sentinel lymph nodes received further treatment. Treatment for histologically positive lymph nodes consisted of ALND (Addenbrookes; Genoa; GIVOM Sentinella; NSABP B‐32; Milan; SNAC) or the choice of ALND or RT to the axilla (ALMANAC).
Addenbrookes 2; ALMANAC; Genoa; GIVOM Sentinella; NSABP B‐32 and SNAC excluded patients with clinically involved axillary nodes, but it was unclear whether the Milan trial excluded such individuals.
Axillary sampling versus SLNB
We identified no studies for this comparison.
Axillary sampling versus no axillary surgery
We identified no studies for this comparison.
SLNB versus no axillary surgery
We identified no studies for this comparison.
Full axillary surgery with no RT versus no axillary surgery with RT
Four trials compared ALND without RT versus RT alone (N = 2585; Manchester; NSABP B‐04; SE Scotland; WSSA Glasgow). One of these trials (NSABP B‐04) performed a three‐group comparison of ALND, no ANLD plus RT and no ALND with clinically negative axillary nodes. Participants in the ALND arm of this trial did receive limited RT to the chest wall. We included in this review the ALND and no ALND plus RT arms of NSABP B‐04. This trial randomised participants with clinically positive nodes to ALND or no ANLD plus RT; we analysed these results separately. All of these trials included patients with clinically involved axillary nodes provided such nodes were mobile. None of these trials specified that they provided extra treatments for participants with histologically positive axillary nodes.
Excluded studies
We excluded eight trials from this review (see Excluded studies table for full details). We excluded two otherwise relevant trials because treatment allocation was not randomised; instead, investigators decided treatment group on the basis of month of birth (Buenos Aires) or order of entry into the trial (Copenhagen). We excluded the Edinburgh South East Scotland trial (Edinburgh SES) because it did not involve axillary surgery or lymph node biopsy.
We excluded five trials comparing ALND versus no further axillary surgery because trial entry or inclusion depended on the results of SLNB (AATRM‐048‐13‐2000; ACOSOG Z0011; IBCSG‐23‐01; IPO‐P; OTOASOR). All of these trials excluded patients with clinically involved axillary nodes before their primary surgery. The IPO‐P trial included only those with negative SLNB. Remaining trials included only patients with a positive SLNB (AATRM‐048‐13‐2000; ACOSOG Z0011; IBCSG‐23‐01; OTOASOR). AATRM‐048‐13‐2000 included only patients with sentinel lymph node micrometastases.
Risk of bias in included studies
We summarised in Figure 2 the risk of bias of included studies.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
Allocation
In all, 17 trials clearly reported random sequence generation (Addenbrookes; Addenbrookes 2; ALMANAC; Cape Town; Cardiff; Edinburgh 1; Genoa; GIVOM Sentinella; Guy's; Hammersmith; IBCSG‐10‐93; Malmo; Milan; Milan 2; Milan 3; NSABP B‐32; SNAC), and the remaining nine trials provided unclear information on this (E'dburgh Sample/Clear; Institut Bergonie; Institut Curie; Manchester; NSABP B‐04; Ostersund;SE Scotland; WSSA Glasgow; Xu 2003).
Allocation concealment was adequate in 15 trials (Addenbrookes; ALMANAC; Cape Town; Cardiff; E'dburgh Sample/Clear; Edinburgh 1; Genoa; GIVOM Sentinella; IBCSG‐10‐93; Milan; Milan 2; Milan 3; NSABP B‐32; SE Scotland; SNAC) and unclear in the other 11 trials (Addenbrookes 2; Guy's; Hammersmith; Institut Bergonie; Institut Curie; Malmo; Manchester; NSABP B‐04; Ostersund; WSSA Glasgow; Xu 2003). In trials with unclear risk of selection bias, we did not observe obvious differences in the baseline characteristics of treatment groups, although Malmo, Ostersund and WSSA Glasgow poorly reported baseline characteristics.
Blinding
Two studies were at high risk of detection bias due to lack of blinding of outcome assessment or disease recurrence and adverse event outcomes (Addenbrookes 2; SNAC2). All other studies were at unclear risk of detection bias due to poor reporting.
Incomplete outcome data
Seventeen trials had low risk of incomplete overall survival data (ALMANAC; Cape Town; Cardiff; E'dburgh Sample/Clear; Edinburgh 1; Genoa; Guy's; IBCSG‐10‐93; Institut Bergonie; Malmo; Manchester; Milan; Milan 3; NSABP B‐32; SE Scotland; WSSA Glasgow; Xu 2003). The remaining trials were at unclear risk of bias due to incomplete outcome data because they did not report overall survival or the completeness of their reporting was uncertain. We observed a similar pattern for outcomes related to breast cancer recurrence and disease control in the axilla (Figure 2).
We judged five trials to be at low risk of bias because they provided incomplete data for short‐term adverse events (Addenbrookes 2; ALMANAC; NSABP B‐32; SNAC; Xu 2003); all of these trials involved SLNB. Three trials were at high risk (IBCSG‐10‐93; Ostersund; SE Scotland), and the remainder were at uncertain risk. We noted a similar pattern for long‐term adverse events, with three trials at low risk of bias (Addenbrookes 2; Hammersmith; Xu 2003), seven trials at high risk (E'dburgh Sample/Clear; Guy's; IBCSG‐10‐93; Milan; NSABP B‐32; Ostersund; SE Scotland) and the remainder at uncertain risk.
Selective reporting
Three trials were at low risk of bias due to selective reporting (Addenbrookes; ALMANAC; Edinburgh 1). Addenbrookes 2 and Milan 3 were at high risk of bias due to selective reporting of some outcomes on the basis of statistical significance. The remaining trials were at uncertain risk of bias due to selective reporting.
Other potential sources of bias
Trials typically reported intention‐to‐treat analyses, but in four trials it was unclear whether such analyses were performed (Cape Town; NSABP B‐04; Ostersund; WSSA Glasgow). We included two trials that performed per‐protocol analysis (Malmo; Milan) because study authors stated that per‐protocol results were similar to intention‐to‐treat results (Malmo), or because protocol violations were few (Milan).
Effects of interventions
See: Summary of findings for the main comparison No axillary surgery compared with full axillary surgery for operable primary breast cancer; Summary of findings 2 Axillary sampling compared with full axillary surgery for operable primary breast cancer; Summary of findings 3 Sentinel node biopsy compared with full axillary surgery for operable primary breast cancer; Summary of findings 4 Radiotherapy alone compared with full axillary surgery for operable primary breast cancer
We recorded in Table 1 time‐to‐event statistics extracted for each trial. We listed in Table 2 the definitions of adverse event outcomes used in each study, and we summarised in Table 3 adverse events at various time points after treatment.
| Study | Outcome reported | Observed | Expected | Variance | HR | 95% CIs | P value | Follow‐up | Notes |
| Overall mortality | ALND: 107/112 No ALND: 108/121 | o‐e = ‐3.1 | 46.5 | 0.94 | (0.70 to 1.25) | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition The number of patients reported by Clarke 2005 differs from that reported by Brinkley (1971). | |
| Breast cancer mortality | ALND: 74/112 No ALND: 78/121 | o‐e = ‐2.2 | 32.8 | ‐ | ‐ | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Isolated local recurrence | ALND: 7 events/1148 women‐years No ALND: 15 events/1218 women‐years | o‐e = 3.3 | 5.4 | 1.8 | (0.79 to 4.28) | NA | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Overall mortality | ALDN: 7/476 SLNB: 7/478 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 year | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Axillary recurrence | ALDN: 4/476 SLNB: 1/478 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 year | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall mortality | ALND: 21/43 Simple: 30/52 | o‐e = 4.74 | 12.35 | 1.47 | (0.84 to 2.56) | 0.1775 | 10 years | Tierney et al (2007) method 7 used log‐rank test results from figure 1. Cape Town | |
| Overall mortality (node‐negative) | ALND: 14/21 Simple: 26/30 | o‐e = 1.8 | 7.6 | ‐ | ‐ | NA | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9a; Groote‐Schuur), then O‐E sign changed to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition. Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Overall mortality (node‐positive) | ALND: 19/22 Simple: 22/25 | o‐e = ‐1.9 | 7.7 | ‐ | ‐ | NA | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9b; Groote‐Schuur), then O‐E sign changed to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition. Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Isolated local recurrence (node‐negative) | ALND: 3/206 women‐years Simple: 8/232 women‐years | o‐e = 1.7 | 2.3 | 2.09 | (0.58 to 7.63) | NA | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9a; Groote‐Schuur), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | ||
| Isolated local recurrence (node‐positive) | ALND: 5/134 women‐years Simple: 9/173 women‐years | o‐e = 0.0 | 2.0 | 1.00 | (0.25 to 4.00) | NA | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9b; Groote‐Schuur), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | ||
| Axillary recurrence | ALND: 2/43 Simple: 8/52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Any locoregional recurrence | ALND: 11/43 Simple: 19/52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Distant metastases | ALND: 11/43 Simple: 13/52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival | ALND: N = 97 Sampling: N =103 Total events = 152 Fig 2 data: ALND: 23/97 Sampling: 13/103 | o‐e: 7.4 | 38 | 1.21 | (0.29 to 0.99) | 0.23 | 20 years | HR calculated using log‐rank P value from Stewart et al (1994, page 42) by Tierney 2007 method 8, 9. Owing to non‐proportionality of hazard rates, HR cannot be included in meta‐analysis | |
| Disease‐free survival | ALND: 97 Sampling: 103 | 5.87 | 7.75 | 2.13 | (1.05 to 4.31) | 0.035 | 20 years | Log‐rank P value Tierney 2007 method 8, 9 (page 43 & Fig 5 Stewart et al, 1994) | |
| Locoregional recurrence (chest wall, axilla, supraclavicular/internal mammary nodes) | ALND: 19/94 Sampling: 31/99 Fig 4: ALND: 11/97 Sampling: 22/103 | o‐e: 6.46 | 11.78 | 1.73 | (0.87 to 3.42) | NA | 20 years | Tierney et al (2007) method 4 used and data from Figure 4 & page 42 Stewart et al (1994) | |
| Distant relapse | ALND: 43/94 Sampling: 59/99 | o‐e: 8.4 | 24.87 | 1.4 | (0.99 to 1.71) | 0.092 | 20 years | Data from Table 2, Stewart et al (1994): excludes patients with radiotherapy violations. Per‐protocol analysis ‐ not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Breast cancer recurrence (total) (locoregional and distant relapse) | ALND: 62/94 Sampling: 90/99 | o‐e: 12.77 | 36.71 | 1.42 | (1.18 to 1.61) | 0.035 | 20 years | Calculated from Stewart et al (1994) (excludes RT violations) per‐protocol analysis Risk of overestimation not certain as these are first events or total events.‐ not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival | ALND: ?/232 Sampling: ?/234 Total events = 53 ALND: 207/232 Sampling: 190/234 | o‐e: ‐4.66 | 13.25 | 0.7 | (0.41 to 1.21) | 0.20 | 5 years | HR calculated using log rank P ‐ figure 2, Chetty (2000) | |
| Axillary recurrence | ALND: /232 Sampling: /234 | o‐e: ‐0.15 | 13.25 | 0.99 | (0.58 to 1.69) | 0.94 | Up to 8 years | Log‐rank P value Tierney 2007 method 7, 8, 9 used Fig 3 Chetty (2000) | |
| Local recurrence in the breast | ALND: 14/232 Sampling: 15/234 | o‐e: ‐0.10 | 7.24 | 0.99 | (0.48 to 2.04) | 0.97 | Up to 8 years | Tierney 2007 method 7, 8, 9 used Table 2 & page 87 Chetty (2000) | |
| Distant recurrence | ALND: 29/232 Sampling: 29/234 | Not available | Not available | Not available | Not available | NA | Up to 8 years | Table 2, Chetty (2000). Unable to estimate HR ‐ not included in analysis | |
| Overall survival | ALND: 76/203 Sampling: 71/203 | o‐e: ‐3.81 | 36.55 | 0.90 | (0.62 to 1.25) | NA | 13 years | Tierney 2007 method 3 used (using 1995 data – Clarke 2005 paper reports more deaths) Fig 1 and page 82 HR (CI) in Forrest et al (1995) ‐ inverted the HR | |
| Distant metastases | ALND: 51/203 Sampling: 53/203 | o‐e: 1.5 | 30.78 | 0.92 | (0.67 to 1.35) | NA | 13 years | Tierney 2007 method 3 used (using 1995 data), Fig 2 and HR (CI) page 82 in Forrest et al (1995), inverted the HR | |
| Locoregional relapse (chest wall, axilla, supraclavicular) | ALND: 38/203 Sampling: 29/203 | o‐e: ‐4.9 | 16.32 | 0.74 | (0.46 to 1.20) | NA | 13 years | Tierney 2007 method 3 used (using 1995 data) Method 3 Fig 3 from HR (CI), page 82 in Forrest et al (1995), inverted the HR | |
| Overall survival | ALND: 4/115 SLNB: 5/110 | o‐e: 0.58 | 2.22 | 1.32 | (0.35 to 4.92) | 0.679 | 5 years | Log‐rank P value (Canavese 2009 ‐ fig 3) Tierney 2007 method 7 used Fig 3 KM curve gives P = 0.679. I assumed that was correct as it appears on the graph. The text value (page 20) may be a typo 0.697. HR are similar; CI differ | |
| Axillary recurrence | ALND: 1/115 SLNB: 0/110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 years | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Breast cancer recurrence (local and contralateral recurrence, axillary and distant metastases) | ALND: 10/115 SLNB: 8/110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 years | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| 5‐Year event‐free survival | ALND: 12/115 SLNB: 10/110 | o‐e: ‐0.85 | 5.45 | 0.86 | (0.37 to 1.98) | 0.715 | 5 years | Log‐rank P value from Fig 2, Canavese (2009) method 7 Tierney 2007 used | |
| Overall survival | ALND: 14/352 SLNB: 21/345 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 years | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Disease‐free survival | ALND: 28/352 SLNB: 39/345 | o‐e = 1.18 | 16.3 | 1.08 | 0.769 | 5 years | Method 7 Tierney 2007 used | ||
| Axillary recurrence | ALND: 0/352 SLNB: 1/345 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Locoregional recurrence | ALND: 3/352 SLNB: 16/345 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Distant recurrence | ALND: 16/352 SLNB: 11/345 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall mortality (clinically node negative) | ALND: 178/241 No ALND (wide excision): 185/233 | o‐e = 13.8 | 80.7 | 1.26 | (0.98 to 1.63) | 0.1 | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research intervention | |
| Overall mortality (clinically node positive) | ALND: 82/85 No ALND (wide excision): 64/71 | o‐e = 4.3 | 30.9 | 1.15 | (0.81 to 1.64) | 0.4 | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research intervention | |
| Breast cancer mortality (clinically node negative) | ALND: 122/241 No ALND (wide excision): 142/233 | o‐e = 13.8 | 58.8 | ‐ | ‐ | 0.07 | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research intervention Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Breast cancer mortality (clinically node positive) | ALND: 53/85 No ALND (wide excision): 54/71 | o‐e = 6.2 | 23.6 | ‐ | ‐ | 0.2 | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research intervention. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Isolated local recurrence (clinically node negative) | ALND: 35 events/3267 women‐years No ALND: 81 events/2383 women‐years | o‐e = 29.5 | 26.4 | 3.06 | (2.09 to 4.48) | < .00001 | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research intervention | |
| Isolated local recurrence (clinically node positive) | ALND: 17 events/873 women‐years No ALND: 31 events/519 women‐years | o‐e = 10.5 | 10.8 | 2.64 | (1.46 to 4.80) | 0.001 | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research intervention | |
| Overall survival | Radical: 35/76 Simple: 40/76 | o‐e = 1.44 | 11.78 | 1.13 | (0.64 to 2.00) | NA | 8 years | Extracted from Fig 3, Burn et al (1968) Tierney 2007 method 10 on Simple is input as "research" and radical as "control". Min and max follow‐up input as 3‐96 months | |
| Local recurrence | Radical: 10/76 Simple: 11/76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4‐9 years | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Mean time to recurrence | Radical: 15.7 months Simple: 25.9 months | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4‐9 years | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival | ALND: 72/234 Surgery only: 71/239 | o‐e = 1.76 (survival curves cross) | 36.05 | 1.05 | (0.76 to 1.46) | 0.77 | 6‐7 years | HR reported on page 340 of IBCSG (2006), used Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Disease‐free survival | ALND: 92/234 Surgery only: 89/239 | o‐e = 2.6 | 44.69 | 1.06 | (0.79 to 1.42) | 0.69 | 6‐7 years | HR reported on page 340 of IBCSG (2006), used Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Axilla recurrence (as first event) | ALND: 2/234 Surgery only: 6/239 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6‐7 years | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival (whole follow‐up period) ITT | no ALND: NR ALND: NR | o‐e = 6.42 | 7.04 | 2.49 | 90% CI (1.34 to 4.63) | NA | Whole follow‐up period (unclear how long that is) | HR reported on page 566 of Avril (2011), used Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Event‐free survival (whole follow‐up period) ITT | no ALND: 44/297 ALND: 31/297 | o‐e = 8.75 | 18.37 | 1.61 | 90% CI (1.1 to 2.37) | NA | Whole follow‐up period (unclear how long that is) | HR reported on page 566 of Avril (2011), used Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Axillary event | Within 5 years: no ALND: 4/297 ALND: 0/310 After 5 years: no ALND: 2/297 ALND: 0/310 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Lymph node (excl axillary) event | Within 5 years: no ALND: 1/297 ALND: NA After 5 years: no ALND: 0/297 ALND: NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Breast/chest wall event | Within 5 years: no ALND: 5/297 ALND: 4/310 After 5 years: no ALND: 0/297 ALND: 8/310 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Metastatic event | Within 5 years: no ALND: 4/297 ALND: 1/310 After 5 years: no ALND: 2/297 ALND: 2/310 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Contralateral breast cancer | Within 5 years: no ALND: 2/297 ALND: 1/310 After 5 years: no ALND: 2/297 ALND: 1/310 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Other site cancer | Within 5 years: no ALND: 5/297 ALND: 5/310 After 5 years: no ALND: 5/297 ALND: 4/310 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Overall survival | RT: 43/331; ALND: 29/326 | o‐e = 7 | 17.3 | 1.50 | (0.94 to 2.40) | NA | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | ||
| Isolated local recurrence | RT: 39/2045 women‐years; ALND: 34/2126 women‐years | o‐e = 1.6 | 17.5 | 1.10 | (0.69 to 1.75) | NA | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | ||
| Axilla recurrence | RT: 12/332; ALND: 5/326 | o‐e = 3.86 | 3.53 | 3.93 | ‐ | 0.04 | Table 2 in Louis‐Sylvestre (2004), method 7 in Tierney 2007 | ||
| Disease‐free survival | RT: 5 years : 82 (SD = 2.1)% 10 years : 72 (SD = 2.5)% 15 years : 65.5 (SD = 2.7)% | ALND: 5 years: 83.3 (SD 2)% 10 years: 72.6 (SD 2.5)% 15 years: 64.3 (SD 2.9)%. | NA | NA | NA | NA | o‐e cannot be extracted because P values not reported past NS in Table 2 in Louis‐Sylvestre (2004). Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Metastases | RT: 5 years: 12.8 (SD 1.9)% 10 years: 21 (SD 2.3)% 15 years: 24.9 (SD 2.5)% | ALND: 5 years: 10.8 (SD 1.7)% 10 years: 18.3 (SD 2.2)% 15 years: 25.8 (SD 2.6)% | NA | NA | NA | NA | O‐e cannot be extracted because P values not reported past NS in Table 2 in Louis‐Sylvestre (2004). Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Overall survival | ALND + RT: ?/97 Mastectomy alone: ?/98 (total event rate = 91) | o‐e = ‐4.19 | 22.75 | 0.83 | (0.55 to 1.25) | 0.38 | 15‐20 years | Using P = 0.38 reported on page 558 of Borgstrom (1994) and Tierney 2007 method 8. The o‐e is calculated on the basis of a total event rate of N = 91, and total N = 97 in the ALND + RT group and N = 98 in mastectomy alone group (i.e. intent‐to‐treat numbers), and using the only P value reported, which was for per‐protocol analysis that study authors stated did not differ from intention‐to‐treat analyses | |
| Chest wall recurrence | ALND + RT: 2/97 Mastectomy alone: 11/98 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15‐20 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival | Radical: 126/149 Simple + RT: 140/159 | o‐e = 5.4 | 58.6 | 1.10 | (0.85 to 1.42) | NA | 15 years | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Death from breast cancer | Radical: 100/149 Simple + RT: 112/159 | o‐e = 2.8 | 46 | 1.06 | (0.80 to 1.42) | NA | 15 years | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Local recurrence | Radical: 48 events/997 women‐years Simple + RT: 41 events/1113 women‐years | o‐e = ‐5.7 | 19.9 | 0.75 | (0.48 to 1.17) | NA | 15 years | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Death from any cause (OS) | ALND = 23/257 SLNB = 15/259 | o‐e = ‐4.34 | 9.08 | 0.62 | (0.32 to 1.19) | 0.15 | 10 years | Log‐rank P (Tierney 2007 method 7); ALND is control | |
| Breast cancer recurrence (local recurrence, regional lymph node metastases, distant metastases) | ALND = 26/257 SLNB = 23/259 | o‐e = ‐2.25 | 12.02 | 0.83 | (0.47 to 1.46) | 0.52 | 10 years | Log‐rank P (Tierney 2007 method 7); ALND is control | |
| Distant metastasis | ALND = 20/257 SLNB = 17/259 | o‐e = ‐2.04 | 9.19 | 0.80 | (0.42 to 1.53) | 0.50 | 10 years | Log‐rank P from table 4 Veronesi (2010) (Tierney 2007 method 7); ALND is control | |
| Axillary metastasis | ALND = 0/257 SLNB = 2/259 | o‐e = 0.97 | 0.50 | 6.96 | (0.44 to 111.3) | 0.17 | 10 years | Log‐rank P from table 4 Veronesi (2010) (Tierney 2007 method 8 and 9); ALND is control | |
| Local recurrence | ALND = 4/257 SLNB = 4/259 | o‐e = ‐0.12 | 2.00 | 0.94 | (0.24 to 3.76) | 0.93 | 10 years | Log‐rank P from table 4 Veronesi (2010) (Tierney 2007 method 7); ALND is control | |
| Supraclavicular metastasis | ALND = 2/257 SLNB = 0/259 | o‐e = ‐1.02 | 0.50 | 0.13 | (0.01 to 2.09) | 0.15 | 10 years | Log‐rank P from table 4 Veronesi (2010) (Tierney 2007 method 8, 9); ALND is control | |
| Contralateral breast cancer | ALND = 10/257 SLNB = 9/259 | o‐e = ‐0.81 | 4.47 | 0.84 | (0.34 to 2.07) | 0.71 | 10 years | Log‐rank P from table 4 Veronesi (2010) (Tierney 2007 method 7); ALND is control | |
| Overall survival | ALND = 31/109 No ALND = 35/110 | o‐e = ‐2.72 | 16.43 | 0.85 | (0.52 to 1.37) | Median = 150 months | HR reported on page 922 of Martelli (2012). Using Tierney 2007 method 3 o Please note, the curves cross; also the HR used for extraction of o‐e and its variance is adjusted for tumour grade and oestrogen‐receptor status | ||
| Breast cancer deaths | ALND: 8/109 No ALND: 10/110 | o‐e = 1.33 | 4.06 | 1.39 | ‐ | ‐ | Median = 150 months | HR reported in Table 3 of Martelli (2012). Tierney 2007 method 3 o Please note, the curves cross; also the HR used for extraction of o‐e and its variance is adjusted for tumour grade and oestrogen‐receptor status. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Axillary relapse | ALND: 0/109 No ALND: 4/110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Median = 150 months | Table 2 of Martelli (2012), cannot calculate o‐e | |
| Recurrence (ipsilateral breast tumour) | ALND: 4/109 No ALND: 7/110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Median = 150 months | Table 2 of Martelli (2012), cannot calculate o‐e | |
| Distant metastases | ALND: 9/109 No ALND: 9/110 | o‐e = ‐2.68 | 5.93 | 0.64 | (0.28 to 1.42) | NA | Median = 150 months | HR reported in Table 3 of Martelli (2012). Tierney 2007 method 3 Please note, the curves cross; also the HR used for extraction of o‐e and its variance is adjusted for tumour grade and oestrogen‐receptor status | |
| Overall survival | 10‐year ALND: 93.3% (95% CI 89.4‐95.8) no ALND: 91.5% (95% CI 87‐94.4) | o‐e = 1.76 | 12.33 | 1.15 | (0.66 to 2.02) | P = .436 | Median = 127.5 months | Agresti (2014) Figure 3A and Tierney 2007 method 11 Please note, the curves cross at the very end, also HR used for extraction of o‐e | |
| Death from breast cancer | ALND: 17/272 no ALND: 15/245 | NA | NA | NA | NA | P = 1.00 | Median = 127.5 months | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Disease‐free survival | 10‐year ALND: 92.4% (95% CI 88.5‐95.1) no ALND: 91.3% (95% CI 86.7‐94.3) | o‐e= ‐0.13 | 10.7 | 0.99 | (0.54 to 1.8) | P = .97 | Median = 127.5 months | Agresti (2014) Figure 3A andTierney 2007 method 11 Please note, the curves cross at the very end; also the HR used for extraction of o‐e | |
| Distant metastases | ALND: 23/272 no ALND: 20/245 | NA | NA | NA | NA | P = 1.00 | Median = 127.5 months | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Axillary recurrence | ALND: 0/272; no ALND: 22/245 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Median = 127.5 months | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Local recurrence | ALND: 14/272 no ALND: 11/245 | NA | NA | NA | NA | P = .839 | Median = 127.5 months | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Contralateral breast cancer | ALND: 13/272 no ALND: 14/245 | `NA | NA | NA | NA | P = .695 | Median = 127.5 months | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival: node negative: ALND vs no ALND | ALND = 259/389 No ALND = 256/384 | o‐e = ‐5 | 117.3 | 0.96 | (0.80 to 1.15) | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 Lancet (Appendix web figure 9a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Overall survival: node negative: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 259/389 No ALND + RT = 271/386 | o‐e = 8.6 | 122.2 | 1.07 | (0.90 to 1.28) | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Overall survival: node positive: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 244/301 No ALND + RT = 244/305 | o‐e = 8.3 | 109.4 | 1.08 | (0.89 to 1.30) | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Local isolated recurrence: node negative: ALND vs no ALND | ALND = 35 events/3949 women‐years No ALND = 94 events/3335 women‐years | o‐e = 31.5 | 29.2 | 2.94 | (2.05 to 4.23) | NA | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Local isolated recurrence: node negative: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 35 events/3949 women‐years No ALND + RT = 18 events/3896 women‐years | o‐e = ‐8.7 | 13 | 0.51 | (0.30 to 0.88) | NA | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Local isolated recurrence: node positive: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 45 events/2268 women‐years No ALND + RT = 42 events/2025 women‐years | o‐e = ‐0.5 | 20.8 | 0.98 | (0.64 to 1.50) | NA | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Disease‐free survival: node negative: ALND vs no ALND | ALND = 281/362 No ALND + RT = 287/365 | o‐e = 9.36 | 138.3 | 1.07 | (0.91 to 1.27) | 0.39 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 568 (radical vs total mastectomy) Tierney 2007 method 3, calculated from the date of mastectomy, events considered in determination of disease‐free survival were the first local, regional or distant recurrence of tumour; contralateral breast cancer or a second primary tumour other than a tumour in the breast; and death with no evidence of cancer | |
| Disease‐free survival: node negative: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 281/362 No ALND + RT = 292/352 | o‐e = 8.3 | 142.39 | 1.06 | (0.90 to 1.25) | 0.49 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 568 (radical vs total mastectomy + RT) Tierney 2007 method 3, calculated from the date of mastectomy, events considered in determination of disease‐free survival were the first local, regional or distant recurrence of tumour; contralateral breast cancer or a second primary tumour other than a tumour in the breast; and death with no evidence of cancer | |
| Disease‐free survival: node positive: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 254/292 No ALND + RT = 258/294 | o‐e = 14.46 | 127.57 | 1.12 | (0.94 to 1.33) | 0.20 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 568, Tierney 2007 method 3, calculated from the date of mastectomy, events considered in determination of disease‐free survival were the first local, regional or distant recurrence of tumour; contralateral breast cancer or a second primary tumour other than a tumour in the breast; and death with no evidence of cancer | |
| Relapse‐free survival: node negative: ALND vs no ALND | ALND = 154/362 No ALND + RT = 182/365 | o‐e = 10.17 | 77.61 | 1.14 | (0.91 to 1.42) | 0.27 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 568 Tierney 2007 method 3; calculated from the date of mastectomy, events considered in determination of relapse‐free survival were the first local, regional or distant recurrence; or an event in the contralateral breast | |
| Relapse‐free survival: node negative: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 154/362 No ALND + RT = 163/352 | o‐e = ‐2.9 | 71.05 | 0.96 | (0.76 to 1.21) | 0.74 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 568, Tierney 2007 method 3, calculated from the date of mastectomy, events considered in determination of relapse‐free survival were the first local, regional or distant recurrence; or an event in the contralateral breast | |
| Relapse‐free survival: node positive: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 178/292 No ALND + RT = 183/294 | o‐e = 7.63 | 88.52 | 1.09 | (0.89 to 1.35) | 0.40 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 568, Tierney 2007 method 3, calculated from the date of mastectomy, events considered in determination of relapse‐free survival were the first local, regional or distant recurrence; or an event in the contralateral breast | |
| Time to distant metastasis: node negative: ALND vs no ALND | ALND = 101/362 No ALND + RT = 107/365 | o‐e = 8.44 | 88.52 | 1.1 | (0.89 to 1.35) | 0.39 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 569, Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Time to distant metastasis: node negative: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 101/362 No ALND + RT = 111/352 | o‐e = 6.69 | 86.9 | 1.08 | (0.88 to 1.34) | 0.44 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 569, Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Time to distant metastasis: node positive: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 120/292 No ALND + RT = 127/294 | o‐e = 5.98 | 88.41 | 1.07 | (0.87 to 1.32) | 0.51 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 569, Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Overall survival (all randomised participants, i.e. node+ and node‐) | ALND = 228 (deaths)/2807 SLN = 252 (deaths)/2804 | 10.32 | 119.7 | 1.09 | (0.91 to 1.3) | 0.35 | 10 years | From Julian (2013) using Tierney 2007 method 4. Contacted author (Krag) to confirm direction of effect | |
| Disease‐free survival (all randomised participants, i.e. node+ and node‐) | ALND = 455/2807 SLN = 475/2804 | 4.6 | 232.39 | 1.02 | (0.9 to 1.16) | 0.72 | 10 years | From Julian (2013) using Tierney 2007 method 4. Contacted author (Krag) to confirm direction of effect | |
| Local/regional recurrence (all randomised participants, i.e. node+ and node‐) | ALND = 121/2807 SLN = 112/2804 | ‐2.37 | 58.16 | 0.96 | (0.74 to 1.24) | 0.77 | 10 years | From Julian (2013) using Tierney 2007 method 4. Contacted author (Krag) to confirm direction of effect | |
| Axillary recurrence (all randomised participants, i.e. node+ and node‐) | ALND = 6/2807 SLN = 14/2804 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years | o‐e cannot be calculated. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival (for SLN‐neg) | ALND = 219 (dead)/1975 SLN = 245 (dead)/2011 | o‐e = 12.07 | 115.64 | 1.11 | (0.93 to 1.33) | 0.27 | 10 years | From Julian (2013) using Tierney 2007 method 4 | |
| Disease‐free survival (for SLN‐neg) | ALND = 456 (diseased)/1975 SLN = 465 (diseased)/2011 | o‐e = 2.29 | 230.23 | 1.01 | (0.89 to 1.15) | 0.92 | 10 years | From Julian (2013) using Tierney 2007 method 4 | |
| Local regional recurrence | ALND = 85 (events)/1975 SLN = 80 (events)/2011 | o‐e = ‐2.11 | 41.21 | 0.95 | (0.7 to 1.29) | 0.77 | 10 years | From Julian (2013) using Tierney 2007 method 4 | |
| Local recurrence in SLN‐negative participants | ALND = 54 (events)/1975 SLN = 49 (events)/2011 | o‐e = ‐3.03 | 25.69 | 0.89 | (0.6 to 1.31) | 0.55 | Mean = 95.6 months | From Krag (2010) page 930 using logrank P = 0.55 Tierney 2007 method 7 | |
| Regional recurrence in SLN‐negative participants | ALND = 8 (events)/1975 SLN = 14 (events)/2011 | o‐e = 2.77 | 5.09 | 1.72 | (0.72 to 4.11) | 0.22 | Mean = 95.6 months | From Krag (2010) page 930 using log rank P = 0.22 Tierney 2007 method 7 | |
| Distant recurrence in SLN‐negative patients | ALND = 55 (events)/1975 SLN = 64 (events)/2011 | o‐e = 3.91 | 29.82 | 1.14 | (0.8 to 1.64) | Mean = 95.6 months | From Krag (2010) Figure 4 Tierney 2007 method 3 | ||
| Recurrence in the axilla | ALND: 0/57 Sampling: 1/54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Median: 30 (range, 5‐76) months | From Borup‐Chistesen (1993) table IV. Recurrence is reported only out of N = 111 (57 + 54) participants who did not have metastases in axillary lymph nodes after dissection or biopsy. Cannot calculate o‐e on the basis of available data | |
| Local recurrence | ALND: 4/57 Sampling: 1/54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Median: 30 (range, 5‐76) months | From Borup‐Chistesen (1993) table IV. Recurrence is reported only out of N = 111 (57 + 54) participants who did not have metastases in axillary lymph nodes after dissection or biopsy. Cannot calculate o‐e on the basis of available data | |
| Distant recurrence | ALND: 1/57 Sampling: 4/54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Median: 30 (range, 5‐76) months | From Borup‐Chistesen (1993) table IV. Recurrence is reported only out of N = 111 (57 + 54) participants who did not have metastases in axillary lymph nodes after dissection or biopsy. Cannot calculate o‐e on the basis of available data | |
| Overall survival: node negative: ALND vs Simple + RT | ALND = 143/199 Simple + RT = 143/180 | o‐e = 17.5 | 65.7 | 1.31 | (1.02 to 1.66) | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Overall survival: node positive: ALND vs Simple + RT | ALND = 72/89 Simple + RT = 77/93 | o‐e = 6.3 | 34.1 | 1.20 | (0.86 to 1.68) | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Local isolated recurrence: node negative: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 26 events/2880 women‐years Simple + RT = 21 events/2204 women‐years | o‐e = ‐0.5 | 11.3 | 0.96 | (0.53 to 1.71) | NA | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Local isolated recurrence: node positive: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 24 events/943 women‐years Simple + RT = 17 events/878 women‐years | o‐e = ‐2.9 | 9.8 | 0.74 | (0.40 to 1.39) | NA | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Overall survival ‐ node negative | ALND: 56/101 Simple + RT to chest wall & axilla: 42/85 | o‐e = ‐5.5 | 21.4 | 0.77 | (0.51 to 1.18) | NA | 15 years? | CAUTION: same control group used twice for these data Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figures 9a and 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Overall survival ‐ node positive | ALND: 13/17 Simple + RT to chest wall & axilla: 7/9 | o‐e = ‐0.5 | 3.3 | 0.86 | (0.29 to 2.53) | NA | 15 years? | CAUTION: same control group used twice for these data Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figures 9b and 10b). then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Isolated local recurrence ‐ node negative | ALND: 15/510 py Simple + RT to chest wall & axilla: 13/483 py | o‐e = 0.0 | 6.7 | 1.00 | (0.47 to 2.13) | NA | 5 years? | CAUTION: same control group used twice for these data Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figures 9a and 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Isolated local recurrence ‐ node positive | ALND: 3/69 py Simple + RT to chest wall & axilla: 1/41 py | o‐e = ‐0.5 | 0.9 | 0.57 | (0.07 to 4.53) | NA | 5 years? | CAUTION: same control group used twice for these data Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figures 9b and 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| 10‐year overall survival | Level I clearance: 75/93 ALND: 71/88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years | o‐e could not be calculated as no P values reported. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| 10‐year disease‐free survival | Level I clearance: 72/93 ALND: 68/88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years | o‐e could not be calculated as no P values reported. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Breast cancer recurrence | Level I clearance: 19/93 ALND: 17/88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years? | o‐e could not be calculated as no P values reported. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Local recurrence | Level I clearance: 3.2% ALND: 2.3% | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years? | o‐e could not be calculated as no P values reported. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Distant metastasis | Level I clearance: 19/93 ALND: 15/88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years? | o‐e could not be calculated as no P values reported. Not included in meta‐analysis |
Figures in bold were reported in the original publication; others were derived (see Notes column).
| Study | Oedema | Shoulder function | Skin graft | Delayed healing | Activity | Attitude | Other | Notes |
| Slight: 0‐2.5 cm Moderate: 2.5‐4.5 cm Severe > 4.5 cm Circumference of both arms measured 7.5 cm below the acromion, 18 cm above and 10 cm below the olecranon and at the wrist Presumably difference between arm circumference | Arm function: Good: uses arm freely Fair: cannot do usual tasks Poor: very unsatisfactory use of arm Appears to be assessed by patient questionnaire | Good: normal activity, back at work or resumed usual activities Fair: light work only because of operation; not resumed usual activities Poor: inactive. Assessed by patient questionnaire | Good: no complaints Fair: some complaints Poor: very unhappy about experience Assessed by patient questionnaire | |||||
| Lympheoedema (subjective) – according to patient self‐report or physician diagnosis Lympheoedema (objective): 2 cm or greater postop increase in ipsilateral arm circumference | Axillary paraesthesia – patient reported Brachial plexus injury – determined by physician on examining the patient | |||||||
| 1. Mild oedema 2. Gross oedema (estimated by measuring the circumference of each arm with the arm extended at points 11 inches and 22 inches from the tips of the middle finger. An increase of 1 inch in the circumference of the arm on the side of the operation at either or both points was taken to indicate some degree of oedema) | Stiff shoulder | Need for skin graft | Sufficient to cause postponement of radiotherapy until at least 2 months after the operation. Although incidence of delayed healing varied between surgeons, each showed the same trend of higher incidence following a radical operation | |||||
| Subjective lymphoedema: patient reported Objective lymphoedema: circumferential arm measurement at 4 cm intervals from the wrist (approximately 10 measurements) used to calculate arm volume. Volume corrected using measurements from contralateral arm | Range of movement measured by recording degrees of flexion, abduction and internal and external rotation using goniometer Sensory function tested using pinprick, light touch | Global Severity Index (GSI; low values better), Beck's Depression Inventory, Spielberger's State‐Trait anxiety, MAC, SF‐36 (measured psychological morbidity and quality of life) | ||||||
| Change in ipsilateral arm volume at each follow‐up visit was expressed as a % increase from pretreatment value. Ratios of presurgery to postsurgery arm volumes were compared on a log‐transformed scale. The contralateral arm was used as a control for evaluations of arm volume Also patient rated as mild, moderate or severe | Assessed by goniometric measurement of arm movement (flexion, abduction, internal rotation and external rotation). Changes between visits calculated by subtraction The contralateral arm was used as a control for arm and shoulder function | QoL: Fact‐B+4 Anxiety: Spielberger STAI | ||||||
| Cardiff ‐ Local | No morbidity data | |||||||
| Cardiff ‐ St Mary's | Oedema of arm 72 cm | Restricted elevation 720 degrees | Measured but not reported | Axillary pain; numbness or paraesthesia on operated sides; aesthetic appearance of axillary scar | ||||
| Arm swelling measured by water displacement, circumference 15 cm above and below the olecranon process | Shoulder mobility assessed by measuring elevation through flexion, abduction, medial and lateral rotation | Shoulder muscle power assessed using graduated spring to measure flexion, extension, abduction and adduction of the shoulder joint | ||||||
| Arm welling (arm circumference 15 cm above and 10 cm below olecranon) | Objective assessment via adduction with internal rotation; abduction with external rotation, difference in height reached between treated and non‐treated arms by stretching above head, measurement of an abduction movement without shoulder rotation whilst lying on a flat, hard surface | Power (cm/kg) of pectoralis major by repeated lifting of a 3.5 kg weight as fast as possible over 45 seconds, comparing treated and untreated arm | Sample from study only, level B evidence | |||||
| Lympheodema was assessed by comparing the circumference of the operated vs the non‐operated arm at 15 cm above the epicondyle Unclear what difference in circumference constituted lymphoedema | Assessed by the surgeon by evaluating active and passive flexion, abduction, internal and external rotation, and classified on a scale 0 (normal mobility) to 3 (severe mobility) restriction Winged scapula reported as present/absent | Axillary and arm pain reported by patients on a scale from 0 (absent) to 3 (continuous/severe) Numbness assessed by the surgeon by comparing skin sensitivity in operated and non‐operated arms. Rated 0 (absent) to 3 (severe) | ||||||
| Reports lymphoedema; categorised as none, slight, moderate and severe | Reports arm function as good, fair or poor | Reports activity as good, fair or poor | Reports attitude as good, fair or poor | Pts in no axillary surgery + RT arm reported fibrosis of breast and sometimes "marbling" of the overlying skin. Both occurred in <5% of cases | ||||
| Impairted function of the shoulder joint and swollen arm: no definitions given, but it is stated that the methodology included volumetric measurement of the upper limb and that an attempt was made to ally objective measurements with the patient’s subjective expression of discomfort or disability | Impairted function of the shoulder joint and swollen arm: no definitions given, but it is stated that the methodology included volumetric measurement of the upper limb and that an attempt was made to ally objective measurements with the patient’s subjective expression of discomfort or disability | In evaluating morbidity, attempts made to ally objective measurements with patient's subjective expression of disability or discomfort. Expectation that after RM, slight increase in volume of ipsilateral arm, or after RT, some discomfort and stiffness to shoulder, but these do not amount to morbidity | ||||||
| ≥ 5% increase in arm circumference from baseline | QOL: A core questionnaire plus a surgical module specific to this trial. Four linear analogue scales on the core questionnaire were used: well‐being, mood, appetite and perceived adjustment/coping. After 1993, 6 additional scales were added: tiredness, hot flashes, nausea/vomiting, perceived social support, arm restriction and subjective health estimation. Surgical module measured swelling, numbness, weakness, pain, stiffness, performance of daily activities and global measure of arm/hand/shoulder/chest bother | |||||||
| No definitions for functional outcomes reported | ||||||||
| No definitions for functional outcomes reported | ||||||||
| An increase in arm volume was defined as an increase > 2 cm, comparing the circumference of the operated upper limb (at 3 points: the wrist, the midpoint of the forearm and the midpoint of the upper arm) with its non‐operated counterpart | Patients were asked to lift their operated arm (maximum possible abduction): abduction ≥ 90° was considered adequate; abduction < 90° was considered abnormal | Patients were asked: Is your arm painful in a resting position (yes/no)? Does the inside of your arm feel more numb (yes/no)? | ||||||
| Arm swelling was assessed by comparing the circumference of treated and untreated arms 15 cm above the lateral epicondyle | Arm mobility was judged by asking the patient to rate restriction in movement on a scale 0 to 100 Numbness assessed by comparing skin sensitivity on inside and outside of the upper arm – classified as yes/no | Aesthetic appearance of scar judged by patient (rated good or bad) | Postoperative pain was evaluated as continuous (> 50% of the day), sporadic or absent | |||||
| Ipsilateral and contralateral measurement of arm circumference at 15 cm below the acromion process and 15 cm below the olecranon: An increase in arm circumference ≥ 2 cm in ipsilateral arm (below or above the elbow) indicated arm oedema | ||||||||
| Arm volume measured using volume of water displaced determined by the difference between treated and untreated arms (relative arm volume difference = [ipsilateral‐contralateral]/[contralateral] × 100%) | Arm mobility in degrees was determined by measuring the straight lateral abduction of both ipsilateral and contralateral arms using a standard orthopaedic goniometer to determine the angle between lateral chest wall and humerus (relative shoulder abduction deficit = [ipsilateral‐contralateral]/[contralateral] × 100%) | Numbness and tingling were assessed by self‐report by asking patients if they were currently experiencing any numbness or any tingling anywhere in ipsilateral and contralateral arms. OR of SLN compared with ALND Adverse events: no details reported | ||||||
| Arm volume measured using volume of water displaced. A cutoff of 10% increase in volume was used as the arbitrary cut point | Shoulder mobility (flexion, abduction and rotation) was determined with the help of a 360° scale placed on a wall with the centre at shoulder height | |||||||
| Arm volume was estimated using 6 measures of arm circumference at 10 cm intervals starting 10 cm from the tip of the index finger. Upper limb swelling was expressed as percentage change in volume from baseline | Abduction and flexion measured using goniometer Arm morbidity measured using the 15‐item SSSS scale developed for the study, with each rated from 0 (no trouble at all) to 10 (worst I can imagine) and averaged to obtain overall score | |||||||
| Increase in circumference of forearm by at least 3 cm | Failure to abduct the arm beyond a right angle | |||||||
| Postoperative swelling: middle grade (diameter is 3–6 cm enlargement on the involved upper arm or forearm compared with the contralateral part) |
| Study | Outcome | Measurement | Follow‐up period 1 | Follow‐up period 2 | Notes |
| Wound infection | Determined by treating physician | SLND: 11/371; SLND + ALND: 31/373 | |||
| Axillary seroma | Determined by treating physician | SLND: 21/371; SLND + ALND: 53/373 | |||
| Brachial plexus injury | Determined by treating physician | At 6 months: SLND: 3/415; SLND + ALND: 5/406 At 1 year: SLND: 0/415; SLND + ALND: 1/406 | |||
| Axillary paraesthesia | Patient reported | 30 days: SLND: 43/371; SLND + ALND: 174/373 | 6 months: SLND: 35/288; SLND + ALND: 146/335 | ||
| Axillary paraesthesia | Patient reported | 12 months: SLND: 24/268; SLND + ALND: 113/287 | |||
| Lymphoedema (objective) | Arm measurement | 30 days: SLND: 17/272; SLND + ALND: 23/255 | 6 months: SLND: 21/271; SLND + ALND: 29/270 | ||
| Lymphoedema (objective) | Arm measurement | 12 months: SLND: 14/226; SLND + ALND: 26/242 | |||
| Lymphoedema (subjective) | Patient reported/physician diagnosis | 6 months: SLND: 19/339; SLND + ALND: 27/327 | 12 months: SLND: 12/268; SLND + ALND: 37/288 | ||
| Lymphoedema (subjective) | Patient reported/physician diagnosis | > 12 months: SLND: 14/253; SLND + ALND: 52/272 | |||
| Mild oedema | Follow‐up was at least 12 months in most cases. ALND = 7/91; Simple = 5/113 | ||||
| Stiff shoulder | ALND = 6/91; Simple = 8/113 | ||||
| Skin graft | Need for skin graft | ALND = 4/91; Simple = 2/113 | |||
| Delayed healing | Need to delay postoperative RT | ALND = 18/91; Simple = 7/113 | |||
| Gross oedema | Arm measurement | ALND = 0/91; Simple = 0/113 | ALND = 12/45; Simple = 6/53 | ||
| Seroma | ALND: 33/155; SLNB: 20/143 | ||||
| Lymphoedema (objective) | Arm volume changes | 12 months: ALND: mean (SE) = 56.4 (10.9); SLNB: mean (SE) = 18.6 (13.8), difference mean (SE) = 37.8 (17.6) Mean (1, 3, 6, 12 months): ALND: mean (SE) = 53.1 (8.1); SLNB: mean (SE) = 17.7 (9.2), difference mean (SE) = 35.4 (12.2) | Max: ALND: mean (SE) = 113.7 (9.7); SLNB: mean (SE) = 78.4 (12), difference mean (SE) = 35.3 (15.3) | ||
| Lymphoedema (subjective) | Patient reported | 1 month: OR = 0.34 (95% CI 0.11 to 0.9); 3 months: OR = 0.4 (95% CI 0.16 to 0.94); 6 months: OR = 0.25 (95% CI 0.08 to 0.66) | 12 months: OR = 0.36 (95% CI 0.15 to 0.86); mean: OR = 0.3 (95% CI 0.18 to 0.68) | Odds ratios: SLNB/ALND; i.e. lower favours SLNB | |
| Paraesthesia | ALND: 130/155; SLNB: 92/140 | ||||
| Numbness | ALND: 115/155; SLNB: 68/143 | ||||
| Loss of pinprick | ALND: 118/155; SLNB: 77/140 | ||||
| Loss of light touch | ALND: 121/155; SLNB: 81/140 | ||||
| QOL (immediate postop) | Study authors note QOL scores were usually higher (better) in the SLND group and significantly so in the immediate postoperative period (P < 0.01). No significant effect of node positive/negative | ||||
| MAC scale (12 months) | Study authors no significant difference in MAC scores during 1 year follow‐up. No significant effect of node positive/negative | ||||
| BSI – somatisation (immediate postop) | SLND group scored lower (better) than ALND in the immediate postoperative period (P < 0.001) | ||||
| Quality of life | GSI level | 12 months: ALND: mean (SE, N) = 49.7 (1.1, 143); SLNB: mean (SE, N) = 48.4 (0.9, 134), difference mean (SE) = 1.3 (1.4) | OR for morbid GSI: study/control (95% CI) 0.55 (0.08 to 2.94) | ||
| Quality of life | SF‐36 (immediate postoperative) | Physical combined: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 38.6 (8.2, 143); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 42.3 (10.4, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 3.7 (1.2 to 6.1) Physical functioning: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 41.3 (9, 143); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 44.5 (8.1, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 3.2 (1.1 to5.4) | Vitality: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 48.2 (10.2, 143); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 51.8 (9.8, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 3.7 (1.1 to 6.2) | ||
| Shoulder movement (mean reduction) | Flexion, extension, abduction, internal rotation, external rotation | Flexion: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 13 (32.9, 141); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 6.7 (15.6, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 6.3 (0.1 to 12.6); Extension: ALND: mean (SD, N) = ‐1.5 (10.7, 139); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = ‐2.2 (8.1, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 0.7 (‐1.5 to 3.3); Abduction: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 6.3 (11.5, 138); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 3.1 (15.7, 132), difference mean (95% CI) = 3.2 (‐0.5 to 6.3) | Internal rotation: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 1.7 (12.7, 139); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 0.3 (12, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 1.4 (‐1.5 to 4.4); External rotation: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 2.9 (12.3, 139); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 1.5 (11, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 1.4 (‐1.5 to 4.4) | ||
| Axillary drain usage | ALND: 359/453; SLNB: 75/449 | ||||
| Infection rate of surgical wounds | ALND: 72/476; SLNB: 52/478 | ||||
| Lymphoedema | Patient‐assessed; moderate/severe | 1 month: ALND: 7/419; SLNB: 1/428 3 months: ALND: 12/395; SLNB: 4/417 | 6 months: ALND: 13/414; SLNB: 2/432 12 months: ALND: 10/403 SLNB: 4/412 | ||
| Lymphoedema | Mean (95% CI) change in arm vol compared with pretreatment | 1 month: ALND = 1.022 (1.013‐1.032); SLNB = 1.003 (0.997‐1.01) 3 months: ALND = 1.044 (1.035‐1.053); SLNB = 1.019 (1.01‐1.028) | 6 months: ALND = 1.058 (1.048‐1.069); SLNB = 1.022 (1.011‐1.032) 12 months: ALND = 1.061 (1.048‐1.074); SLNB = 1.028 (1.016‐1.039) | ||
| Sensory loss | Median area of sensory loss (cm2; range) | 1 month: ALND = 40 (1‐489); SLNB = 32 (2‐254) 3 months: ALND = 47 (0‐1139); SLNB = 48 (0‐327) | 6 months: ALND = 39 (0.4‐2827); SLNB = 32 (0‐201) 12 months: ALND = 35 (0.8‐1013); SLNB = 59 (0.2‐342) | Event rates for self‐assessed sensory loss also reported in Mansel 2006 for these follow‐up periods, but not extracted | |
| Intercostobrachial nerve damage | Clinician assessment; severe | 1 month: ALND: 10/392; SLNB: 6/409 3 months: ALND: 10/373; SLNB: 4/397 | 6 months: ALND: 10/394; SLNB: 4/410 12 months: ALND: 5/384 SLNB: 5/400 | ||
| Shoulder function | Mean change in shoulder function (degrees): flexion | 1 month: ALND = 9.8; SLNB = 5.8 3 months: ALND = 3.7; SLNB = 2 | 6 months: ALND = 1.6; SLNB = 2 12 months: ALND = 0.1; SLNB = 2.7 | 95% CI can also be extracted | |
| Shoulder function | Mean change in shoulder function (degrees): abduction | 1 month: ALND = 12.9; SLNB = 6.5 3 months: ALND = 4.2; SLNB = 1.9 | 6 months: ALND = 2.3; SLNB = 1.5 12 months: ALND = 1.9; SLNB = 2.5 | 95% CI can also be extracted | |
| Shoulder function | Mean change in shoulder function (degrees): external rotation | 1 month: ALND = 1.2; SLNB = 0.7 3 months: ALND = 1.2; SLNB = 0.2 | 6 months: ALND = 1; SLNB = 0.6 12 months: ALND = 0.7; SLNB = 0.6 | 95% CI can also be extracted | |
| Shoulder function | Mean change in shoulder function (degrees): internal rotation | 1 month: ALND = 0.9; SLNB = 0.4 3 months: ALND = 0.7; SLNB = 1 | 6 months: ALND = 0.8; SLNB = 0.2 12 months: ALND = 0.4; SLNB = 1.7 | 95% CI can also be extracted | |
| Quality of life | Measures: mean trial outcome index; trial outcome index reduced by ≥ 5 points from baseline (n/N); mean arm functioning subscale score; substantial arm swelling or tenderness (n/N); substantial numbness on ipsilateral side (n/N); mean FACT‐B+4 score | Means (95% CI) and event rates can be extracted for each time point (baseline, 1, 3, 6 and 12 months) | |||
| State and trait anxiety | Mean and 95% CI can be extracted for each time point (baseline, 1, 3, 6 and 12 months) | ||||
| Morbidity | Objective complaints: restricted elevation 720 degrees | Not stated: full axillary surgery, neg nodes = 25% (×2 = 7.47, P < 0.01); no axilary surgery, neg nodes = 0%; full axillary surgery + radical RT, positive nodes = 67%; no axillary surgery + local RT = 37% | Sample of 85 patients only from Cardiff site | ||
| Morbidity | Objective complaints: oedema of arm, 72 cm | Not stated: full axillary surgery, neg nodes = 46% (×2 = 6.02, P < 0.03); no axillary surgery, neg nodes = 15%; full axillary surgery + radical RT, positive nodes = 58%; no axillary surgery + local RT = 37% | Sample of 85 patients only from Cardiff site | ||
| Morbidity | Subjective complaints: limited arm movement | Not stated: full axillary surgery, neg nodes = 21%; no axillary surgery, neg nodes = 8%; full axillary surgery + radical RT, positive nodes = 8%; no axillary surgery + local RT = 21% | Sample of 85 patients only from Cardiff site | ||
| Morbidity | Subjective complaints: swollen arm | Not stated: full axillary surgery, neg nodes = 43%; no axillary surgery, neg nodes = 23%; full axillary surgery + radical RT, positive nodes = 58%; no axillary surgery + local RT = 37% | Sample of 85 patients only from Cardiff site | ||
| Morbidity | Lateral shoulder rotation (mean (SE) difference (cm) from preoperative value (N)) | 6 months: Sampling + RT: 1.91 (SE = 0.56) (N = 64), sampling ‐ RT: 0.34 (SE = 0.59) (N = 59); ALND: 0.13 (SE = 0.39) (N = 132) | 12 months: Sampling + RT: 1.75 (SE = 0.56) (N = 66), Sampling ‐ RT: 0.72 (SE = 0.62) (N = 55); ALND: 0.77 (0.4) (N = 128) | Figure 4, Chetty 2000 paper | |
| Morbidity | Lateral shoulder rotation (mean (SE) difference (cm) from preoperative value (N)) | 24 months: Sampling + RT: 1.57 (SE = 0.6) (N = 60), Sampling ‐ RT: ‐0.48 (SE = 0.65) (N = 52); ALND: 0.38 (SE = 0.43) (N = 117) | 36 months: Sampling + RT: 2.19 (SE = 0.59) (N = 59), Sampling ‐ RT: 0.43 (SE = 0.64) (N = 50); ALND: 0.24 (SE = 0.43) (N = 110) | Figure 4, Chetty 2000 paper | |
| Morbidity | Arm volume (mean (SE) percentage of preoperative arm volume (N)) | 6 months: Sampling + RT: 100.69 (SE = 0.779) (N = 56), Sampling ‐ RT: 102.04 (SE = 0.766) (N = 58); ALND: 103.57 (SE = 0.519) (N = 126) | 12 months: Sampling + RT: 100.95 (SE = 0.81) (N = 59), Sampling ‐ RT: 102.47 (SE = 0.85) (N = 54); ALND: 103.74 (SE = 0.57) (N = 119) | Figure 5, Chetty 2000 paper | |
| Morbidity | Arm volume (mean (SE) percentage of preoperative arm volume (N)) | 24 months: Sampling + RT: 100.84 (SE = 1.03) (N = 54), Sampling ‐ RT: 100.81 (SE = 1.06) (N = 51); ALND: 104.37 (SE = 0.73) (N = 108) | 36 months: Sampling + RT: 100.01 (SE = 1.03) (N = 52), Sampling ‐ RT: 101.28 (SE = 1.07) (N = 48); ALND: 104.07 (SE = 0.73) (N = 103) | Figure 5, Chetty 2000 paper | |
| Morbidity | Subjective arm | Not stated; full axillary surgery, positive node (Nil 8/12; intermittent 1/12; persistent 3/12); full axillary surgery, ‐negative node (nil 22/28; intermittent 1/28; persistent 5/28); Sample + RT, positive node (nil 17/28; intermittent 2/28; persistent 9/28); Sample, negative node (nil 23/26; intermittent 1/26; persistent 2/26) | Morbidity data to be included in discussion only; sample chosen from alphabetical pt list of patients free of local or systemic disease | ||
| Morbidity | Subjective mobility | Not stated; full axillary surgery, positive node (normal 12/12; reduced 0/12); full axillary surgery, negative node (normal 22/28; reduced 6/28); Sample + RT, negative node (normal 12/28; reduced 16/28); Sample, negative node (normal 24/26; reduced 2/26) | See comments in Aitken paper | ||
| Morbidity | Subjective interference with daily activities | Not stated; full axillary surgery, positive node (nil 12/12; occasional 0/12; severe 0/12); full axillary surgery, negative node (nil 24/28; occasional 4/28; severe 0/28); Sample + RT, positive node (nil 16/28; occasional 8/28; severe 4/28); Sample, negative node (nil 24/26; occasional 4/26; severe 0/26) | See comments in Aitken paper | ||
| Morbidity | Objective assessment ‐ shoulder joint mobility | See comments in Aitken paper | |||
| Psychological morbidity | Use in discussion only | ||||
| Lymphoedema | Assessed by physician, reported as odds ratio (95% CI): SLNB/ALND | 6 months: 0.37 (0.2 to 0.7) 12 months: 0.48 (0.2 to 0.9) | 18 months: 0.59 (0.3 to 1.2) 24 months: 0.52 (0.2 to 1.1) | ||
| Shoulder movement restriction | Assessed by physician, reported as odds ratio (95% CI): SLNB/ALND | 6 months: 0.47 (0.3 to 0.8) 12 months: 0.73 (0.4 to 1.4) 12 months: raw data extracted from graph (SLNB 17/336, ALND 23/341) | 18 months: 0.62 (0.3 to 1.3) 24 months: 0.44 (0.2 to 1.0) | ||
| Axillary/arm pain | Assessed by physician, reported as odds ratio (95% CI): SLNB/ALND | 6 months: 0.52 (0.3 to 0.8) 12 months: 0.76 (0.5 to 1.3) 12 months: raw data extracted from graph (SLNB 30/336, ALND 39/341) | 18 months: 0.84 (0.5 to 1.5) 24 months: 0.90 (0.5 to 1.6) | ||
| Numbness | Assessed by physician, reported as odds ratio (95% CI): SLNB/ALND | 6 months: 0.64 (0.4 to 0.9) 12 months: 0.53 (0.3 to 0.8) 12 months: raw data extracted from graph (SLNB 41/336, ALND 71/341) | 18 months: 0.37 (0.2 to 0.6) 24 months: 0.54 (0.3 to 0.9) | ||
| Winged scapula | Assessed by physician | Study authors report rate too low to analyse | |||
| Health‐related quality of life: SF‐36 – physical component | Assessed by patients using validated questionnaires | No significant differences found between group means of SF‐36 physical component (Del Bianco, 2008) | |||
| Health‐related quality of life: SF‐36 – mental component | Assessed by patients using validated questionnaires | No significant differences found between group means of SF‐36 mental component (Del Bianco, 2008) | |||
| Health‐related quality of life: SF‐36 HRQOL domains | Assessed by patients using validated questionnaires | No significant differences found between groups on all HRQOL domains of SF‐36 (Zavagno, 2008) | |||
| Health‐related quality of life: psychological general well‐being index | Assessed by patients using validated questionnaires | 6, 12 months: significantly better PGWB general and anxiety domain scores in SLNB group than in ALND group (Del Bianco, 2008) | 24 months: no significant differences between PGWB general and anxiety domain scores of both groups.(Del Bianco, 2008) | ||
| Morbidity | Arm function | 3 months: ALND: Good: 44/90, Fair: 41/90, Poor: 5/90; No ALND: Good: 59/77, Fair: 18/77, Poor: 0/77 | 15 months: ALND: Good: 83/100, Fair: 14/100, Poor: 3/100; No ALND: Good: 70/88, Fair: 17/88, Poor: 1/88 | Sample only | |
| Morbidity | Lymphoedema | 3 months: ALND: None: 18/93, Slight: 66/93, Moderate: 6/93, Severe: 3/93; No ALND: None: 36/81, Slight: 43/81, Moderate: 0/81, Severe: 2/81 | 15 months: ALND: None: 27/104, Slight: 71/104 Moderate: 6/104, Severe: 0/104; No ALND: None: 39/91, Slight: 52/91, Moderate: 0/91, Severe: 0/91 | Sample only | |
| Morbidity | Activity | 3 months: ALND: Good: 45/92, Fair: 46/92, Poor: 1/92; No ALND: Good: 62/80, Fair: 16/80, Poor: 2/80 | 15 months: ALND: Good: 85/101, Fair: 14/101, Poor: 2/101; No ALND: Good: 78/92, Fair: 13/92, Poor: 1/92 | Sample only | |
| Morbidity | Attitude | 3 months: ALND: Good: 81/92, Fair: 9/92, Poor: 2/92; No ALND: Good: 71/80, Fair: 7/80, Poor: 2/80 | 15 months: ALND: Good: 91/101, Fair: 8/101, Poor: 2/101; No ALND: Good: 87/92, Fair: 5/92, Poor: 0/92 | Sample only | |
| Postoperative deaths | Radical: 0/95; Simple: 0/100 | ||||
| Morbidity | Shoulder function | At 4‐year minimum follow‐up in survivors: Radical: 6/95; Simple = 18/100 | Consequential morbidity, at time of publication Methodology not reported, all patients included | ||
| Morbidity | Arm swelling (including volumetric measurement of upper limb) | At 4‐year minimum follow‐up in survivors: Radical: 7/95; Simple = 3/100 | Consequential morbidity, at time of publication Methodology not reported, all patients included | ||
| Lymphoedema | Physician reported | Not significantly different between treatments | |||
| Arm circumference | Physician reported | Not significantly different between treatments | |||
| Performance of daily activities | Physician reported | Not significantly different between treatments | |||
| Arm pain | Physician reported | Baseline: ALND 5/175, surgery 8/194; 1st postoperative: ALND 38/164, surgery 12/168; 3 months: ALND 16/161, surgery 9/171; 6 months: ALND 17/174, surgery 11/177 | 9 months: ALND 21/160, surgery 8/164; 12 months: ALND 13/189, surgery 8/190; 18 months: ALND 14/173, surgery 7/183; 24 months: ALND 12/165, surgery 8/164 | ||
| Restricted arm movement | Physician reported | Baseline: ALND 9/174, surgery 6/194; 1st postoperative: ALND 64/163, surgery 25/168; 3 months: ALND 23/161, surgery 10/170; 6 months: ALND 21/176, surgery 9/176 | 9 months: ALND 21/160, surgery 7/163; 12 months: ALND 19/188, surgery 6/187; 18 months: ALND 10/171, surgery 7/182; 24 months: ALND 12/165, surgery 7/164 | ||
| QOL ‐ bothered scores | Patient reported | No significant differences at any time point (baseline, 1st postoperative, 3, 6, 9, 12, 18 and 24 months) | |||
| QOL ‐ arm movement scores | Patient reported | At 1st postoperative surgery alone, reported less restriction in use of their arm than ALND (P < .0001). Otherwise, no significant differences | |||
| QOL ‐ numbness scores | Patient reported | At 1st postoperative surgery alone, reported less severe postsurgery numbness than ALND (P < .0001). Otherwise, no significant differences | |||
| QOL ‐ coping scores | Patient reported | No significant differences at any time point (baseline, 1st postoperative, 3, 6, 9, 12, 18 and 24 months) | |||
| Postoperative infection | Physician assessed | Surgery alone: 0/467 ALND: 1/464 | |||
| Sensory neuropathy | Physician assessed | Any: Surgery alone: 55/453 ALND: 82/447 Grade 3‐4: Surgery alone: 0/453 ALND: 1/447 | |||
| Lymphoedema | Physician assessed | Defined as long term: Any: Surgery alone: 15/453 ALND: 59/447 Grade 3‐4: Surgery alone: 0/453 ALND: 3/447 | |||
| Motor neuropathy | Physician assessed | Any: Surgery alone: 13/453 ALND: 37/447 Grade 3‐4: Surgery alone: 1/453 ALND: 3/447 | |||
| Arm fatigue | Unclear | Moderate/severe: no ALND: N = 4/258; ALND: N = 24/273 | |||
| Shoulder mobility | Unclear | Restricted somewhat or severely: no ALND: N = 5/257; ALND: N = 21/271 | |||
| Parasthesia | Unclear | Moderate/severe: no ALND: N = 6/258; ALND: N = 41/274 | |||
| Lymphoedema | Unclear | Minor/major difference: no ALND: N = 3/258; ALND: N = 29/275 | |||
| Other functional impairments | Unclear | Minor/major: no ALND: N = 12/263; ALND: N = 16/276 | |||
| Number of patients with functional impairments | Unclear | Minor: no ALND: N = 23/265; ALND: N = 78/278 | |||
| Upper limb circumference > 2 cm | Measured as per definition | 6 months: Obs: 6/57; ALND: 10/49 12 months: Obs: 8/57; ALND: 15/49 | 24 months: Obs: 8/57; ALND: 14/49 48 months: Obs: 4/57; ALND: 19/49 | ||
| Pain at rest | Patient reported | 6 months: Obs: 9/57; ALND: 9/49 12 months: Obs: 11/57; ALND: 14/49 | 24 months: Obs: 9/57; ALND: 10/49 48 months: Obs: 3/57; ALND: 7/49 | ||
| Parasthesias | Patient reported? | 6 months: Obs: 10/57; ALND: 28/49 12 months: Obs: 6/57; ALND: 29/49 | 24 months: Obs: 5/57; ALND: 34/49 48 months: Obs: 6/57; ALND: 30/49 | ||
| Shoulder dysfunction | Measured as per definition | 6 months: Obs: 5/57; ALND: 5/49 12 months: Obs: 4/57; ALND: 8/49 | 24 months: Obs: 0/57; ALND: 6/49 48 months: Obs: 2/57; ALND: 11/49 | ||
| Morbidity | Axillary pain (sporadic/continuous) | 6 months: ALND: 91/100; SNLB = 16/100 | 24 months: ALND: 39/100; SNLB = 8/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Numbness/Parasthesia on operated side | 6 months: ALND: 85/100; SNLB = 2/100 | 24 months: ALND: 68/100; SNLB = 1/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm mobility, 80%‐100% | 6 months: ALND: 73/100; SNLB = 100/100 | 24 months: ALND: 79/100; SNLB = 100/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm mobility, 60%‐79% | 6 months: ALND: 22/100; SNLB = 0/100 | 24 months: ALND: 18/100; SNLB = 0/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm mobility, 40%‐59% | 6 months: ALND: 5/100; SNLB = 0/100 | 24 months: ALND: 2/100; SNLB = 0/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm mobility, 20%‐39% | 6 months: ALND: 0/100; SNLB = 0/100 | 24 months: ALND: 1/100; SNLB = 0/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm mobility, < 20% | 6 months: ALND: 0/100; SNLB = 0/100 | 24 months: ALND: 0/100; SNLB = 0/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Aesthetic appearance of axillary scar: bad | 6 months: ALND: 9/100; SNLB = 2/100 | 24 months: ALND: 15/100; SNLB = 0/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm swelling < 1 cm difference in circumference | 6 months: ALND: 44/100; SNLB = 11/100 | 24 months: ALND: 38/100; SNLB = 6/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm swelling 1‐2 cm difference in circumference | 6 months: ALND: 17/100; SNLB = 0/100 | 24 months: ALND: 25/100; SNLB = 1/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm swelling >2 cm difference in circumference | 6 months: ALND: 8/100; SNLB = 0/100 | 24 months: ALND: 12/100; SNLB = 0/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm swelling, any | 6 months: ALND: 69/100; SNLB = 11/100 | 24 months: ALND: 75/100; SNLB = 7/100 | ||
| Arm oedema | Arm swelling ≥ 2 cm difference in circumference | No. of patients with data: ALND: N = 577; no ALND + RT: N = 568 no ALND: N = 312 both node + and node‐ patients. Final measurement was 2 to 5 years after surgery Arm oedema recorded at least once: ALND: 58.1%; no ALND + RT: 38.2%; no ALND: 39.1% (P < 0.001) Oedema always: ALND: 3.6%; no ALND + RT: 0.9%; no ALND: 1% No measurement after first oedema: ALND: 9.2%; no ALND + RT: 5.8%; no ALND: 3.2% Oedema always after first oedema: ALND: 6.1%; no ALND + RT: 3.2%; no ALND: 2.6% Intermittent, final measurement oedema: ALND: 11.8%; no ALND + RT: 4.9%; no ALND: 8.6%; Total with oedema on final measurement: ALND: 30.7%; no ALND + RT: 14.8%; no ALND: 15.4% (P < 0.001) | Oedema once, then resolution: ALND: 15.9%; no ALND + RT: 15.3%; no ALND: 16.7% Intermittent, final measurement no oedema: ALND: 11.4%; no ALND + RT: 8.1%; no ALND: 7.1% Total with no oedema on final measurement (after at least 1 measurement of oedema): ALND: 27.3%; no ALND + RT: 23.4%; no ALND: 23.8 Arm oedema ≥ 4 cm difference in circumference recorded at least once: ALND: 21.5%; no ALND + RT: 11.4%; no ALND: 13.1% | ||
| Adverse events (grade 3 or greater surgery related) | No details reported | ALND: 14/2788 SLN: 12/2800 Must include most of SLN positive and negative patients | Peri‐surgery | ||
| Arm mobility/shoulder abduction deficit (objective) | Physician assessed | 6 months: < 5%: ALND: 1299/1667; SLN: 1468/1744 5%‐10%: ALND: 218/1667; SLN: 176/1744 ≥ 10%: ALND: 150/1667; SLN: 99/1744 | |||
| Arm volume difference (objective) | Physician assessed | 6 months: < 5%: ALND: 1187/1677; SLN: 1363/1759 5%‐10%: ALND: 277/1677; SLN: 236/1759 ≥ 10%: ALND: 211/1677; SLN: 158/1759 | 12 months: < 5%: ALND: 1170/1639; SLN: 1345/1705 5%‐10%: ALND: 252/1639; SLN: 215/1705 ≥ 10%: ALND: 216/1639; SLN: 147/1705 | These data are also available for 18 and 30 months | |
| Arm volume difference (objective) | Physician assessed | 24 months: < 5%: ALND: 1062/1517; SLN: 1184/1504 5%‐10%: ALND: 243/1517; SLN: 197/1504 ≥ 10%: ALND: 212/1517; SLN: 123/1504 | 36 months: < 5%: ALND: 990/1421; SLN: 1156/1459 5%‐10%: ALND: 227/1421; SLN: 194/1459 ≥ 10%: ALND: 203/1421; SLN: 109/1459 | These data are also available for 18 and 30 months | |
| Tingling (subjective) | Self‐reported | 6 months: ALND (N = 388/1693), SLN (N = 184/1766) 12 months: ALND (N = 305/1640), SLN (N = 158/1713) 18 months: ALND (N = 272/1566), SLN (N = 138/1638) | 24 months: ALND (N = 236/1521), SLN (N = 137/1588) 30 months: ALND (N = 219/1448), SLN (N = 116/1502) 36 months: ALND (N = 193/1431), SLN (N = 110/1463) | ||
| Numbness (subjective) | Self‐reported | 6 months: ALND (N = 821/1693), SLN (N = 257/1769) 12 months: ALND (N = 679/1641), SLN (N = 216/1713) 18 months: ALND (N = 592/1567), SLN (N = 174/1638) | 24 months: ALND (N = 554/1523), SLN (N = 157/1587) 30 months: ALND (N = 473/1450), SLN (N = 137/1504) 36 months: ALND (N = 445/1430), SLN (N = 119/1463) | ||
| Shoulder abduction deficit ≥ 5% (in those with < 5% at baseline) | Physician assessed | 6 months: ALND (N = 275/1449), SLN (N = 201/1519) | |||
| Shoulder abduction deficit ≥ 5% (in those with < 5% at baseline) | Physician assessed | 36 months: ALND (N = 314/1136), SLN (N = 192/1151) | |||
| Numbness (in those with none at baseline) | Self‐reported | 36 months: ALND (N = 407/1336), SLN (N = 103/1371) | |||
| Tingling (in those with none at baseline) | Self‐reported | 36 months: ALND (N = 175/1329), SLN (N = 90/1343) | |||
| Seroma | Patients with percutaneous aspiration in outpatient department | ALND: 17/50; sampling: 10/50 | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for N = 100/200 | ||
| Postoperative discharge (mL), median (range) | ALND: 250 (25‐1610); sampling: 130 (0‐1785) | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for N = 100/200 | |||
| Duration of postop drainage (days) (median, range) | ALND: 4 (1‐11); sampling: 2.1 (1 ‐11) | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for N = 100/200 | |||
| Arm volume increase | ≥ 10% | ALND: 14/47; sampling: 0/48 | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for ca N = 100/200 | ||
| Subjective sensation of swelling in women without objective increase in arm volume | Any | ALND: 12/33; sampling: 9/48 | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for ca N = 100/200 | ||
| Shoulder mobility (mean decrease compared with baseline) | 7.5° decrease for whole sample of 95 patients | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for ca N = 100/200 | |||
| Axillary paraesthesia (impairment of sensibility in the axilla) | ALND: 17/48; sampling: 19/48 | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for ca N = 100/200 | |||
| Inner upper arm paraesthesia (impairment of sensibility in the inner upper arm) | ALND: 24/48; sampling: 4/48 | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for ca N = 100/200 | |||
| Delayed healing | ALND: 27/100; Simple + RT: 8/100 | ||||
| Haematoma | ALND: 24/100; Simple + RT: 6/100 | ||||
| Infection | ALND: 9/100; Simple + RT: 6/100 | ||||
| DVT | ALND: 4/100; Simple + RT: 1/100 | ||||
| Pulmonary embolism | ALND: 1/100; Simple + RT: 1/100 | ||||
| Chest infection | ALND: 6/100; Simple + RT: 3/100 | ||||
| Severe skin reaction | ALND: 0/100; Simple + RT: 5/100 | ||||
| Nausea and vomiting | ALND: 0/100; Simple + RT: 2/100 | ||||
| Tracheitis | ALND: 0/100; Simple + RT: 2/100 | ||||
| Skin grafts | ALND: 10/100; Simple + RT: 0/100 | ||||
| Arm oedema | ALND: 10/100; Simple + RT: 5/100 | ||||
| Limitation of shoulder movement | ALND: 4/100; Simple + RT: 14/100 | ||||
| Haematoma | Any | ALND: 30/539; SLNB: 38/544 | |||
| Seroma | Any | ALND: 195/539; SLNB: 93/544 | |||
| Infection | Any | ALND: 73/539; SLNB: 48/544 | |||
| Arm morbidity | Mean changes in arm morbidity (patient reported, overall summary average score of 15 items; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported) from baseline | Node+ and node‐ patients: average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months: ALND: 7 (N = 457); SLNB: 4.4 (N = 456) 1 month: ALND: 2.2 (0.2); SLNB: 1.4 (0.15) 6 months: ALND: 1.1 (0.2); SLNB: 0.8 (0.15) 12 months: ALND: 1.05 (0.2); SLNB: 0.8 (0.15) | 24 months: ALND: 1.05 (0.2); SLNB: 0.75 (0.15) 36 months: ALND: 1.05 (0.2); SLNB: 0.7 (0.15) | ||
| Arm symptoms | Mean changes in arm symptoms (patient reported, average of 7 items; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported) from baseline | Node+ and node‐ patients: average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months: ALND: 9.7 (N = 457); SLNB: 5.5 (N = 456) 1 month: ALND: 2.1 (0.2); SLNB: 1.2 (0.1) 6 months: ALND: 1.3 (0.15); SLNB: 0.8 (0.1) 12 months: ALND: 1.25 (0.15); SLNB: 0.7 (0.1) | 24 months: ALND: 1.25 (0.15); SLNB: 0.7 (0.1) 36 months: ALND: 1.2 (0.2); SLNB: 0.65 (0.15) | ||
| Arm swelling | Mean changes in arm swelling (patient reported, 1 item; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported) from baseline | Node+ and node‐ patients: average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months: ALND: 7.3 (N = 457); SLNB: 3.4 (N = 456) 1 month: ALND: 1.25 (0.2); SLNB: 0.75 (0.15) 6 months: ALND: 0.9 (0.15); SLNB: 0.55 (0.1) 12 months: ALND: 0.95 (0.15); SLNB: 0.45 (0.1) | 24 months: ALND: 1 (0.2); SLNB: 0.55 (0.15) 36 months: ALND: 1 (0.2); SLNB: 0.55 (0.15) | ||
| Arm dysfunctions | Mean arm dysfunctions change (patient reported, average of 3 items; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported) from baseline | Node+ and node‐ patients: average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months: ALND: 5.5 (N = 457); SLNB: 3.6 (N = 456) 1 month: ALND: 1.9 (0.15); SLNB: 1.35 (0.15) 6 months: ALND: 0.8 (0.1); SLNB: 0.65 (0.1) 12 months: ALND: 0.75 (0.1); SLNB: 0.6 (0.1) | 24 months: ALND: 0.7 (0.1); SLNB: 0.55 (0.1) 36 months: ALND: 0.8 (0.1); SLNB: 0.5 (0.1) | ||
| Arm disabilities | Mean arm disabilities (patient‐reported change, average of 4 items; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported) from baseline | Node+ and node‐ patients: average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months: ALND: 3.4 (N = 457); SLNB: 2.9 (N = 456) 1 month: ALND: 2.2 (0.2); SLNB: 1.4 (0.15) 6 months: ALND: 0.75 (0.1); SLNB: 0.55 (0.1) 12 months: ALND: 0.65 (0.1); SLNB: 0.45 (0.1) | 24 months: ALND: 0.6 (0.1); SLNB: 0.5 (0.1) 36 months: ALND: 0.7 (0.1); SLNB: 0.45 (0.1) | ||
| Arm volume | Increase in arm volume (percentage change from clinician ratings from baseline; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported) | Average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months: ALND: 4.2% (N = 509); SLNB: 2.8% (N = 519) All patients: 1 month: ALND: 0.8% (0.4); SLNB: 0.9% (0.4), P = 0.67 6 months: ALND: 3.5% (0.8); SLNB: 2.4% (0.7), P = 0.02 12 months: ALND: 4.6% (0.8); SLNB: 3% (0.8), P = 0.001 Node‐negative patients: 1 month: ALND: 0.8% (0.4); SLNB: 0.3% (0.4), P = 0.16 6 months: ALND: 3.5% (0.8); SLNB: 1.9% (0.5), P = 0.004 12 months: ALND: 4.6% (0.8); SLNB: 2.2% (0.7), P = 0.001 | All patients: 24 months: ALND: 5.8% (1); SLNB: 3.9% (0.7), P = 0.006 36 months: ALND: 5.8% (1); SLNB: 4.0% (1), P = 0.02 Node‐negative patients: 24 months: ALND: 5.8% (1); SLNB: 3% (0.7), P = 0.001 36 months: ALND: 5.8% (1); SLNB: 3.1% (1), P= 0.004 | ||
| Arm volume | Number with an increase in arm volume ≥ 15% (percentage change from clinician ratings from baseline) | All patients: 1 month: ALND: 5/544; SLNB: 3/544 6 months: ALND: 29/544; SLNB:21/544 12 months: ALND: 47/544; SLNB: 29/544 (P = 0.02) Node‐negative patients only: 1 month: ALND: 4/363; SLNB: 1/356 6 months: ALND: 16/363; SLNB: 9/356 12 months: ALND: 28/363; SLNB: 13/356 (P = 0.02) | All patients: 24 months: ALND: 81/544; SLNB: /544 (P = 0.001) 36 months: ALND: 82/544; SLNB: /544 (P = 0.01) Node‐negative patients only: 24 months: ALND: 47/363; SLNB: 25/356 (P = 0.01) 36 months: ALND: 49/363; SLNB: 25/356 (P = 0.006) | ||
| Lateral abduction | Lateral abduction (change from clinician ratings from baseline; degrees; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported ‐ have assumed it is SEM for calculations) | Average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months (percentage change from baseline: ALND: 4.4% (N = 509); SLNB: 2.5% (N = 519) Node+ and node‐ patients (read off graph): Baseline: ALND: 158 (1); SLNB: 157 (1) 1 month: ALND: 131 (2); SLNB: 144 (2) 6 months: ALND: 150 (1); SLNB: 151 (1) 12 months: ALND: 150 (1); SLNB: 151 (1) | Node+ and node‐ patients (read off graph): 24 months: ALND: 151 (1); SLNB: 152 (1) 36 months: ALND: 150 (1); SLNB: 151 (1) | ||
| Forward flexion | Forward flexion (degrees; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported ‐ have assumed it is SEM for calculations) | Node+ and node‐ patients (read off graph): Baseline: ALND: 157 (1); SLNB: 158 (1) 1 month: ALND: 137 (2); SLNB: 148 (1.5) 6 months: ALND: 150 (1); SLNB: 152 (1) 12 months: ALND: 151 (1); SLNB: 151 (1) | Node+ and node‐ patients (read off graph): 24 months: ALND: 152 (1); SLNB: 152 (1) 36 months: ALND: 152 (1); SLNB: 151 (1) | ||
| Postoperative swelling (oedema) | Measurement of arm diameter | Level I clearance: 3/93 ALND: 7/88 | |||
| Involved upper limb disorder | Unclear | Level I clearance: 0/93 ALND: 0/88 | |||
| Cerebrovascular accident | Unclear | Level I clearance: 0/93 ALND: 2/88 | |||
| Cardiovascular events | Unclear | Level I clearance: 2/93 ALND: 1/88 |
We reported relative effects of treatments on time‐to‐event outcomes and noted that HRs less than 1.0 favour the 'less axillary surgery' arm, and HRs greater than 1.0 favour the 'more axillary surgery' arm. Similarly, for adverse event rates, ORs less than 1.0 favour the 'less axillary surgery' arm, and ORs greater than 1.0 favour the 'more axillary surgery' arm.
No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery
Overall survival
All 10 trials comparing ALND versus no axillary surgery reported overall survival. The HR for death from any cause was 1.06 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.96 to 1.17; 3849 participants; 10 studies; Analysis 1.1) with no statistically significant heterogeneity (I2 = 26%; P = 0.20). We downgraded evidence for this outcome from high to moderate quality owing to imprecision: The confidence interval of the effect estimate includes both no difference between treatment groups and appreciable harm associated with no axillary surgery (summary of findings Table for the main comparison). For the single trial that did not use RT (NSABP B‐04), the HR was 0.96 (95% CI 0.80 to 1.15; 773 participants; one study; Analysis 1.1). For trials that used RT, the HR was 1.11 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.25; 3076 participants; nine studies; Analysis 1.1) with no statistically significant heterogeneity (I2 = 24%; P = 0.23).
For the subgroup of studies that provided additional treatment to participants with histologically positive axillary nodes (Institut Bergonie; Institut Curie; Milan 3), no axillary surgery was associated with increased risk of overall mortality (HR 1.51, 95% CI 1.09 to 2.09; 1174 participants; three studies; Analysis 1.2.1) with no statistically significant heterogeneity (I2 = 25%; P = 0.27).
For the subgroup of studies that did not provide additional treatment to participants with histologically positive axillary nodes (Addenbrookes; Guy's; Hammersmith; IBCSG‐10‐93; Malmo; Milan 2; NSABP B‐04), the HR for overall mortality was 1.02 (95% CI 0.92 to 1.13; 2675 participants; seven studies; Analysis 1.2.2) with no statistically significant heterogeneity (I2 = 0%; P = 0.59).
For the subgroup of studies with adequate allocation concealment (Addenbrookes; IBCSG‐10‐93; Milan 2; Milan 3), the HR for death from any cause was 0.98 (95% CI 0.81 to 1.18; 1442 participants; four studies; Analysis 1.13.1) with no statistically significant heterogeneity (I2 = 0%; P = 0.81).
Disease control in the axilla
Trials comparing full axillary surgery with no axillary surgery did not report disease control in the axilla.
Breast cancer recurrence
Local recurrence
Included studies not separately report time to local recurrence.
Locoregional recurrence
We were able to extract locoregional recurrence time‐to‐event data for four of the nine included trials. No axillary surgery was associated with increased risk of locoregional recurrence (with HR ranging from 1.10 to 3.06; 20,863 person‐years of follow‐up; four studies; Analysis 1.3) but heterogeneity was substantial (I2 = 71%; P = 0.007); for this reason, we downgraded evidence for this outcome to moderate quality (summary of findings Table for the main comparison).
For the single trial that provided additional treatment to participants with histologically positive axillary nodes (Institut Curie), the HR for locoregional recurrence was 1.10 (95% CI 0.69 to 1.75; 4171 person‐years of follow‐up; one study; Analysis 1.4.1). For the remaining trials (Addenbrookes; Guy's; NSABP B‐04), which provided no specific additional treatment to participants with histologically positive axillary nodes, no axillary surgery was associated with increased risk of locoregional recurrence (HR 2.83, 95% CI 2.25 to 3.57; 16,692 person‐years of follow‐up; three studies) with no statistically significant heterogeneity (I2 = 0%; P = 0.74).
In subgroup analyses of trials according to use of RT (Analysis 1.3), no axillary surgery was associated with increased risk of locoregional recurrence (HR ranging from 1.10 to 3.06; 13,579 person‐years of follow‐up; three studies; Analysis 1.3.2) but heterogeneity was substantial (I2 = 75%; P = 0.008). For the single trial that did not use RT (NSABP B‐04), no axillary surgery was associated with increased risk of locoregional recurrence (HR 2.94, 95% CI 2.05 to 4.23; 7284 person‐years of follow‐up; one study; Analysis 1.3.1).
We judged allocation concealment as adequate in only one of the trials reporting locoregional recurrence (Addenbrookes). We were uncertain about whether no axillary surgery was associated with increased risk of locoregional recurrence in this trial (HR 1.84, 95% CI 0.79 to 4.28).
Distant metastasis
We were able to extract distant metastasis time‐to‐event data for two trials (Milan 2; NSABP B‐04). The HR for distant metastasis was 1.06 (95% CI 0.87 to 1.30; 946 participants; two studies; Analysis 1.5) with moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 40%; P = 0.20).
One of the trials (Milan 2) had adequate allocation concealment, but its results indicate uncertainty about the relative rates of distant metastasis with the two treatment options (HR 0.64, 95% CI 0.28 to 1.42; 219 participants; one study).
Institut Curie reported the rate of metastases but provided insufficient detail for extraction of time‐to‐event outcomes. In this trial, at 15 years of follow‐up, the rate of metastasis was 24.9% for no axillary surgery versus 25.8% for axillary lymph node dissection (P reported as not significant).
Long‐term adverse events
Lymphoedema
Four of the included trials reported the rate of lymphoedema, defined as an increase in arm circumference, at 12 or more months after surgery (Addenbrookes; Guy's; Institut Bergonie; NSABP B‐04). The Addenbrookes, Guy's and Institut Bergonie trials used RT. NSABP B‐04 was a three‐arm trial, but we included the two "no radiotherapy" arms for this comparison. No axillary surgery was associated with decreased risk of lymphoedema at 12 or more months post surgery (OR 0.31, 95% CI 0.23 to 0.43; fixed‐effect model; 1714 participants; four studies; Analysis 1.6). We downgraded evidence for this outcome to low quality owing to substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 69%; P = 0.02) and unclear blinding of the outcome assessment (summary of findings Table for the main comparison). A random‐effects model yielded a similar result (OR 0.22, 95% CI 0.08 to 0.57; random‐effects model; 1714 participants; four studies; I2 = 69%; P = 0.02; Analysis 1.7).
Subgroup analysis of trials that did not provide additional treatment to participants with histologically positive axillary lymph nodes (Addenbrookes; Guy's, NSABP B‐04) revealed that no axillary surgery was associated with decreased risk of lymphoedema (OR 0.40, 95% CI 0.28 to 0.55; 1182 participants; three studies) and showed no important heterogeneity (I2 = 0%; P = 0.54).
We judged allocation concealment as adequate in only one of the trials reporting lymphoedema (Addenbrookes). Its results were consistent with results of the pooled analysis (HR 0.35; 95% CI 0.12 to 1.03; 98 participants).
Arm or shoulder movement impairment
Five trials (Addenbrookes; Guy's; Hammersmith; IBCSG‐10‐93; Institut Bergonie), involving 1495 participants, reported impairment of arm or shoulder function at 12 or more months after surgery (Analysis 1.8). Results show considerable heterogeneity (I2 = 78%; P = 0.001), with the OR for any impairment of function ranging from 0.24 to 3.26. We downgraded evidence for this outcome to very low quality owing to heterogeneity and unclear blinding of outcome assessment (summary of findings Table for the main comparison).
Differences between trials in the definitions of arm and shoulder impairment are a possible source of this heterogeneity. All trials provided RT, but in both Guy's and Hammersmith trials, the no axillary surgery group received more extensive RT than the ALND group.
Analysis restricted to trials with adequate allocation concealment (Addenbrookes; IBCSG‐10‐93) suggests fewer participants with arm or shoulder movement impairment in the no axillary surgery than in the ALND group (HR 0.46, 95% CI 0.23 to 0.93) but with potentially important heterogeneity (I2 = 59%; P = 0.12).
Arm pain
One study reported arm pain. In IBCSG‐10‐93, the OR for arm pain at 12 or more months was 0.60 (95% CI 0.24 to 1.47; 379 participants; Analysis 1.9).
Paraesthesia
One study reported on paraesthesia. In Institut Bergonie, paraesthesia at 12 or more months after surgery was less likely in the no axillary surgery group (OR 0.14, 95% CI 0.06 to 0.32; 532 participants; Analysis 1.10).
Short‐term adverse events
One trial (Addenbrookes) reported acute adverse events (surgical complications).
Delayed healing
Delayed healing was less likely in the no axillary surgery group (OR 0.27, 95% CI 0.11 to 0.67; 204 participants; one study; Analysis 1.11).
Skin grafts
Skin grafts were less likely in the no axillary surgery group (OR 0.39, 95% CI 0.07 to 2.19; 204 participants; one study; Analysis 1.12).
Quality of life
IBCSG‐10‐93 was the only trial that measured quality of life outcomes; investigators reported no statistically significant differences in quality of life, bother and coping scores between treatment groups during the two years of postoperative follow‐up.
Psychological and psychosocial outcomes
The included studies did not report on these outcomes.
Axillary sampling versus full axillary surgery
Overall survival
Five trials (Cape Town; Cardiff; E'dburgh Sample/Clear; Edinburgh 1; Xu 2003) reported time to death from any cause, but we excluded Cardiff data from the meta‐analysis owing to non‐proportionality of hazard rates (i.e. survival curves cross at 12 years' follow‐up) and the published report provided insufficient detail to include Xu 2003. In the remaining three trials (Cape Town; E'dburgh Sample/Clear; Edinburgh 1), heterogeneity in the HR for overall mortality was substantial (HR 0.94, 95% CI 0.73 to 1.21; 967 participants; three studies; I2 = 45%; P = 0.16; Analysis 2.1). We downgraded this evidence to low quality owing to substantial heterogeneity and serious imprecision (summary of findings Table 2).
Subgroup analysis of the two trials that provided RT (E'dburgh Sample/Clear; Edinburgh 1) yielded an HR of 0.84 (95% CI 0.64 to 1.11; 872 participants; two studies; Analysis 2.1) with no significant heterogeneity (I2 = 0%; P = 0.44), and for the trial that did not use RT (Cape Town), an HR of 1.47 (95% CI 0.84 to 2.56; 85 participants).
We conducted no sensitivity analysis for this outcome because all trials were at low risk of bias owing to allocation concealment.
Disease control in the axilla
Included studies did not report disease control in the axilla, but two trials reported axillary recurrence (see below).
Breast cancer recurrence
Local recurrence
Five trials that performed six treatment comparisons reported local recurrence (Cape Town (1) and (2); Cardiff; Edinburgh 1; Ostersund; Xu 2003), but we could not extract time‐to‐event data from Ostersund and Xu 2003. The HR for local recurrence was 1.41 (95% CI 0.94 to 2.12; 1404 participants; three studies; Analysis 2.2) with no heterogeneity (I2 = 0%; P = 0.91). In the Ostersund trial, one out of 54 participants in the axillary sampling arm experienced local recurrence compared with four of 57 participants in the ALND arm. In Xu 2003, local recurrence rates were 3.2% and 2.3% in the axillary sampling and ALND arms, respectively (181 participants; P value reported as greater than 0.05). We downgraded evidence for local recurrence to low quality on the basis of few events and serious imprecision (summary of findings Table 2). We performed no sensitivity analysis for this outcome because all trials were at low risk of bias owing to allocation concealment.
Axillary recurrence
Two trials reported axillary recurrence rates (Cape Town; Edinburgh 1), but we were able to extract time‐to‐event data only from Edinburgh 1, yielding an HR for axillary recurrence of 0.99 (95% CI 0.58 to 1.69; 466 participants; Analysis 2.3) with axillary lymph node sampling versus dissection. In Cape Town, rates of axillary recurrence were 8/52 for axillary lymph node sampling and 2/43 for ALND.
Locoregional recurrence
Two trials (Cape Town; E'dburgh Sample/Clear) reported locoregional recurrence, but we could extract time‐to‐event data only from E'dburgh Sample/Clear, yielding an HR for locoregional recurrence of 0.74 (95% CI 0.46 to 1.20; 406 participants; one study; Analysis 2.4). In the Cape Town trial, 19 of 52 participants in the axillary sampling group experienced locoregional recurrence compared with 11 of 43 in the ALND group.
Distant metastasis
Four trials reported distant metastasis (Cape Town; Cardiff; E'dburgh Sample/Clear; Xu 2003). We were able to extract time‐to‐event data only extracted from the Cardiff and E'dburgh Sample/Clear trials, but we did not include data from Cardiff in the meta‐analysis owing to the non‐proportionality of HRs. In E'dburgh Sample/Clear, the HR for distant metastasis was 1.05 (95% CI 0.74 to 1.49; 406 participants; Analysis 2.5). In the Cape Town trial, distant metastasis occurred at a rate of 13 of 52 participants in the axillary sampling group compared with 11 of 43 participants in the ALND group. In Xu 2003, distant metastasis rates were 19/93 and 15/88 in the axillary sampling and ALND arms, respectively (181 participants; P value reported as greater than 0.05).
Long‐term adverse events
Lymphoedema
Two trials reported on lymphoedema. In the Cardiff trial, lymphoedema at 12 or more months after surgery (defined as an increase in arm circumference) was less likely in the axillary sampling group than in the ALND group (OR 0.32, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.81; 85 participants; one study; Analysis 2.6). In Xu 2003, postoperative lymphoedema occurred in 3/93 participants in the axillary sampling group compared with 7/88 in the ALND group, but it was unclear at what time this measurement was taken.
Arm or shoulder movement impairment
One trial (Edinburgh 1) reported shoulder lateral rotation at 12‐months follow‐up, noting a relatively small decrease in range of movement when compared with baseline in both the axillary sampling and ALND groups (mean difference (MD) ‐0.05 cm, 95% CI ‐1.50 to 1.40; 191 participants; one study; Analysis 2.7).
Short‐term adverse events
Seroma
One trial collected data on seroma formation. In the Ostersund trial, seroma occurred at a rate of 10 of 50 participants in the axillary sampling group compared with 17 of 50 participants in the ALND group (OR 0.49, 95% CI 0.20 to 1.20; 100 participants; one study; Analysis 2.8).
Quality of life
The included studies did not report this outcome.
Psychological and psychosocial outcomes
The included studies did not report these outcomes.
Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery
Overall survival
Five trials reported overall mortality (ALMANAC; Genoa; GIVOM Sentinella; Milan; NSABP B‐32), but we were able to extract time‐to‐event data from only three studies (Genoa; Milan; NSABP B‐32). The HR for overall mortality was 1.05 (95% CI 0.89 to 1.25; 6352 participants; three studies; Analysis 3.1) with minimal heterogeneity (I2 = 28%; P = 0.25). We rated evidence for overall mortality as moderate quality owing to imprecision. The confidence interval of the effect estimate included both no differences between treatment groups and appreciable harm associated with SLNB (summary of findings Table 3). In the ALMANAC trial, the overall mortality rate for the year after surgery was seven out of 478 women (1.5%) in the sentinel node group versus seven out of 476 women (1.5%) in the full axillary surgery group. In the GIVOM Sentinella trial, the overall mortality rate over the five years after surgery was 21 out of 345 women (6.1%) in the sentinel node group versus 14 out of 352 women (4.0%) in the full axillary surgery group.
We conducted no sensitivity analysis for this outcome because all trials were at low risk of bias owing to allocation concealment.
Disease control in the axilla
The included studies did not report disease control in the axilla, although five trials reported axillary recurrence (see below).
Breast cancer recurrence
Local recurrence
Data reveal uncertainty about the relative effectiveness of SLNB and ALND in terms of local recurrence (HR 0.94, 95% CI 0.24 to 3.77; 516 participants; one study; Milan; Analysis 3.2).
Axillary recurrence
Five trials, involving 7487 participants, reported axillary recurrence (ALMANAC; GIVOM Sentinella; Genoa; NSABP B‐32; Milan), but event rates were low, and we were able to extract time‐to‐event data only from Milan. Results derived from Milan suggest uncertainty about whether axillary recurrence is more likely with SLNB than with ALND (HR 6.96, 95% CI 0.44 to 111.25; 516 participants; one study; Analysis 3.3). In ALMANAC, the rate of axillary local recurrence during the first year after surgery was 1/478 (0.2%) in the SLNB group versus 4/476 (0.8%) in the ALND group. In GIVOM Sentinella, axillary recurrence rates over the five years after surgery were 1/345 (0.3%) in the SLNB group versus 0/352 (0%) in the ALND group. In Genoa, axillary recurrence rates were 0/110 (0%) in the SLNB group versus 1/115 (0.8%) in the ALND group. In NSABP B‐32, axillary recurrence rates were 14/2804 (0.5%) in the SLNB group versus 6/2807 (0.2%) in the ALND group.
We conducted no sensitivity analysis for this outcome because all trials were at low risk of bias owing to allocation concealment.
Locoregional recurrence
Two trials reported locoregional recurrence (GIVOM Sentinella; NSABP B‐32), but we were able to extract time‐to‐event data only from NSABP B‐32. Data reveal uncertainty about whether SLNB or ALND was more effective in terms of locoregional recurrence (HR 0.96, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.24; 5611 participants; one study; Analysis 3.4). In GIVOM Sentinella, locoregional recurrence rates were 16/345 (4.6%) in the SLNB group versus 3/352 (0.9%) in the ALND group.
Distant metastasis
Two studies reported distant metastases (GIVOM Sentinella; Milan), but we were able to extract time‐to‐event data only from Milan. The relative effectiveness of SLNB and ALND in terms of distant metastasis was uncertain (HR 0.80, 95% CI 0.42 to 1.53; 516 participants; one study; Analysis 3.5). In GIVOM Sentinella, distant metastasis rates were 11/3345 (3.2%) in the SLNB group versus 16/352 (4.5%) in the ALND group.
Long‐term adverse events
Lymphoedema
Four studies reported objectively measured lymphoedema at 12 or more months after surgery (ALMANAC; GIVOM Sentinella; Milan; SNAC). Investigators measured lymphoedema by using arm circumference (GIVOM Sentinella; Milan) or arm volume (ALMANAC; SNAC). Increased arm circumference at 12 months after surgery was less likely with SLNB than with ALND (OR 0.48, 95% CI 0.26 to 0.92; 677 participants ‐ Analysis 3.6 OR 0.04, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.60; 200 participants ‐ Analysis 3.6 and OR 0.60, 95% CI 0.37 to 0.96, 1088 participants ‐ Analysis 3.6) for the GIVOM Sentinella, Milan and SNAC trials, respectively. We did not pool results owing to heterogeneity (I2 = 51%; P = 0.13), and we conducted no sensitivity analysis for this outcome because all trials were at low risk of bias owing to allocation concealment.
The ALMANAC trial reported the mean ratio in arm volume at baseline compared with 12 months after surgery. In the sentinel lymph node group, this was 1.03 (95% CI 1.02 to 1.04) compared with 1.06 (95% CI 1.05 to 1.07) in the ALND group (P = 0.096; two sided t‐test).
In ALMANAC, Addenbrookes 2 and SNAC, patient‐reported lymphoedema (of any severity) was less likely in the SLNB group than in the ALND group (OR 0.33, 95% CI 0.23 to 0.47; fixed‐effect model; 1903 participants; three studies; Analysis 3.7) with no heterogeneity (I2 = 0%; P = 0.96). The random‐effects model produced the same result. We downgraded evidence on patient‐reported lymphoedema to moderate quality owing to incomplete follow‐up (summary of findings Table 3). Restricting this analysis to trials with adequate allocation concealment (ALMANAC and SNAC) yielded a similar result (OR 0.33, 95% CI 0.22 to 0.48; fixed‐effect model).
Shoulder or arm movement impairment
The Addenbrookes 2, ALMANAC and SNAC trials measured change in the range of shoulder movement from baseline to 12 months after surgery. Results showed no statistically significant differences between SLNB and ALND groups when change in the range of movement was compared from baseline to 12 months post surgery, for flexion (MD 1.55°, 95% CI ‐0.19° to 3.29°; 2257 participants; three studies; Analysis 3.8), abduction (MD ‐1.02°, 95% CI ‐2.79° to 0.75°; 2252 participants; three studies; Analysis 3.9), internal rotation (MD 0.50°; 95% CI ‐1.10° to 2.09°; 1227 participants; two studies; Analysis 3.10) or external rotation (MD ‐0.56°; 95% CI ‐2.21° to 1.09°; 1227 participants; two studies; Analysis 3.11). Except for external rotation, heterogeneity was substantial or considerable for all shoulder movement comparisons.
In two trials (GIVOM Sentinella and Milan), subjective arm movement impairment was less likely with SLNB than with ALND. This difference was statistically significant in the Milan trial (OR 0.02, 95% CI < 0.00 to 0.31; 200 participants; Analysis 3.12) but not in the GIVOM Sentinella trial (OR 0.74, 95% CI 0.39 to 1.41; 677 participants; Analysis 3.12), and heterogeneity in the pooled estimate was considerable (I2 = 88%; P = 0.004). We downgraded evidence on subjective arm movement impairment to low quality owing to heterogeneity and lack of blinding (summary of findings Table 3). We conducted no sensitivity analysis for this outcome because all trials were at low risk of bias owing to allocation concealment.
The SNAC trial reported subjective arm disability rated on a scale from 0 (no trouble at al) to 10 (the worst I can imagine). At one year postoperatively, mean arm disability ratings were low in both groups: 0.65 (standard error (SE) 0.1) in the ALND group compared with 0.45 (SE 0.1) in the SLNB group.
Pain
Two trials reported pain at 12 or more months after surgery (GIVOM Sentinella; Milan). Pain was less likely to be reported in the sentinel lymph node group than in the axillary dissection group. This difference was statistically significant in the Milan trial (OR 0.14, 95% CI 0.06 to 0.31; 200 participants; Analysis 3.13) but not in the GIVOM Sentinella trial (OR 0.76, 95% CI 0.46 to 1.25; 677 participants; Analysis 3.13), and heterogeneity was considerable in the pooled estimate (I2 = 92%; P = 0.0005). We downgraded evidence on pain to low quality owing to heterogeneity and lack of blinding (summary of findings Table 3).
Paraesthesia
Two trials reported paraesthesia at 12 or more months after surgery (Addenbrookes 2; Milan). Both trials found that paraesthesia was less likely in the sentinel lymph node group than in the axillary dissection group. For the Milan trial (OR < 0.00, 95% CI <0.00 to 0.04; 200 participants; Analysis 3.14) and the Addenbrookes 2 trial (OR 0.37, 95% CI 0.21 to 0.64; 295 participants; Analysis 3.14), heterogeneity was considerable in the pooled estimate (I2 = 95%; P < 0.00001). We downgraded evidence on paraesthesia to low quality owing to heterogeneity and lack of blinding (summary of findings Table 3).
Numbness
Three trials reported numbness or sensory deficit at 12 or more months after surgery (Addenbrookes 2;ALMANAC; GIVOM Sentinella). All found that numbness was less likely in the SLNB group than in the ALND group (OR 0.43, 95% CI 0.34 to 0.54; 1799 participants; Analysis 3.15) with limited heterogeneity (I2 = 20%; P = 0.29). Restricting this analysis to trials with adequate allocation concealment (ALMANAC; GIVOM Sentinella) yielded a similar result (OR 0.47, 95% CI 0.36 to 0.61).
Short‐term adverse events
Seroma
The Addenbrookes 2 and SNAC trials reported that seroma was less likely with SLNB than with ALND (OR 0.60, 95% CI 0.33 to 1.11; 298 participants; Analysis 3.16; OR 0.36; 95% CI 0.27 to 0.48; 1083 participants; Analysis 3.16 respectively) but with considerable heterogeneity (I2 = 53%; P = 0.14).
Wound infection
The ALMANAC and SNAC trials reported that wound infection was less likely with SLNB than with ALND (OR 0.65, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.85; 2074 participants; Analysis 3.17).
Brachial plexus injury
The ALMANAC trial reported the rate of brachial plexus injury at six months postoperatively (OR 0.38, 95% CI 0.12 to 1.22; 804 participants).
Quality of life
We did not conduct statistical meta‐analysis because of differences in the scales used, but results from three trials (Addenbrookes 2; ALMANAC; GIVOM Sentinella) suggested that SLNB was associated with better quality of life, at least in the immediate postoperative period.
Addenbrookes 2 reported that quality of life scores were usually higher (better) in the SLND group than in the ALND group, and significantly so in the immediate postoperative period (P < 0.01).
ALMANAC measured a trial outcome index (TOI, derived from the sum of scores on physical and well‐being subscales and on breast cancer concerns subscales of the FACT‐B+4 (Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy, Breast, for patients with lymphoedema questionnaire) before surgery and repeatedly in the following 18 months. Participants in the SLND group recovered more quickly to their baseline TOI value than those in the ALND group. This occurred at 12 months for the SLND group compared with 18 months for the ALND group (P < 0.01). Global quality of life (measured with the total FACT‐B+4 score) was significantly better in the SLND group than in the ALND group at most time points following surgery (at one month, P < 0.001; at three months, P = 0.04; at six months, P = 0.059; at 12 months, P = 0.024; at 18 months, P = 0.019). .
GIVOM Sentinella reported no significant differences between SLNB and ALND groups on the physical and health‐related quality of life components of the Short Form (SF)‐36 measure.
Psychological and psychosocial outcomes
Although three trials reported psychological outcomes, we did not pool their results owing to insufficient detail in reporting and differences in measurement scales used.
The Addenbrookes 2 trial reported no significant differences between SLND and ALND groups in Mental Adjustment to Cancer scores, depressive symptoms (measured on the Beck Depression Inventory) or state anxiety (measured by the Spielberger State/Trait Anxiety Inventory) during the first year after surgery.
ALMANAC reported that Spielberger State/Trait Anxiety Inventory scores were slightly lower (better) in the SLNB group than in the ALND group during the first year after surgery, but this difference was not statistically significant.
GIVOM Sentinella reported no significant differences between SLNB and ALND groups on the mental health‐related quality of life components of the SF‐36. Participants in the SLNB group scored significantly better than those in the ALND group in general and anxiety domains of the psychological well‐being measure within the first 12 months after surgery, but this difference was no longer statistically significant at two years after surgery.
Full axillary surgery with no radiotherapy versus no axillary surgery with radiotherapy
Overall survival
Four studies involving seven treatment comparisons reported that overall survival was reduced among participants treated with RT compared with those treated with ALND (HR 1.10, 95% CI 1.00 to 1.21; 2469 participants; Analysis 4.1) with no heterogeneity (I2 = 0%; P = 0.63). We graded this evidence as high quality (summary of findings Table 4). Only one of the trials (SE Scotland) was at low risk of bias owing to allocation concealment; this trial was consistent with the pooled analysis showing reduced overall survival among patients treated with RT compared with those treated with ALND (HR 1.27, 95% CI 1.04 to 1.54).
Disease control in the axilla
Trials included in this comparison did not report disease control in the axilla.
Breast cancer recurrence
Local recurrence
Four studies involving seven treatment comparisons reported that local recurrence was less likely among participants treated with RT compared in those treated with ALND (HR 0.80, 95% CI 0.64 to 0.99; 22256 person‐years of follow‐up; four studies;Analysis 4.2) with no heterogeneity (I2 = 0%; P = 0.63). We graded this evidence as high quality (summary of findings Table 4). Only one trial (SE Scotland) was at low risk of bias owing to allocation concealment; results showed uncertainty about whether local recurrence was less likely in patients treated with RT compared with those treated with ALND (HR 0.85, 95% CI 0.56 to 1.30).
Locoregional recurrence
The trials included for this comparison did not report locoregional recurrence.
Distant metastasis
One trial (NSABP B‐04) that performed two treatment comparisons reported that the HR for distant metastasis for RT alone versus ALND alone was 1.07 (95% CI 0.93 to 1.25; 1313 participants; Analysis 4.3).
Long‐term adverse events
Lymphoedema
One trial (SE Scotland) reported lymphoedema at 12 or more months after treatment and used a definition of 2 cm or greater increase in arm circumference. In the RT group, 5 out of 100 participants had lymphoedema compared with 10 out of 100 in the axillary surgery group (OR 0.47, 95% CI 0.16 to 1.44; 200 participants; Analysis 4.4).
Short‐term adverse events
Delayed healing, wound infection and skin graft
One trial (SE Scotland) involving 200 participants reported that acute adverse events ‐ delayed healing (OR 0.24, 95% CI 0.10 to 0.55; Analysis 4.5), wound infection (OR 0.65, 95% CI 0.22 to 1.89; Analysis 4.6), skin graft (OR 0.04, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.74; Analysis 4.7) and haematoma (OR 0.20, 95% CI 0.08 to 0.52; Analysis 4.8) ‐ were less likely with radiotherapy than with axillary surgery.
Quality of life
The trials included for this comparison did not report quality of life.
Psychological and psychosocial outcomes
The trials included for this comparison did not report psychological and psychosocial outcomes.
Less axillary surgery versus axillary lymph node dissection
Overall survival
When all trials were combined, the HR for overall mortality was 1.08 (95% CI 1.01 to 1.16, when HR > 1 favours ALND; 12,864 participants; 19 studies; Analysis 5.1) with no significant heterogeneity (I2 = 12%; P = 0.30).
Trials comparing no axillary surgery (with or without RT) versus ALND reported increased mortality with less axillary surgery (HR 1.10, 95% CI 1.02 to 1.19; 5545 participants; 13 studies; I2 = 6%; obtained by combining analyses 5.1.1 and 5.1.4 (not shown)), but trials comparing axillary sampling or SLNB versus ALND did not report increased mortality (HR 1.01, 95% CI 0.88 to 1.17; 7319 participants; six studies; obtained by combining analyses 5.1.2 and 5.1.3 (not shown)).
We performed subgroup analysis that was based on use of radiotherapy. Trials using RT in both treatment groups reported no difference in overall survival between less axillary surgery and more axillary surgery groups (HR 1.06, 95% CI 0.96 to 1.16; 10,075 participants; 13 studies; Analysis 5.2.1) with no important heterogeneity (I2 = 28%; P = 0.15). Similarly, results showed no differences between groups for trials that did not use RT in either group (HR 1.00, 95% CI 0.85 to 1.19; 1093 participants; three trials; Analysis 5.2.3) with no important heterogeneity (I2 = 8%; P = 0.34). Trials that used RT only in the less axillary surgery arm reported reduced overall survival for the less axillary surgery arm compared with the ALND arm (HR 1.10, 95% CI 1.00 to 1.21; 2469 participants; four trials; Analysis 5.2.2) with no heterogeneity (I2 = 0%; P = 0.52).
We conducted subgroup analysis according to whether additional treatment was given to participants with histologically positive nodes and excluded trials in which one of the treatment arms received no axillary staging. Trials that provided additional treatment to participants with histologically positive axillary nodes (E'dburgh Sample/Clear; Edinburgh 1; Genoa; Milan) reported uncertainty whether less axillary surgery was the more effective treatment in terms of overall survival (HR 0.82, 95% CI 0.64 to 1.05; 1613 participants; four trials; Analysis 5.3) with no heterogeneity (I2 = 0%; P=0.61). They also described uncertainty about relative effectiveness in the only trial (Cape Town) that did not provide additional treatment to those with histologically positive nodes (HR 1.47, 95% CI 0.84 to 2.56; 95 participants; Analysis 5.3).
Breast cancer recurrence
Local recurrence
Study results show uncertainty about whether local recurrence was reduced with less axillary surgery when compared with ALND (HR 0.90, 95% CI 0.75 to 1.09, when HR > 1 favours ALND; 24,176 participants; eight studies; Analysis 5.4).
Locoregional recurrence
Locoregional recurrence was more likely with less surgery than with ALND (HR 1.53, 95% CI 1.31 to 1.78, when HR > 1 favours ALND; 26,880 participant years of follow‐up; seven studies; Analysis 5.5).
Distant metastasis
Results reveal uncertainty about whether distant metastasis was more likely in patients treated with less axillary surgery than in those receiving ALND (HR 1.07, 95% CI 0.95 to 1.20, when HR >1 favours ALND; 2665 participants; five studies; Analysis 5.6).
Long‐term adverse effects
Lymphoedema (defined as an increase in arm circumference at 12 or more months postoperatively) was less likely with less axillary surgery than with ALND (OR 0.37, 95% CI 0.29 to 0.46; fixed‐effect model; 3964 participants; nine studies; I2 = 52%; Analysis 5.7). The random‐effects model produced a similar result (OR 0.35, 95% CI 0.23 to 0.53; random‐effects model; 3964 participants; nine studies; I2 = 52%).
Paraesthesia
Three trials reported paraesthesia at 12 or more months after surgery (Institut Bergonie; Addenbrookes 2; Milan). All trials found paraesthesia less likely in the less axillary surgery group than in the more axillary surgery group. For Institut Bergonie (OR 0.14, 95% CI 0.06 to 0.32; 532 participants; Analysis 5.8), for Milan (OR < 0.00, 95% CI <0.00 to 0.04; 200 participants; Analysis 5.8) and for Addenbrookes 2 (OR 0.37, 95% CI 0.21 to 0.64; 295 participants; Analysis 5.8); heterogeneity was considerable in the pooled estimate (I2 = 91%; P < 0.0001).
Pain
Three trials reported pain at 12 or more months after surgery (IBCSG‐10‐93; GIVOM Sentinella; Milan). Pain was less likely to be reported in the less surgery group than in the more surgery group. This difference was statistically significant in the Milan trial (OR 0.14, 95% CI 0.06 to 0.31; 200 participants; Analysis 5.9) but not in the GIVOM Sentinella trial (OR 0.76, 95% CI 0.46 to 1.25; 677 participants; Analysis 5.9) or the IBCSG‐10‐93 trial (OR 0.60 95% CI 0.24 to 1.47; 379 participants; Analysis 5.9), and heterogeneity was considerable in the pooled estimate (I2 = 84%; P < 0.0001).
Short‐term side effects
Delayed healing
The Addenbrookes and SE Scotland trials reported delayed wound healing was less likely with less surgery than with more surgery (OR 0.25, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.46; 404 participants; fixed‐effect model; two studies; I2 = 0%; Analysis 5.10). The random‐effects model produced a similar result (OR 0.25, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.47; 404 participants; random‐effects model; two studies; I2 = 0%).
Seroma
Seroma was less likely with less axillary surgery than with ALND (OR 0.40, 95% CI 0.32 to 0.52; 1481 participants; fixed‐effect model; three studies; I2 = 14%; Analysis 5.11). The random‐effects model produced a similar result (OR 0.42, 95% CI 0.31 to 0.56; 1481 participants; random‐effects model; three studies; I2 = 14%).
Wound infection
Wound infection was less likely with less axillary surgery than with ALND (OR 0.65, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.84; fixed‐effect model; 2274 participants; three studies; I2 = 0%; Analysis 5.12). The random‐effects model yielded the same result.
Skin graft
Data reveal uncertainty about whether skin graft was less likely with less axillary surgery than with ALND (OR 0.15, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.57; fixed‐effect model; 404 participants; two studies; I2 = 49%; Analysis 5.13). The random‐effects model suggested that skin graft was less likely with less axillary surgery than with ALND (OR 0.17, 95% CI 0.02 to 1.64; random‐effects model; 404 participants; two studies; I2 = 49%).
Haematoma
The SNAC and SE Scotland trials reported haematoma. In the SNAC trial there were similar rates of haematoma in the less surgery group than more surgery group (OR 1.27, 95% CI 0.78 to 2.09; 1083 participants; Analysis 5.14). In the SE Scotland trial haematoma was less likely in the less surgery group than the more surgery group (OR 0.20, 95% CI 0.08 to 0.52; 200 participants; Analysis 5.14. There was considerable heterogeneity in the pooled estimate (I2 = 91%; P = 0.0007).
Quality of life, psychological and psychosocial outcomes
Only trials comparing SLND versus ALND reported these outcomes, so we could perform no additional analyses.
Discusión
Resumen de los resultados principales
El riesgo de mortalidad general no aumentó cuando las pacientes fueron tratados con muestreo axilar o biopsia de ganglios linfáticos centinela (BGLC) versus disección de ganglios linfáticos axilares (DGLA). El tratamiento que omite todas las intervenciones quirúrgicas axilares se asoció con un mayor riesgo de mortalidad general en comparación con la DGLA, pero esto se observó sólo en los ensayos que compararon la radioterapia (RT) sola versus la DGLA.
La disección de ganglios linfáticos axilares se asoció con mayor riesgo de linfedema y eventos adversos quirúrgicos en comparación con la intervención quirúrgica menor.
Compleción y aplicabilidad general de las pruebas
No se encontró ningún ensayo que realizara las siguientes comparaciones: biopsia del ganglio centinela versus muestreo axilar, ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar versus muestreo axilar y ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar versus biopsia del ganglio centinela.
Los datos de los eventos adversos fueron limitados, sobre todo para los ensayos más antiguos que compararon ninguna intervención quirúrgica, RT o muestreo axilar versus DGLA. Los datos de calidad de vida se limitaron a tres ensayos. Los ensayos de ganglios linfáticos centinela aportaron datos limitados sobre la supervivencia general a largo plazo y la recidiva del cáncer de mama; estos ensayos con frecuencia estaban diseñados para comparar la calidad de vida y los efectos adversos. La heterogeneidad significativa en los resultados de los eventos adversos con frecuencia se debió a las diferencias en las definiciones de eventos adversos entre los ensayos.
Algunos ensayos informaron los datos de una manera que impidió la inclusión en el metanálisis del tiempo transcurrido hasta el evento, y aunque se estableció contacto con los autores de los estudios, no se obtuvieron datos adicionales.
La aplicabilidad de algunas de las comparaciones en esta revisión a la práctica actual del cáncer de mama es dudosa, en particular para las comparaciones que no incluyen ninguna intervención quirúrgica axilar. Existen diferencias en el uso de los tratamientos adyuvantes entre la práctica actual y muchos de los ensayos incluidos, ya que en la actualidad se dispone de tratamientos sistémicos adyuvantes más efectivos. Asimismo, los regímenes de RT usados en los ensayos más antiguos probablemente sean menos efectivos y se asocian con más efectos secundarios.
Es probable que haya diferencias entre las pacientes con cáncer de mama actuales y las que participaron en los ensayos más antiguos. Además, el cáncer de mama tiene una mayor probabilidad de ser detectado en un estadio más temprano.
Calidad de la evidencia
El riesgo de sesgo de selección de los estudios incluidos era bajo o poco claro. Habitualmente, el sesgo de selección era poco claro porque las publicaciones de los ensayos no informaron en su totalidad los métodos de generación de secuencias ni la ocultación de la asignación al azar utilizada, y no se obtuvo respuesta de los autores de los estudios cuando se los contactó para solicitarles información adicional acerca de la realización del ensayo. Se realizaron análisis de sensibilidad para los ensayos con ocultación adecuada de la asignación, y se encontró que estos resultados en general fueron compatibles con los resultados de los análisis principales.
El riesgo de sesgo de deserción tendió a ser inferior para la supervivencia y para la recidiva del cáncer de mama que para los eventos adversos. Este hecho se debió en ocasiones a que las evaluaciones de los eventos adversos se realizaron para un subconjunto de la población de los ensayos. Podría haber diferencias sistemáticas entre este subgrupo de pacientes, en que se evaluaron los eventos adversos, y la población del ensayo en su totalidad, sobre todo en el caso de la evaluación de los eventos adversos a largo plazo, cuando las pacientes pueden haber muerto o cuyo estado puede haber sido muy crítico como para participar.
Los ensayos incluidos no aplicaron el cegamiento (y quizás no era posible), pero este hecho se consideró una fuente de sesgo sólo para los resultados con subjetividad potencial en la medición (es decir, recidiva del cáncer de mama y eventos adversos). El sesgo de detección podría llevar a la sobrestimación de los eventos adversos en las pacientes con una intervención quirúrgica axilar más extendida. De igual manera, en las pacientes sometidas a una intervención quirúrgica axilar menos extensa podría verificarse más en detalle la presencia de una recidiva del cáncer de mama.
Por estos motivos se redujo la calidad de la evidencia para efectos adversos (tabla 1 de Resumen de los hallazgos, tabla 2 de Resumen de los hallazgos, tabla 3 de Resumen de los hallazgos y tabla 4 de Resumen de los hallazgos).
Sesgos potenciales en el proceso de revisión
En los metanálisis de los resultados del tiempo transcurrido hasta el evento realizados para esta revisión, se usó el modelo de efectos fijos porque sólo los métodos metanalíticos de efectos fijos están disponibles en RevMan para los resultados “O–E” y “Variance”. Esta situación podría afectar la interpretación de los resultados, ya que se obtienen intervalos de confianza más estrechos para el cociente de riesgos instantáneos agrupado en presencia de heterogeneidad que los que se obtendrían con un modelo de efectos aleatorios. Este es, en particular, el caso del Análisis 5.1 (que compara la supervivencia general con más intervención quirúrgica versus intervención quirúrgica menor), en que es poco probable que sea verdadera la presuposición fundamental del modelo de efectos fijos, dados los diferentes tipos de intervenciones y las poblaciones de pacientes incluidas.
Acuerdos y desacuerdos con otros estudios o revisiones
Kell 2010 informó un metanálisis de siete ensayos de BGLC versus vaciamiento axilar (Addenbrookes 2; ALMANAC; GIVOM Sentinella; Milan; SNAC; ACOSOG Z0011; NSABP B‐32). En comparación con el vaciamiento axilar, la BGLC se asoció con un menor riesgo de infección posoperatoria de la herida (odds ratio [OR] 0,58; intervalo de confianza [IC] del 95%: 0,42 a 0,80), de seroma posoperatorio (OR 0,40; IC del 95%: 0,31 a 0,51) y de edema del brazo a los seis meses después de la intervención (OR 0,30; IC del 95%: 0,14 a 0,66). Estos resultados son consistentes con los hallazgos de la revisión actual.
Wang 2011 también analizó ensayos que examinaron el ganglio linfático centinela versus el vaciamiento axilar (Addenbrookes 2; ALMANAC; GIVOM Sentinella; Genoa; Milan; SNAC; ACOSOG Z0011; NSABP B‐32). La comparación de la BGLC con la DGLA no indicó ninguna diferencia estadísticamente significativa en la supervivencia general (cociente de riesgos instantáneos [CRI] 1,07; IC del 95%: 0,90 a 1,27) ni la recidiva de ganglios linfáticos regionales (OR 1,65; IC del 95%: 0,77 a 3,56). Las complicaciones posoperatorias fueron menos probables con la BGLC que con la DGLA, incluido el linfedema (OR 0,24; IC del 95%: 0,11 a 0,53), el adormecimiento (OR 0,19; IC del 95%: 0,11 a 0,33), la infección (OR 0,50; IC del 95%: 0,36 a 0,70) y el seroma (OR 0,39; IC del 95%: 0,31 a 0,49). Estos resultados son consistentes con los hallazgos de la revisión actual.
En el Grupo de investigadores del cáncer de mama temprano, el metanálisis de los datos de pacientes individuales (Clarke 2005) indicó que el vaciamiento axilar versus la RT axilar efectiva implicaba escasa diferencia absoluta (< 10%) en el riesgo de recidiva local a cinco años, así como una diferencia pequeña en la mortalidad por cáncer de mama (cuando se combinó con otras comparaciones del tratamiento local). En esta revisión se observó un aumento de la mortalidad general con la RT sin intervención quirúrgica axilar en comparación con el vaciamiento axilar, aunque la diferencia absoluta a cinco años correspondió a un porcentaje bajo (Tabla 4 de Resumen de hallazgos); y si hubiese sido posible un modelo de efectos aleatorios, habría una mayor incertidumbre en torno a este cálculo.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.

Comparison 1 No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 1 All‐cause mortality (radiotherapy subgroups).

Comparison 1 No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 2 All‐cause mortality (extra treatment for positive node subgroups).

Comparison 1 No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 3 Locoregional recurrence (radiotherapy subgroups).

Comparison 1 No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 4 Locoregional recurrence (extra treatment for positive‐node subgroups).

Comparison 1 No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 5 Distant metastasis.

Comparison 1 No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 6 Lymphoedema (≥ 12 months postop) ‐ fixed‐effect model.

Comparison 1 No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 7 Lymphoedema (≥ 12 months postop) ‐ random‐effects model.

Comparison 1 No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 8 Arm or shoulder movement impairment (≥ 12 months postop).

Comparison 1 No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 9 Pain (≥ 12 months postop).

Comparison 1 No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 10 Paraesthesia (≥ 12 months postop).

Comparison 1 No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 11 Delayed healing.

Comparison 1 No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 12 Skin graft.

Comparison 1 No axillary surgery versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 13 All‐cause mortality (allocation concealment subgroups).

Comparison 2 Axillary sampling versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 1 All‐cause mortality.

Comparison 2 Axillary sampling versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 2 Local recurrence.

Comparison 2 Axillary sampling versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 3 Axillary recurrence.

Comparison 2 Axillary sampling versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 4 Locoregional recurrence.
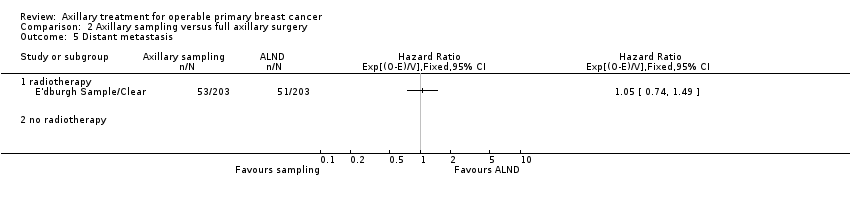
Comparison 2 Axillary sampling versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 5 Distant metastasis.

Comparison 2 Axillary sampling versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 6 Lymphoedema. Increase in arm circumference (≥ 12 months postop).

Comparison 2 Axillary sampling versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 7 Shoulder lateral rotation (12 months postop).

Comparison 2 Axillary sampling versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 8 Seroma.

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 1 All‐cause mortality.

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 2 Local recurrence.

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 3 Axillary recurrence.

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 4 Locoregional recurrence.

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 5 Distant metastasis.

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 6 Lymphoedema. Increase in arm circumference (≥ 12 months postop).

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 7 Lymphoedema. Patient reported (at 12 or more months postop).

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 8 Shoulder flexion (12 months postop).

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 9 Shoulder abduction (12 months postop).

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 10 Shoulder internal rotation (12 months postop).

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 11 Shoulder external rotation (12 months postop).

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 12 Subjective arm movement impairment (≥ 12 months postop).

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 13 Pain (≥ 12 months postop).

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 14 Paraesthesia (≥ 12 months postop).

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 15 Numbness (≥ 12 months postop).

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 16 Seroma.

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 17 Wound infection.

Comparison 3 Sentinel node biopsy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 18 Brachial plexus injury at 6 months postop.

Comparison 4 Radiotherapy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 1 All‐cause mortality.

Comparison 4 Radiotherapy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 2 Local recurrence.

Comparison 4 Radiotherapy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 3 Distant metastasis.

Comparison 4 Radiotherapy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 4 Lymphoedema. Increase in arm circumference (≥ 12 months postop).

Comparison 4 Radiotherapy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 5 Delayed healing.

Comparison 4 Radiotherapy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 6 Wound infection.

Comparison 4 Radiotherapy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 7 Skin graft.

Comparison 4 Radiotherapy versus full axillary surgery, Outcome 8 Haematoma.

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 1 All‐cause mortality.

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 2 All‐cause mortality (radiotherapy subgroups).

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 3 All‐cause mortality (additional treatment for histologically positive nodes).

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 4 Local recurrence.

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 5 Locoregional recurrence.

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 6 Distant metastasis.

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 7 Lymphoedema. Increase in arm volume at 12 months postop.

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 8 Paraesthesia (≥ 12 months postop).

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 9 Pain (≥ 12 months postop).

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 10 Delayed healing.

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 11 Seroma.

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 12 Wound infection.

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 13 Skin graft.

Comparison 5 Less surgery versus ALND, Outcome 14 Haematoma.
| No axillary surgery compared with full axillary surgery for operable primary breast cancer | |||||
| Patient or population: women with operable primary breast cancer | |||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | Number of participants | Quality of the evidence | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | ||||
| Full axillary surgery | No axillary surgery | ||||
| All‐cause mortality | 92% overall survival at 5 yearsa | 92% overall survival at 5 years | HR 1.06 | 3849 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ |
| Locoregional recurrence | 86% locoregional recurrence‐free survival at 5 yearsc | 71% locoregional recurrence‐free survival at 5 years | HR 2.35 | 20,863d | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ |
| Lymphoedema | 236 per 1000 | 87 per 1000 | OR 0.31 | 1714 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Arm or shoulder movement impairment | 91 per 1000 | 67 per 1000 | OR 0.72 | 1495 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | |||||
| aAssumed risk is taken from full axillary surgery arm of Institut Curie. | |||||
| Axillary sampling compared with full axillary surgery for operable primary breast cancer | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with operable primary breast cancer | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | Number of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Full axillary surgery | Axillary sampling | |||||
| All‐cause mortality | 82% overall survival at 5 yearsa | 83% overall survival at 5 years | HR 0.94 | 967 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | |
| Local recurrence | 85% local recurrence‐free survival at 5 yearsd | 80% local recurrence free survival at 5 years | HR 1.41 (0.94 to 2.12) | 1404 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence. | ||||||
| aAssumed risk is taken from full axillary surgery arm of E'dburgh Sample/Clear. | ||||||
| Sentinel node biopsy compared with full axillary surgery for operable primary breast cancer | |||||
| Patient or population: women with operable primary breast cancer | |||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | Number of participants | Quality of the evidence | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | ||||
| Full axillary surgery | Sentinel node biopsy | ||||
| All‐cause mortality | 96% overall survival at 5 yearsa | 96% overall survival at 5 years | HR 1.05 | 6352 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ |
| Lymphoedema | 132 per 1000 | 48 per 1000 | OR 0.33 | 815 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Subjective arm movement impairment | 100 per 1000 | 40 per 1000 | OR 0.38 | 877 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ |
| Paraesthesia | 776 per 1000 | 343 per 1000 | OR 0.15 | 495 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Pain | 177 per 1000 | 86 per 1000 | OR 0.44 | 877 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ |
| Numbness | 346 per 1000 | 185 per 1000 | OR 0.43 | 1799 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence. | |||||
| aAssumed risk taken from the full axillary surgery arm of Milan. | |||||
| Radiotherapy alone compared with full axillary surgery for operable primary breast cancer | |||||
| Patient or population: women with operable primary breast cancer | |||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | Number of participants | Quality of the evidence | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | ||||
| Full axillary surgery | Radiotherapy alone | ||||
| All‐cause mortality | 81% overall survival at 5 yearsa | 79% overall survival at 5 years | HR 1.1 | 2469 | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ |
| Local recurrence | 90% local recurrence‐free survival at 5 yearsb | 92% local recurrence‐free survival at 5 yearsa | HR 0.8 | 22,256c | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence. | |||||
| aAssumed risk from full axillary surgery arm of NSABP B‐04 using mean 5‐year overall survival in combined N+ and N‐ groups. | |||||
| Study | Outcome reported | Observed | Expected | Variance | HR | 95% CIs | P value | Follow‐up | Notes |
| Overall mortality | ALND: 107/112 No ALND: 108/121 | o‐e = ‐3.1 | 46.5 | 0.94 | (0.70 to 1.25) | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition The number of patients reported by Clarke 2005 differs from that reported by Brinkley (1971). | |
| Breast cancer mortality | ALND: 74/112 No ALND: 78/121 | o‐e = ‐2.2 | 32.8 | ‐ | ‐ | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Isolated local recurrence | ALND: 7 events/1148 women‐years No ALND: 15 events/1218 women‐years | o‐e = 3.3 | 5.4 | 1.8 | (0.79 to 4.28) | NA | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Overall mortality | ALDN: 7/476 SLNB: 7/478 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 year | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Axillary recurrence | ALDN: 4/476 SLNB: 1/478 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 year | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall mortality | ALND: 21/43 Simple: 30/52 | o‐e = 4.74 | 12.35 | 1.47 | (0.84 to 2.56) | 0.1775 | 10 years | Tierney et al (2007) method 7 used log‐rank test results from figure 1. Cape Town | |
| Overall mortality (node‐negative) | ALND: 14/21 Simple: 26/30 | o‐e = 1.8 | 7.6 | ‐ | ‐ | NA | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9a; Groote‐Schuur), then O‐E sign changed to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition. Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Overall mortality (node‐positive) | ALND: 19/22 Simple: 22/25 | o‐e = ‐1.9 | 7.7 | ‐ | ‐ | NA | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9b; Groote‐Schuur), then O‐E sign changed to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition. Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Isolated local recurrence (node‐negative) | ALND: 3/206 women‐years Simple: 8/232 women‐years | o‐e = 1.7 | 2.3 | 2.09 | (0.58 to 7.63) | NA | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9a; Groote‐Schuur), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | ||
| Isolated local recurrence (node‐positive) | ALND: 5/134 women‐years Simple: 9/173 women‐years | o‐e = 0.0 | 2.0 | 1.00 | (0.25 to 4.00) | NA | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9b; Groote‐Schuur), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | ||
| Axillary recurrence | ALND: 2/43 Simple: 8/52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Any locoregional recurrence | ALND: 11/43 Simple: 19/52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Distant metastases | ALND: 11/43 Simple: 13/52 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival | ALND: N = 97 Sampling: N =103 Total events = 152 Fig 2 data: ALND: 23/97 Sampling: 13/103 | o‐e: 7.4 | 38 | 1.21 | (0.29 to 0.99) | 0.23 | 20 years | HR calculated using log‐rank P value from Stewart et al (1994, page 42) by Tierney 2007 method 8, 9. Owing to non‐proportionality of hazard rates, HR cannot be included in meta‐analysis | |
| Disease‐free survival | ALND: 97 Sampling: 103 | 5.87 | 7.75 | 2.13 | (1.05 to 4.31) | 0.035 | 20 years | Log‐rank P value Tierney 2007 method 8, 9 (page 43 & Fig 5 Stewart et al, 1994) | |
| Locoregional recurrence (chest wall, axilla, supraclavicular/internal mammary nodes) | ALND: 19/94 Sampling: 31/99 Fig 4: ALND: 11/97 Sampling: 22/103 | o‐e: 6.46 | 11.78 | 1.73 | (0.87 to 3.42) | NA | 20 years | Tierney et al (2007) method 4 used and data from Figure 4 & page 42 Stewart et al (1994) | |
| Distant relapse | ALND: 43/94 Sampling: 59/99 | o‐e: 8.4 | 24.87 | 1.4 | (0.99 to 1.71) | 0.092 | 20 years | Data from Table 2, Stewart et al (1994): excludes patients with radiotherapy violations. Per‐protocol analysis ‐ not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Breast cancer recurrence (total) (locoregional and distant relapse) | ALND: 62/94 Sampling: 90/99 | o‐e: 12.77 | 36.71 | 1.42 | (1.18 to 1.61) | 0.035 | 20 years | Calculated from Stewart et al (1994) (excludes RT violations) per‐protocol analysis Risk of overestimation not certain as these are first events or total events.‐ not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival | ALND: ?/232 Sampling: ?/234 Total events = 53 ALND: 207/232 Sampling: 190/234 | o‐e: ‐4.66 | 13.25 | 0.7 | (0.41 to 1.21) | 0.20 | 5 years | HR calculated using log rank P ‐ figure 2, Chetty (2000) | |
| Axillary recurrence | ALND: /232 Sampling: /234 | o‐e: ‐0.15 | 13.25 | 0.99 | (0.58 to 1.69) | 0.94 | Up to 8 years | Log‐rank P value Tierney 2007 method 7, 8, 9 used Fig 3 Chetty (2000) | |
| Local recurrence in the breast | ALND: 14/232 Sampling: 15/234 | o‐e: ‐0.10 | 7.24 | 0.99 | (0.48 to 2.04) | 0.97 | Up to 8 years | Tierney 2007 method 7, 8, 9 used Table 2 & page 87 Chetty (2000) | |
| Distant recurrence | ALND: 29/232 Sampling: 29/234 | Not available | Not available | Not available | Not available | NA | Up to 8 years | Table 2, Chetty (2000). Unable to estimate HR ‐ not included in analysis | |
| Overall survival | ALND: 76/203 Sampling: 71/203 | o‐e: ‐3.81 | 36.55 | 0.90 | (0.62 to 1.25) | NA | 13 years | Tierney 2007 method 3 used (using 1995 data – Clarke 2005 paper reports more deaths) Fig 1 and page 82 HR (CI) in Forrest et al (1995) ‐ inverted the HR | |
| Distant metastases | ALND: 51/203 Sampling: 53/203 | o‐e: 1.5 | 30.78 | 0.92 | (0.67 to 1.35) | NA | 13 years | Tierney 2007 method 3 used (using 1995 data), Fig 2 and HR (CI) page 82 in Forrest et al (1995), inverted the HR | |
| Locoregional relapse (chest wall, axilla, supraclavicular) | ALND: 38/203 Sampling: 29/203 | o‐e: ‐4.9 | 16.32 | 0.74 | (0.46 to 1.20) | NA | 13 years | Tierney 2007 method 3 used (using 1995 data) Method 3 Fig 3 from HR (CI), page 82 in Forrest et al (1995), inverted the HR | |
| Overall survival | ALND: 4/115 SLNB: 5/110 | o‐e: 0.58 | 2.22 | 1.32 | (0.35 to 4.92) | 0.679 | 5 years | Log‐rank P value (Canavese 2009 ‐ fig 3) Tierney 2007 method 7 used Fig 3 KM curve gives P = 0.679. I assumed that was correct as it appears on the graph. The text value (page 20) may be a typo 0.697. HR are similar; CI differ | |
| Axillary recurrence | ALND: 1/115 SLNB: 0/110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 years | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Breast cancer recurrence (local and contralateral recurrence, axillary and distant metastases) | ALND: 10/115 SLNB: 8/110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 years | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| 5‐Year event‐free survival | ALND: 12/115 SLNB: 10/110 | o‐e: ‐0.85 | 5.45 | 0.86 | (0.37 to 1.98) | 0.715 | 5 years | Log‐rank P value from Fig 2, Canavese (2009) method 7 Tierney 2007 used | |
| Overall survival | ALND: 14/352 SLNB: 21/345 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 years | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Disease‐free survival | ALND: 28/352 SLNB: 39/345 | o‐e = 1.18 | 16.3 | 1.08 | 0.769 | 5 years | Method 7 Tierney 2007 used | ||
| Axillary recurrence | ALND: 0/352 SLNB: 1/345 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Locoregional recurrence | ALND: 3/352 SLNB: 16/345 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Distant recurrence | ALND: 16/352 SLNB: 11/345 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall mortality (clinically node negative) | ALND: 178/241 No ALND (wide excision): 185/233 | o‐e = 13.8 | 80.7 | 1.26 | (0.98 to 1.63) | 0.1 | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research intervention | |
| Overall mortality (clinically node positive) | ALND: 82/85 No ALND (wide excision): 64/71 | o‐e = 4.3 | 30.9 | 1.15 | (0.81 to 1.64) | 0.4 | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research intervention | |
| Breast cancer mortality (clinically node negative) | ALND: 122/241 No ALND (wide excision): 142/233 | o‐e = 13.8 | 58.8 | ‐ | ‐ | 0.07 | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research intervention Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Breast cancer mortality (clinically node positive) | ALND: 53/85 No ALND (wide excision): 54/71 | o‐e = 6.2 | 23.6 | ‐ | ‐ | 0.2 | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research intervention. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Isolated local recurrence (clinically node negative) | ALND: 35 events/3267 women‐years No ALND: 81 events/2383 women‐years | o‐e = 29.5 | 26.4 | 3.06 | (2.09 to 4.48) | < .00001 | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research intervention | |
| Isolated local recurrence (clinically node positive) | ALND: 17 events/873 women‐years No ALND: 31 events/519 women‐years | o‐e = 10.5 | 10.8 | 2.64 | (1.46 to 4.80) | 0.001 | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research intervention | |
| Overall survival | Radical: 35/76 Simple: 40/76 | o‐e = 1.44 | 11.78 | 1.13 | (0.64 to 2.00) | NA | 8 years | Extracted from Fig 3, Burn et al (1968) Tierney 2007 method 10 on Simple is input as "research" and radical as "control". Min and max follow‐up input as 3‐96 months | |
| Local recurrence | Radical: 10/76 Simple: 11/76 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4‐9 years | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Mean time to recurrence | Radical: 15.7 months Simple: 25.9 months | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4‐9 years | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival | ALND: 72/234 Surgery only: 71/239 | o‐e = 1.76 (survival curves cross) | 36.05 | 1.05 | (0.76 to 1.46) | 0.77 | 6‐7 years | HR reported on page 340 of IBCSG (2006), used Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Disease‐free survival | ALND: 92/234 Surgery only: 89/239 | o‐e = 2.6 | 44.69 | 1.06 | (0.79 to 1.42) | 0.69 | 6‐7 years | HR reported on page 340 of IBCSG (2006), used Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Axilla recurrence (as first event) | ALND: 2/234 Surgery only: 6/239 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6‐7 years | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival (whole follow‐up period) ITT | no ALND: NR ALND: NR | o‐e = 6.42 | 7.04 | 2.49 | 90% CI (1.34 to 4.63) | NA | Whole follow‐up period (unclear how long that is) | HR reported on page 566 of Avril (2011), used Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Event‐free survival (whole follow‐up period) ITT | no ALND: 44/297 ALND: 31/297 | o‐e = 8.75 | 18.37 | 1.61 | 90% CI (1.1 to 2.37) | NA | Whole follow‐up period (unclear how long that is) | HR reported on page 566 of Avril (2011), used Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Axillary event | Within 5 years: no ALND: 4/297 ALND: 0/310 After 5 years: no ALND: 2/297 ALND: 0/310 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Lymph node (excl axillary) event | Within 5 years: no ALND: 1/297 ALND: NA After 5 years: no ALND: 0/297 ALND: NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Breast/chest wall event | Within 5 years: no ALND: 5/297 ALND: 4/310 After 5 years: no ALND: 0/297 ALND: 8/310 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Metastatic event | Within 5 years: no ALND: 4/297 ALND: 1/310 After 5 years: no ALND: 2/297 ALND: 2/310 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Contralateral breast cancer | Within 5 years: no ALND: 2/297 ALND: 1/310 After 5 years: no ALND: 2/297 ALND: 1/310 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Other site cancer | Within 5 years: no ALND: 5/297 ALND: 5/310 After 5 years: no ALND: 5/297 ALND: 4/310 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Overall survival | RT: 43/331; ALND: 29/326 | o‐e = 7 | 17.3 | 1.50 | (0.94 to 2.40) | NA | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | ||
| Isolated local recurrence | RT: 39/2045 women‐years; ALND: 34/2126 women‐years | o‐e = 1.6 | 17.5 | 1.10 | (0.69 to 1.75) | NA | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | ||
| Axilla recurrence | RT: 12/332; ALND: 5/326 | o‐e = 3.86 | 3.53 | 3.93 | ‐ | 0.04 | Table 2 in Louis‐Sylvestre (2004), method 7 in Tierney 2007 | ||
| Disease‐free survival | RT: 5 years : 82 (SD = 2.1)% 10 years : 72 (SD = 2.5)% 15 years : 65.5 (SD = 2.7)% | ALND: 5 years: 83.3 (SD 2)% 10 years: 72.6 (SD 2.5)% 15 years: 64.3 (SD 2.9)%. | NA | NA | NA | NA | o‐e cannot be extracted because P values not reported past NS in Table 2 in Louis‐Sylvestre (2004). Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Metastases | RT: 5 years: 12.8 (SD 1.9)% 10 years: 21 (SD 2.3)% 15 years: 24.9 (SD 2.5)% | ALND: 5 years: 10.8 (SD 1.7)% 10 years: 18.3 (SD 2.2)% 15 years: 25.8 (SD 2.6)% | NA | NA | NA | NA | O‐e cannot be extracted because P values not reported past NS in Table 2 in Louis‐Sylvestre (2004). Not included in meta‐analysis | ||
| Overall survival | ALND + RT: ?/97 Mastectomy alone: ?/98 (total event rate = 91) | o‐e = ‐4.19 | 22.75 | 0.83 | (0.55 to 1.25) | 0.38 | 15‐20 years | Using P = 0.38 reported on page 558 of Borgstrom (1994) and Tierney 2007 method 8. The o‐e is calculated on the basis of a total event rate of N = 91, and total N = 97 in the ALND + RT group and N = 98 in mastectomy alone group (i.e. intent‐to‐treat numbers), and using the only P value reported, which was for per‐protocol analysis that study authors stated did not differ from intention‐to‐treat analyses | |
| Chest wall recurrence | ALND + RT: 2/97 Mastectomy alone: 11/98 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 15‐20 years | Cannot calculate o‐e. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival | Radical: 126/149 Simple + RT: 140/159 | o‐e = 5.4 | 58.6 | 1.10 | (0.85 to 1.42) | NA | 15 years | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Death from breast cancer | Radical: 100/149 Simple + RT: 112/159 | o‐e = 2.8 | 46 | 1.06 | (0.80 to 1.42) | NA | 15 years | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Local recurrence | Radical: 48 events/997 women‐years Simple + RT: 41 events/1113 women‐years | o‐e = ‐5.7 | 19.9 | 0.75 | (0.48 to 1.17) | NA | 15 years | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Death from any cause (OS) | ALND = 23/257 SLNB = 15/259 | o‐e = ‐4.34 | 9.08 | 0.62 | (0.32 to 1.19) | 0.15 | 10 years | Log‐rank P (Tierney 2007 method 7); ALND is control | |
| Breast cancer recurrence (local recurrence, regional lymph node metastases, distant metastases) | ALND = 26/257 SLNB = 23/259 | o‐e = ‐2.25 | 12.02 | 0.83 | (0.47 to 1.46) | 0.52 | 10 years | Log‐rank P (Tierney 2007 method 7); ALND is control | |
| Distant metastasis | ALND = 20/257 SLNB = 17/259 | o‐e = ‐2.04 | 9.19 | 0.80 | (0.42 to 1.53) | 0.50 | 10 years | Log‐rank P from table 4 Veronesi (2010) (Tierney 2007 method 7); ALND is control | |
| Axillary metastasis | ALND = 0/257 SLNB = 2/259 | o‐e = 0.97 | 0.50 | 6.96 | (0.44 to 111.3) | 0.17 | 10 years | Log‐rank P from table 4 Veronesi (2010) (Tierney 2007 method 8 and 9); ALND is control | |
| Local recurrence | ALND = 4/257 SLNB = 4/259 | o‐e = ‐0.12 | 2.00 | 0.94 | (0.24 to 3.76) | 0.93 | 10 years | Log‐rank P from table 4 Veronesi (2010) (Tierney 2007 method 7); ALND is control | |
| Supraclavicular metastasis | ALND = 2/257 SLNB = 0/259 | o‐e = ‐1.02 | 0.50 | 0.13 | (0.01 to 2.09) | 0.15 | 10 years | Log‐rank P from table 4 Veronesi (2010) (Tierney 2007 method 8, 9); ALND is control | |
| Contralateral breast cancer | ALND = 10/257 SLNB = 9/259 | o‐e = ‐0.81 | 4.47 | 0.84 | (0.34 to 2.07) | 0.71 | 10 years | Log‐rank P from table 4 Veronesi (2010) (Tierney 2007 method 7); ALND is control | |
| Overall survival | ALND = 31/109 No ALND = 35/110 | o‐e = ‐2.72 | 16.43 | 0.85 | (0.52 to 1.37) | Median = 150 months | HR reported on page 922 of Martelli (2012). Using Tierney 2007 method 3 o Please note, the curves cross; also the HR used for extraction of o‐e and its variance is adjusted for tumour grade and oestrogen‐receptor status | ||
| Breast cancer deaths | ALND: 8/109 No ALND: 10/110 | o‐e = 1.33 | 4.06 | 1.39 | ‐ | ‐ | Median = 150 months | HR reported in Table 3 of Martelli (2012). Tierney 2007 method 3 o Please note, the curves cross; also the HR used for extraction of o‐e and its variance is adjusted for tumour grade and oestrogen‐receptor status. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Axillary relapse | ALND: 0/109 No ALND: 4/110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Median = 150 months | Table 2 of Martelli (2012), cannot calculate o‐e | |
| Recurrence (ipsilateral breast tumour) | ALND: 4/109 No ALND: 7/110 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Median = 150 months | Table 2 of Martelli (2012), cannot calculate o‐e | |
| Distant metastases | ALND: 9/109 No ALND: 9/110 | o‐e = ‐2.68 | 5.93 | 0.64 | (0.28 to 1.42) | NA | Median = 150 months | HR reported in Table 3 of Martelli (2012). Tierney 2007 method 3 Please note, the curves cross; also the HR used for extraction of o‐e and its variance is adjusted for tumour grade and oestrogen‐receptor status | |
| Overall survival | 10‐year ALND: 93.3% (95% CI 89.4‐95.8) no ALND: 91.5% (95% CI 87‐94.4) | o‐e = 1.76 | 12.33 | 1.15 | (0.66 to 2.02) | P = .436 | Median = 127.5 months | Agresti (2014) Figure 3A and Tierney 2007 method 11 Please note, the curves cross at the very end, also HR used for extraction of o‐e | |
| Death from breast cancer | ALND: 17/272 no ALND: 15/245 | NA | NA | NA | NA | P = 1.00 | Median = 127.5 months | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Disease‐free survival | 10‐year ALND: 92.4% (95% CI 88.5‐95.1) no ALND: 91.3% (95% CI 86.7‐94.3) | o‐e= ‐0.13 | 10.7 | 0.99 | (0.54 to 1.8) | P = .97 | Median = 127.5 months | Agresti (2014) Figure 3A andTierney 2007 method 11 Please note, the curves cross at the very end; also the HR used for extraction of o‐e | |
| Distant metastases | ALND: 23/272 no ALND: 20/245 | NA | NA | NA | NA | P = 1.00 | Median = 127.5 months | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Axillary recurrence | ALND: 0/272; no ALND: 22/245 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Median = 127.5 months | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Local recurrence | ALND: 14/272 no ALND: 11/245 | NA | NA | NA | NA | P = .839 | Median = 127.5 months | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Contralateral breast cancer | ALND: 13/272 no ALND: 14/245 | `NA | NA | NA | NA | P = .695 | Median = 127.5 months | Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival: node negative: ALND vs no ALND | ALND = 259/389 No ALND = 256/384 | o‐e = ‐5 | 117.3 | 0.96 | (0.80 to 1.15) | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 Lancet (Appendix web figure 9a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Overall survival: node negative: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 259/389 No ALND + RT = 271/386 | o‐e = 8.6 | 122.2 | 1.07 | (0.90 to 1.28) | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Overall survival: node positive: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 244/301 No ALND + RT = 244/305 | o‐e = 8.3 | 109.4 | 1.08 | (0.89 to 1.30) | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Local isolated recurrence: node negative: ALND vs no ALND | ALND = 35 events/3949 women‐years No ALND = 94 events/3335 women‐years | o‐e = 31.5 | 29.2 | 2.94 | (2.05 to 4.23) | NA | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 9a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Local isolated recurrence: node negative: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 35 events/3949 women‐years No ALND + RT = 18 events/3896 women‐years | o‐e = ‐8.7 | 13 | 0.51 | (0.30 to 0.88) | NA | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Local isolated recurrence: node positive: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 45 events/2268 women‐years No ALND + RT = 42 events/2025 women‐years | o‐e = ‐0.5 | 20.8 | 0.98 | (0.64 to 1.50) | NA | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Disease‐free survival: node negative: ALND vs no ALND | ALND = 281/362 No ALND + RT = 287/365 | o‐e = 9.36 | 138.3 | 1.07 | (0.91 to 1.27) | 0.39 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 568 (radical vs total mastectomy) Tierney 2007 method 3, calculated from the date of mastectomy, events considered in determination of disease‐free survival were the first local, regional or distant recurrence of tumour; contralateral breast cancer or a second primary tumour other than a tumour in the breast; and death with no evidence of cancer | |
| Disease‐free survival: node negative: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 281/362 No ALND + RT = 292/352 | o‐e = 8.3 | 142.39 | 1.06 | (0.90 to 1.25) | 0.49 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 568 (radical vs total mastectomy + RT) Tierney 2007 method 3, calculated from the date of mastectomy, events considered in determination of disease‐free survival were the first local, regional or distant recurrence of tumour; contralateral breast cancer or a second primary tumour other than a tumour in the breast; and death with no evidence of cancer | |
| Disease‐free survival: node positive: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 254/292 No ALND + RT = 258/294 | o‐e = 14.46 | 127.57 | 1.12 | (0.94 to 1.33) | 0.20 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 568, Tierney 2007 method 3, calculated from the date of mastectomy, events considered in determination of disease‐free survival were the first local, regional or distant recurrence of tumour; contralateral breast cancer or a second primary tumour other than a tumour in the breast; and death with no evidence of cancer | |
| Relapse‐free survival: node negative: ALND vs no ALND | ALND = 154/362 No ALND + RT = 182/365 | o‐e = 10.17 | 77.61 | 1.14 | (0.91 to 1.42) | 0.27 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 568 Tierney 2007 method 3; calculated from the date of mastectomy, events considered in determination of relapse‐free survival were the first local, regional or distant recurrence; or an event in the contralateral breast | |
| Relapse‐free survival: node negative: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 154/362 No ALND + RT = 163/352 | o‐e = ‐2.9 | 71.05 | 0.96 | (0.76 to 1.21) | 0.74 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 568, Tierney 2007 method 3, calculated from the date of mastectomy, events considered in determination of relapse‐free survival were the first local, regional or distant recurrence; or an event in the contralateral breast | |
| Relapse‐free survival: node positive: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 178/292 No ALND + RT = 183/294 | o‐e = 7.63 | 88.52 | 1.09 | (0.89 to 1.35) | 0.40 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 568, Tierney 2007 method 3, calculated from the date of mastectomy, events considered in determination of relapse‐free survival were the first local, regional or distant recurrence; or an event in the contralateral breast | |
| Time to distant metastasis: node negative: ALND vs no ALND | ALND = 101/362 No ALND + RT = 107/365 | o‐e = 8.44 | 88.52 | 1.1 | (0.89 to 1.35) | 0.39 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 569, Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Time to distant metastasis: node negative: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 101/362 No ALND + RT = 111/352 | o‐e = 6.69 | 86.9 | 1.08 | (0.88 to 1.34) | 0.44 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 569, Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Time to distant metastasis: node positive: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 120/292 No ALND + RT = 127/294 | o‐e = 5.98 | 88.41 | 1.07 | (0.87 to 1.32) | 0.51 | 25 years | FIsher (2008) page 569, Tierney 2007 method 3 | |
| Overall survival (all randomised participants, i.e. node+ and node‐) | ALND = 228 (deaths)/2807 SLN = 252 (deaths)/2804 | 10.32 | 119.7 | 1.09 | (0.91 to 1.3) | 0.35 | 10 years | From Julian (2013) using Tierney 2007 method 4. Contacted author (Krag) to confirm direction of effect | |
| Disease‐free survival (all randomised participants, i.e. node+ and node‐) | ALND = 455/2807 SLN = 475/2804 | 4.6 | 232.39 | 1.02 | (0.9 to 1.16) | 0.72 | 10 years | From Julian (2013) using Tierney 2007 method 4. Contacted author (Krag) to confirm direction of effect | |
| Local/regional recurrence (all randomised participants, i.e. node+ and node‐) | ALND = 121/2807 SLN = 112/2804 | ‐2.37 | 58.16 | 0.96 | (0.74 to 1.24) | 0.77 | 10 years | From Julian (2013) using Tierney 2007 method 4. Contacted author (Krag) to confirm direction of effect | |
| Axillary recurrence (all randomised participants, i.e. node+ and node‐) | ALND = 6/2807 SLN = 14/2804 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years | o‐e cannot be calculated. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Overall survival (for SLN‐neg) | ALND = 219 (dead)/1975 SLN = 245 (dead)/2011 | o‐e = 12.07 | 115.64 | 1.11 | (0.93 to 1.33) | 0.27 | 10 years | From Julian (2013) using Tierney 2007 method 4 | |
| Disease‐free survival (for SLN‐neg) | ALND = 456 (diseased)/1975 SLN = 465 (diseased)/2011 | o‐e = 2.29 | 230.23 | 1.01 | (0.89 to 1.15) | 0.92 | 10 years | From Julian (2013) using Tierney 2007 method 4 | |
| Local regional recurrence | ALND = 85 (events)/1975 SLN = 80 (events)/2011 | o‐e = ‐2.11 | 41.21 | 0.95 | (0.7 to 1.29) | 0.77 | 10 years | From Julian (2013) using Tierney 2007 method 4 | |
| Local recurrence in SLN‐negative participants | ALND = 54 (events)/1975 SLN = 49 (events)/2011 | o‐e = ‐3.03 | 25.69 | 0.89 | (0.6 to 1.31) | 0.55 | Mean = 95.6 months | From Krag (2010) page 930 using logrank P = 0.55 Tierney 2007 method 7 | |
| Regional recurrence in SLN‐negative participants | ALND = 8 (events)/1975 SLN = 14 (events)/2011 | o‐e = 2.77 | 5.09 | 1.72 | (0.72 to 4.11) | 0.22 | Mean = 95.6 months | From Krag (2010) page 930 using log rank P = 0.22 Tierney 2007 method 7 | |
| Distant recurrence in SLN‐negative patients | ALND = 55 (events)/1975 SLN = 64 (events)/2011 | o‐e = 3.91 | 29.82 | 1.14 | (0.8 to 1.64) | Mean = 95.6 months | From Krag (2010) Figure 4 Tierney 2007 method 3 | ||
| Recurrence in the axilla | ALND: 0/57 Sampling: 1/54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Median: 30 (range, 5‐76) months | From Borup‐Chistesen (1993) table IV. Recurrence is reported only out of N = 111 (57 + 54) participants who did not have metastases in axillary lymph nodes after dissection or biopsy. Cannot calculate o‐e on the basis of available data | |
| Local recurrence | ALND: 4/57 Sampling: 1/54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Median: 30 (range, 5‐76) months | From Borup‐Chistesen (1993) table IV. Recurrence is reported only out of N = 111 (57 + 54) participants who did not have metastases in axillary lymph nodes after dissection or biopsy. Cannot calculate o‐e on the basis of available data | |
| Distant recurrence | ALND: 1/57 Sampling: 4/54 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Median: 30 (range, 5‐76) months | From Borup‐Chistesen (1993) table IV. Recurrence is reported only out of N = 111 (57 + 54) participants who did not have metastases in axillary lymph nodes after dissection or biopsy. Cannot calculate o‐e on the basis of available data | |
| Overall survival: node negative: ALND vs Simple + RT | ALND = 143/199 Simple + RT = 143/180 | o‐e = 17.5 | 65.7 | 1.31 | (1.02 to 1.66) | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Overall survival: node positive: ALND vs Simple + RT | ALND = 72/89 Simple + RT = 77/93 | o‐e = 6.3 | 34.1 | 1.20 | (0.86 to 1.68) | NA | 15 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Local isolated recurrence: node negative: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 26 events/2880 women‐years Simple + RT = 21 events/2204 women‐years | o‐e = ‐0.5 | 11.3 | 0.96 | (0.53 to 1.71) | NA | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Local isolated recurrence: node positive: ALND vs no ALND + RT | ALND = 24 events/943 women‐years Simple + RT = 17 events/878 women‐years | o‐e = ‐2.9 | 9.8 | 0.74 | (0.40 to 1.39) | NA | 5 years? | Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figure 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Overall survival ‐ node negative | ALND: 56/101 Simple + RT to chest wall & axilla: 42/85 | o‐e = ‐5.5 | 21.4 | 0.77 | (0.51 to 1.18) | NA | 15 years? | CAUTION: same control group used twice for these data Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figures 9a and 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Overall survival ‐ node positive | ALND: 13/17 Simple + RT to chest wall & axilla: 7/9 | o‐e = ‐0.5 | 3.3 | 0.86 | (0.29 to 2.53) | NA | 15 years? | CAUTION: same control group used twice for these data Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figures 9b and 10b). then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Isolated local recurrence ‐ node negative | ALND: 15/510 py Simple + RT to chest wall & axilla: 13/483 py | o‐e = 0.0 | 6.7 | 1.00 | (0.47 to 2.13) | NA | 5 years? | CAUTION: same control group used twice for these data Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figures 9a and 10a), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| Isolated local recurrence ‐ node positive | ALND: 3/69 py Simple + RT to chest wall & axilla: 1/41 py | o‐e = ‐0.5 | 0.9 | 0.57 | (0.07 to 4.53) | NA | 5 years? | CAUTION: same control group used twice for these data Taken from Clarke 2005 (Appendix web figures 9b and 10b), then inverted to reflect that more surgery is our control and less surgery is our research condition | |
| 10‐year overall survival | Level I clearance: 75/93 ALND: 71/88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years | o‐e could not be calculated as no P values reported. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| 10‐year disease‐free survival | Level I clearance: 72/93 ALND: 68/88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years | o‐e could not be calculated as no P values reported. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Breast cancer recurrence | Level I clearance: 19/93 ALND: 17/88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years? | o‐e could not be calculated as no P values reported. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Local recurrence | Level I clearance: 3.2% ALND: 2.3% | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years? | o‐e could not be calculated as no P values reported. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Distant metastasis | Level I clearance: 19/93 ALND: 15/88 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10 years? | o‐e could not be calculated as no P values reported. Not included in meta‐analysis | |
| Figures in bold were reported in the original publication; others were derived (see Notes column). | |||||||||
| Study | Oedema | Shoulder function | Skin graft | Delayed healing | Activity | Attitude | Other | Notes |
| Slight: 0‐2.5 cm Moderate: 2.5‐4.5 cm Severe > 4.5 cm Circumference of both arms measured 7.5 cm below the acromion, 18 cm above and 10 cm below the olecranon and at the wrist Presumably difference between arm circumference | Arm function: Good: uses arm freely Fair: cannot do usual tasks Poor: very unsatisfactory use of arm Appears to be assessed by patient questionnaire | Good: normal activity, back at work or resumed usual activities Fair: light work only because of operation; not resumed usual activities Poor: inactive. Assessed by patient questionnaire | Good: no complaints Fair: some complaints Poor: very unhappy about experience Assessed by patient questionnaire | |||||
| Lympheoedema (subjective) – according to patient self‐report or physician diagnosis Lympheoedema (objective): 2 cm or greater postop increase in ipsilateral arm circumference | Axillary paraesthesia – patient reported Brachial plexus injury – determined by physician on examining the patient | |||||||
| 1. Mild oedema 2. Gross oedema (estimated by measuring the circumference of each arm with the arm extended at points 11 inches and 22 inches from the tips of the middle finger. An increase of 1 inch in the circumference of the arm on the side of the operation at either or both points was taken to indicate some degree of oedema) | Stiff shoulder | Need for skin graft | Sufficient to cause postponement of radiotherapy until at least 2 months after the operation. Although incidence of delayed healing varied between surgeons, each showed the same trend of higher incidence following a radical operation | |||||
| Subjective lymphoedema: patient reported Objective lymphoedema: circumferential arm measurement at 4 cm intervals from the wrist (approximately 10 measurements) used to calculate arm volume. Volume corrected using measurements from contralateral arm | Range of movement measured by recording degrees of flexion, abduction and internal and external rotation using goniometer Sensory function tested using pinprick, light touch | Global Severity Index (GSI; low values better), Beck's Depression Inventory, Spielberger's State‐Trait anxiety, MAC, SF‐36 (measured psychological morbidity and quality of life) | ||||||
| Change in ipsilateral arm volume at each follow‐up visit was expressed as a % increase from pretreatment value. Ratios of presurgery to postsurgery arm volumes were compared on a log‐transformed scale. The contralateral arm was used as a control for evaluations of arm volume Also patient rated as mild, moderate or severe | Assessed by goniometric measurement of arm movement (flexion, abduction, internal rotation and external rotation). Changes between visits calculated by subtraction The contralateral arm was used as a control for arm and shoulder function | QoL: Fact‐B+4 Anxiety: Spielberger STAI | ||||||
| Cardiff ‐ Local | No morbidity data | |||||||
| Cardiff ‐ St Mary's | Oedema of arm 72 cm | Restricted elevation 720 degrees | Measured but not reported | Axillary pain; numbness or paraesthesia on operated sides; aesthetic appearance of axillary scar | ||||
| Arm swelling measured by water displacement, circumference 15 cm above and below the olecranon process | Shoulder mobility assessed by measuring elevation through flexion, abduction, medial and lateral rotation | Shoulder muscle power assessed using graduated spring to measure flexion, extension, abduction and adduction of the shoulder joint | ||||||
| Arm welling (arm circumference 15 cm above and 10 cm below olecranon) | Objective assessment via adduction with internal rotation; abduction with external rotation, difference in height reached between treated and non‐treated arms by stretching above head, measurement of an abduction movement without shoulder rotation whilst lying on a flat, hard surface | Power (cm/kg) of pectoralis major by repeated lifting of a 3.5 kg weight as fast as possible over 45 seconds, comparing treated and untreated arm | Sample from study only, level B evidence | |||||
| Lympheodema was assessed by comparing the circumference of the operated vs the non‐operated arm at 15 cm above the epicondyle Unclear what difference in circumference constituted lymphoedema | Assessed by the surgeon by evaluating active and passive flexion, abduction, internal and external rotation, and classified on a scale 0 (normal mobility) to 3 (severe mobility) restriction Winged scapula reported as present/absent | Axillary and arm pain reported by patients on a scale from 0 (absent) to 3 (continuous/severe) Numbness assessed by the surgeon by comparing skin sensitivity in operated and non‐operated arms. Rated 0 (absent) to 3 (severe) | ||||||
| Reports lymphoedema; categorised as none, slight, moderate and severe | Reports arm function as good, fair or poor | Reports activity as good, fair or poor | Reports attitude as good, fair or poor | Pts in no axillary surgery + RT arm reported fibrosis of breast and sometimes "marbling" of the overlying skin. Both occurred in <5% of cases | ||||
| Impairted function of the shoulder joint and swollen arm: no definitions given, but it is stated that the methodology included volumetric measurement of the upper limb and that an attempt was made to ally objective measurements with the patient’s subjective expression of discomfort or disability | Impairted function of the shoulder joint and swollen arm: no definitions given, but it is stated that the methodology included volumetric measurement of the upper limb and that an attempt was made to ally objective measurements with the patient’s subjective expression of discomfort or disability | In evaluating morbidity, attempts made to ally objective measurements with patient's subjective expression of disability or discomfort. Expectation that after RM, slight increase in volume of ipsilateral arm, or after RT, some discomfort and stiffness to shoulder, but these do not amount to morbidity | ||||||
| ≥ 5% increase in arm circumference from baseline | QOL: A core questionnaire plus a surgical module specific to this trial. Four linear analogue scales on the core questionnaire were used: well‐being, mood, appetite and perceived adjustment/coping. After 1993, 6 additional scales were added: tiredness, hot flashes, nausea/vomiting, perceived social support, arm restriction and subjective health estimation. Surgical module measured swelling, numbness, weakness, pain, stiffness, performance of daily activities and global measure of arm/hand/shoulder/chest bother | |||||||
| No definitions for functional outcomes reported | ||||||||
| No definitions for functional outcomes reported | ||||||||
| An increase in arm volume was defined as an increase > 2 cm, comparing the circumference of the operated upper limb (at 3 points: the wrist, the midpoint of the forearm and the midpoint of the upper arm) with its non‐operated counterpart | Patients were asked to lift their operated arm (maximum possible abduction): abduction ≥ 90° was considered adequate; abduction < 90° was considered abnormal | Patients were asked: Is your arm painful in a resting position (yes/no)? Does the inside of your arm feel more numb (yes/no)? | ||||||
| Arm swelling was assessed by comparing the circumference of treated and untreated arms 15 cm above the lateral epicondyle | Arm mobility was judged by asking the patient to rate restriction in movement on a scale 0 to 100 Numbness assessed by comparing skin sensitivity on inside and outside of the upper arm – classified as yes/no | Aesthetic appearance of scar judged by patient (rated good or bad) | Postoperative pain was evaluated as continuous (> 50% of the day), sporadic or absent | |||||
| Ipsilateral and contralateral measurement of arm circumference at 15 cm below the acromion process and 15 cm below the olecranon: An increase in arm circumference ≥ 2 cm in ipsilateral arm (below or above the elbow) indicated arm oedema | ||||||||
| Arm volume measured using volume of water displaced determined by the difference between treated and untreated arms (relative arm volume difference = [ipsilateral‐contralateral]/[contralateral] × 100%) | Arm mobility in degrees was determined by measuring the straight lateral abduction of both ipsilateral and contralateral arms using a standard orthopaedic goniometer to determine the angle between lateral chest wall and humerus (relative shoulder abduction deficit = [ipsilateral‐contralateral]/[contralateral] × 100%) | Numbness and tingling were assessed by self‐report by asking patients if they were currently experiencing any numbness or any tingling anywhere in ipsilateral and contralateral arms. OR of SLN compared with ALND Adverse events: no details reported | ||||||
| Arm volume measured using volume of water displaced. A cutoff of 10% increase in volume was used as the arbitrary cut point | Shoulder mobility (flexion, abduction and rotation) was determined with the help of a 360° scale placed on a wall with the centre at shoulder height | |||||||
| Arm volume was estimated using 6 measures of arm circumference at 10 cm intervals starting 10 cm from the tip of the index finger. Upper limb swelling was expressed as percentage change in volume from baseline | Abduction and flexion measured using goniometer Arm morbidity measured using the 15‐item SSSS scale developed for the study, with each rated from 0 (no trouble at all) to 10 (worst I can imagine) and averaged to obtain overall score | |||||||
| Increase in circumference of forearm by at least 3 cm | Failure to abduct the arm beyond a right angle | |||||||
| Postoperative swelling: middle grade (diameter is 3–6 cm enlargement on the involved upper arm or forearm compared with the contralateral part) |
| Study | Outcome | Measurement | Follow‐up period 1 | Follow‐up period 2 | Notes |
| Wound infection | Determined by treating physician | SLND: 11/371; SLND + ALND: 31/373 | |||
| Axillary seroma | Determined by treating physician | SLND: 21/371; SLND + ALND: 53/373 | |||
| Brachial plexus injury | Determined by treating physician | At 6 months: SLND: 3/415; SLND + ALND: 5/406 At 1 year: SLND: 0/415; SLND + ALND: 1/406 | |||
| Axillary paraesthesia | Patient reported | 30 days: SLND: 43/371; SLND + ALND: 174/373 | 6 months: SLND: 35/288; SLND + ALND: 146/335 | ||
| Axillary paraesthesia | Patient reported | 12 months: SLND: 24/268; SLND + ALND: 113/287 | |||
| Lymphoedema (objective) | Arm measurement | 30 days: SLND: 17/272; SLND + ALND: 23/255 | 6 months: SLND: 21/271; SLND + ALND: 29/270 | ||
| Lymphoedema (objective) | Arm measurement | 12 months: SLND: 14/226; SLND + ALND: 26/242 | |||
| Lymphoedema (subjective) | Patient reported/physician diagnosis | 6 months: SLND: 19/339; SLND + ALND: 27/327 | 12 months: SLND: 12/268; SLND + ALND: 37/288 | ||
| Lymphoedema (subjective) | Patient reported/physician diagnosis | > 12 months: SLND: 14/253; SLND + ALND: 52/272 | |||
| Mild oedema | Follow‐up was at least 12 months in most cases. ALND = 7/91; Simple = 5/113 | ||||
| Stiff shoulder | ALND = 6/91; Simple = 8/113 | ||||
| Skin graft | Need for skin graft | ALND = 4/91; Simple = 2/113 | |||
| Delayed healing | Need to delay postoperative RT | ALND = 18/91; Simple = 7/113 | |||
| Gross oedema | Arm measurement | ALND = 0/91; Simple = 0/113 | ALND = 12/45; Simple = 6/53 | ||
| Seroma | ALND: 33/155; SLNB: 20/143 | ||||
| Lymphoedema (objective) | Arm volume changes | 12 months: ALND: mean (SE) = 56.4 (10.9); SLNB: mean (SE) = 18.6 (13.8), difference mean (SE) = 37.8 (17.6) Mean (1, 3, 6, 12 months): ALND: mean (SE) = 53.1 (8.1); SLNB: mean (SE) = 17.7 (9.2), difference mean (SE) = 35.4 (12.2) | Max: ALND: mean (SE) = 113.7 (9.7); SLNB: mean (SE) = 78.4 (12), difference mean (SE) = 35.3 (15.3) | ||
| Lymphoedema (subjective) | Patient reported | 1 month: OR = 0.34 (95% CI 0.11 to 0.9); 3 months: OR = 0.4 (95% CI 0.16 to 0.94); 6 months: OR = 0.25 (95% CI 0.08 to 0.66) | 12 months: OR = 0.36 (95% CI 0.15 to 0.86); mean: OR = 0.3 (95% CI 0.18 to 0.68) | Odds ratios: SLNB/ALND; i.e. lower favours SLNB | |
| Paraesthesia | ALND: 130/155; SLNB: 92/140 | ||||
| Numbness | ALND: 115/155; SLNB: 68/143 | ||||
| Loss of pinprick | ALND: 118/155; SLNB: 77/140 | ||||
| Loss of light touch | ALND: 121/155; SLNB: 81/140 | ||||
| QOL (immediate postop) | Study authors note QOL scores were usually higher (better) in the SLND group and significantly so in the immediate postoperative period (P < 0.01). No significant effect of node positive/negative | ||||
| MAC scale (12 months) | Study authors no significant difference in MAC scores during 1 year follow‐up. No significant effect of node positive/negative | ||||
| BSI – somatisation (immediate postop) | SLND group scored lower (better) than ALND in the immediate postoperative period (P < 0.001) | ||||
| Quality of life | GSI level | 12 months: ALND: mean (SE, N) = 49.7 (1.1, 143); SLNB: mean (SE, N) = 48.4 (0.9, 134), difference mean (SE) = 1.3 (1.4) | OR for morbid GSI: study/control (95% CI) 0.55 (0.08 to 2.94) | ||
| Quality of life | SF‐36 (immediate postoperative) | Physical combined: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 38.6 (8.2, 143); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 42.3 (10.4, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 3.7 (1.2 to 6.1) Physical functioning: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 41.3 (9, 143); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 44.5 (8.1, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 3.2 (1.1 to5.4) | Vitality: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 48.2 (10.2, 143); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 51.8 (9.8, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 3.7 (1.1 to 6.2) | ||
| Shoulder movement (mean reduction) | Flexion, extension, abduction, internal rotation, external rotation | Flexion: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 13 (32.9, 141); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 6.7 (15.6, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 6.3 (0.1 to 12.6); Extension: ALND: mean (SD, N) = ‐1.5 (10.7, 139); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = ‐2.2 (8.1, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 0.7 (‐1.5 to 3.3); Abduction: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 6.3 (11.5, 138); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 3.1 (15.7, 132), difference mean (95% CI) = 3.2 (‐0.5 to 6.3) | Internal rotation: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 1.7 (12.7, 139); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 0.3 (12, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 1.4 (‐1.5 to 4.4); External rotation: ALND: mean (SD, N) = 2.9 (12.3, 139); SLNB: mean (SD, N) = 1.5 (11, 134), difference mean (95% CI) = 1.4 (‐1.5 to 4.4) | ||
| Axillary drain usage | ALND: 359/453; SLNB: 75/449 | ||||
| Infection rate of surgical wounds | ALND: 72/476; SLNB: 52/478 | ||||
| Lymphoedema | Patient‐assessed; moderate/severe | 1 month: ALND: 7/419; SLNB: 1/428 3 months: ALND: 12/395; SLNB: 4/417 | 6 months: ALND: 13/414; SLNB: 2/432 12 months: ALND: 10/403 SLNB: 4/412 | ||
| Lymphoedema | Mean (95% CI) change in arm vol compared with pretreatment | 1 month: ALND = 1.022 (1.013‐1.032); SLNB = 1.003 (0.997‐1.01) 3 months: ALND = 1.044 (1.035‐1.053); SLNB = 1.019 (1.01‐1.028) | 6 months: ALND = 1.058 (1.048‐1.069); SLNB = 1.022 (1.011‐1.032) 12 months: ALND = 1.061 (1.048‐1.074); SLNB = 1.028 (1.016‐1.039) | ||
| Sensory loss | Median area of sensory loss (cm2; range) | 1 month: ALND = 40 (1‐489); SLNB = 32 (2‐254) 3 months: ALND = 47 (0‐1139); SLNB = 48 (0‐327) | 6 months: ALND = 39 (0.4‐2827); SLNB = 32 (0‐201) 12 months: ALND = 35 (0.8‐1013); SLNB = 59 (0.2‐342) | Event rates for self‐assessed sensory loss also reported in Mansel 2006 for these follow‐up periods, but not extracted | |
| Intercostobrachial nerve damage | Clinician assessment; severe | 1 month: ALND: 10/392; SLNB: 6/409 3 months: ALND: 10/373; SLNB: 4/397 | 6 months: ALND: 10/394; SLNB: 4/410 12 months: ALND: 5/384 SLNB: 5/400 | ||
| Shoulder function | Mean change in shoulder function (degrees): flexion | 1 month: ALND = 9.8; SLNB = 5.8 3 months: ALND = 3.7; SLNB = 2 | 6 months: ALND = 1.6; SLNB = 2 12 months: ALND = 0.1; SLNB = 2.7 | 95% CI can also be extracted | |
| Shoulder function | Mean change in shoulder function (degrees): abduction | 1 month: ALND = 12.9; SLNB = 6.5 3 months: ALND = 4.2; SLNB = 1.9 | 6 months: ALND = 2.3; SLNB = 1.5 12 months: ALND = 1.9; SLNB = 2.5 | 95% CI can also be extracted | |
| Shoulder function | Mean change in shoulder function (degrees): external rotation | 1 month: ALND = 1.2; SLNB = 0.7 3 months: ALND = 1.2; SLNB = 0.2 | 6 months: ALND = 1; SLNB = 0.6 12 months: ALND = 0.7; SLNB = 0.6 | 95% CI can also be extracted | |
| Shoulder function | Mean change in shoulder function (degrees): internal rotation | 1 month: ALND = 0.9; SLNB = 0.4 3 months: ALND = 0.7; SLNB = 1 | 6 months: ALND = 0.8; SLNB = 0.2 12 months: ALND = 0.4; SLNB = 1.7 | 95% CI can also be extracted | |
| Quality of life | Measures: mean trial outcome index; trial outcome index reduced by ≥ 5 points from baseline (n/N); mean arm functioning subscale score; substantial arm swelling or tenderness (n/N); substantial numbness on ipsilateral side (n/N); mean FACT‐B+4 score | Means (95% CI) and event rates can be extracted for each time point (baseline, 1, 3, 6 and 12 months) | |||
| State and trait anxiety | Mean and 95% CI can be extracted for each time point (baseline, 1, 3, 6 and 12 months) | ||||
| Morbidity | Objective complaints: restricted elevation 720 degrees | Not stated: full axillary surgery, neg nodes = 25% (×2 = 7.47, P < 0.01); no axilary surgery, neg nodes = 0%; full axillary surgery + radical RT, positive nodes = 67%; no axillary surgery + local RT = 37% | Sample of 85 patients only from Cardiff site | ||
| Morbidity | Objective complaints: oedema of arm, 72 cm | Not stated: full axillary surgery, neg nodes = 46% (×2 = 6.02, P < 0.03); no axillary surgery, neg nodes = 15%; full axillary surgery + radical RT, positive nodes = 58%; no axillary surgery + local RT = 37% | Sample of 85 patients only from Cardiff site | ||
| Morbidity | Subjective complaints: limited arm movement | Not stated: full axillary surgery, neg nodes = 21%; no axillary surgery, neg nodes = 8%; full axillary surgery + radical RT, positive nodes = 8%; no axillary surgery + local RT = 21% | Sample of 85 patients only from Cardiff site | ||
| Morbidity | Subjective complaints: swollen arm | Not stated: full axillary surgery, neg nodes = 43%; no axillary surgery, neg nodes = 23%; full axillary surgery + radical RT, positive nodes = 58%; no axillary surgery + local RT = 37% | Sample of 85 patients only from Cardiff site | ||
| Morbidity | Lateral shoulder rotation (mean (SE) difference (cm) from preoperative value (N)) | 6 months: Sampling + RT: 1.91 (SE = 0.56) (N = 64), sampling ‐ RT: 0.34 (SE = 0.59) (N = 59); ALND: 0.13 (SE = 0.39) (N = 132) | 12 months: Sampling + RT: 1.75 (SE = 0.56) (N = 66), Sampling ‐ RT: 0.72 (SE = 0.62) (N = 55); ALND: 0.77 (0.4) (N = 128) | Figure 4, Chetty 2000 paper | |
| Morbidity | Lateral shoulder rotation (mean (SE) difference (cm) from preoperative value (N)) | 24 months: Sampling + RT: 1.57 (SE = 0.6) (N = 60), Sampling ‐ RT: ‐0.48 (SE = 0.65) (N = 52); ALND: 0.38 (SE = 0.43) (N = 117) | 36 months: Sampling + RT: 2.19 (SE = 0.59) (N = 59), Sampling ‐ RT: 0.43 (SE = 0.64) (N = 50); ALND: 0.24 (SE = 0.43) (N = 110) | Figure 4, Chetty 2000 paper | |
| Morbidity | Arm volume (mean (SE) percentage of preoperative arm volume (N)) | 6 months: Sampling + RT: 100.69 (SE = 0.779) (N = 56), Sampling ‐ RT: 102.04 (SE = 0.766) (N = 58); ALND: 103.57 (SE = 0.519) (N = 126) | 12 months: Sampling + RT: 100.95 (SE = 0.81) (N = 59), Sampling ‐ RT: 102.47 (SE = 0.85) (N = 54); ALND: 103.74 (SE = 0.57) (N = 119) | Figure 5, Chetty 2000 paper | |
| Morbidity | Arm volume (mean (SE) percentage of preoperative arm volume (N)) | 24 months: Sampling + RT: 100.84 (SE = 1.03) (N = 54), Sampling ‐ RT: 100.81 (SE = 1.06) (N = 51); ALND: 104.37 (SE = 0.73) (N = 108) | 36 months: Sampling + RT: 100.01 (SE = 1.03) (N = 52), Sampling ‐ RT: 101.28 (SE = 1.07) (N = 48); ALND: 104.07 (SE = 0.73) (N = 103) | Figure 5, Chetty 2000 paper | |
| Morbidity | Subjective arm | Not stated; full axillary surgery, positive node (Nil 8/12; intermittent 1/12; persistent 3/12); full axillary surgery, ‐negative node (nil 22/28; intermittent 1/28; persistent 5/28); Sample + RT, positive node (nil 17/28; intermittent 2/28; persistent 9/28); Sample, negative node (nil 23/26; intermittent 1/26; persistent 2/26) | Morbidity data to be included in discussion only; sample chosen from alphabetical pt list of patients free of local or systemic disease | ||
| Morbidity | Subjective mobility | Not stated; full axillary surgery, positive node (normal 12/12; reduced 0/12); full axillary surgery, negative node (normal 22/28; reduced 6/28); Sample + RT, negative node (normal 12/28; reduced 16/28); Sample, negative node (normal 24/26; reduced 2/26) | See comments in Aitken paper | ||
| Morbidity | Subjective interference with daily activities | Not stated; full axillary surgery, positive node (nil 12/12; occasional 0/12; severe 0/12); full axillary surgery, negative node (nil 24/28; occasional 4/28; severe 0/28); Sample + RT, positive node (nil 16/28; occasional 8/28; severe 4/28); Sample, negative node (nil 24/26; occasional 4/26; severe 0/26) | See comments in Aitken paper | ||
| Morbidity | Objective assessment ‐ shoulder joint mobility | See comments in Aitken paper | |||
| Psychological morbidity | Use in discussion only | ||||
| Lymphoedema | Assessed by physician, reported as odds ratio (95% CI): SLNB/ALND | 6 months: 0.37 (0.2 to 0.7) 12 months: 0.48 (0.2 to 0.9) | 18 months: 0.59 (0.3 to 1.2) 24 months: 0.52 (0.2 to 1.1) | ||
| Shoulder movement restriction | Assessed by physician, reported as odds ratio (95% CI): SLNB/ALND | 6 months: 0.47 (0.3 to 0.8) 12 months: 0.73 (0.4 to 1.4) 12 months: raw data extracted from graph (SLNB 17/336, ALND 23/341) | 18 months: 0.62 (0.3 to 1.3) 24 months: 0.44 (0.2 to 1.0) | ||
| Axillary/arm pain | Assessed by physician, reported as odds ratio (95% CI): SLNB/ALND | 6 months: 0.52 (0.3 to 0.8) 12 months: 0.76 (0.5 to 1.3) 12 months: raw data extracted from graph (SLNB 30/336, ALND 39/341) | 18 months: 0.84 (0.5 to 1.5) 24 months: 0.90 (0.5 to 1.6) | ||
| Numbness | Assessed by physician, reported as odds ratio (95% CI): SLNB/ALND | 6 months: 0.64 (0.4 to 0.9) 12 months: 0.53 (0.3 to 0.8) 12 months: raw data extracted from graph (SLNB 41/336, ALND 71/341) | 18 months: 0.37 (0.2 to 0.6) 24 months: 0.54 (0.3 to 0.9) | ||
| Winged scapula | Assessed by physician | Study authors report rate too low to analyse | |||
| Health‐related quality of life: SF‐36 – physical component | Assessed by patients using validated questionnaires | No significant differences found between group means of SF‐36 physical component (Del Bianco, 2008) | |||
| Health‐related quality of life: SF‐36 – mental component | Assessed by patients using validated questionnaires | No significant differences found between group means of SF‐36 mental component (Del Bianco, 2008) | |||
| Health‐related quality of life: SF‐36 HRQOL domains | Assessed by patients using validated questionnaires | No significant differences found between groups on all HRQOL domains of SF‐36 (Zavagno, 2008) | |||
| Health‐related quality of life: psychological general well‐being index | Assessed by patients using validated questionnaires | 6, 12 months: significantly better PGWB general and anxiety domain scores in SLNB group than in ALND group (Del Bianco, 2008) | 24 months: no significant differences between PGWB general and anxiety domain scores of both groups.(Del Bianco, 2008) | ||
| Morbidity | Arm function | 3 months: ALND: Good: 44/90, Fair: 41/90, Poor: 5/90; No ALND: Good: 59/77, Fair: 18/77, Poor: 0/77 | 15 months: ALND: Good: 83/100, Fair: 14/100, Poor: 3/100; No ALND: Good: 70/88, Fair: 17/88, Poor: 1/88 | Sample only | |
| Morbidity | Lymphoedema | 3 months: ALND: None: 18/93, Slight: 66/93, Moderate: 6/93, Severe: 3/93; No ALND: None: 36/81, Slight: 43/81, Moderate: 0/81, Severe: 2/81 | 15 months: ALND: None: 27/104, Slight: 71/104 Moderate: 6/104, Severe: 0/104; No ALND: None: 39/91, Slight: 52/91, Moderate: 0/91, Severe: 0/91 | Sample only | |
| Morbidity | Activity | 3 months: ALND: Good: 45/92, Fair: 46/92, Poor: 1/92; No ALND: Good: 62/80, Fair: 16/80, Poor: 2/80 | 15 months: ALND: Good: 85/101, Fair: 14/101, Poor: 2/101; No ALND: Good: 78/92, Fair: 13/92, Poor: 1/92 | Sample only | |
| Morbidity | Attitude | 3 months: ALND: Good: 81/92, Fair: 9/92, Poor: 2/92; No ALND: Good: 71/80, Fair: 7/80, Poor: 2/80 | 15 months: ALND: Good: 91/101, Fair: 8/101, Poor: 2/101; No ALND: Good: 87/92, Fair: 5/92, Poor: 0/92 | Sample only | |
| Postoperative deaths | Radical: 0/95; Simple: 0/100 | ||||
| Morbidity | Shoulder function | At 4‐year minimum follow‐up in survivors: Radical: 6/95; Simple = 18/100 | Consequential morbidity, at time of publication Methodology not reported, all patients included | ||
| Morbidity | Arm swelling (including volumetric measurement of upper limb) | At 4‐year minimum follow‐up in survivors: Radical: 7/95; Simple = 3/100 | Consequential morbidity, at time of publication Methodology not reported, all patients included | ||
| Lymphoedema | Physician reported | Not significantly different between treatments | |||
| Arm circumference | Physician reported | Not significantly different between treatments | |||
| Performance of daily activities | Physician reported | Not significantly different between treatments | |||
| Arm pain | Physician reported | Baseline: ALND 5/175, surgery 8/194; 1st postoperative: ALND 38/164, surgery 12/168; 3 months: ALND 16/161, surgery 9/171; 6 months: ALND 17/174, surgery 11/177 | 9 months: ALND 21/160, surgery 8/164; 12 months: ALND 13/189, surgery 8/190; 18 months: ALND 14/173, surgery 7/183; 24 months: ALND 12/165, surgery 8/164 | ||
| Restricted arm movement | Physician reported | Baseline: ALND 9/174, surgery 6/194; 1st postoperative: ALND 64/163, surgery 25/168; 3 months: ALND 23/161, surgery 10/170; 6 months: ALND 21/176, surgery 9/176 | 9 months: ALND 21/160, surgery 7/163; 12 months: ALND 19/188, surgery 6/187; 18 months: ALND 10/171, surgery 7/182; 24 months: ALND 12/165, surgery 7/164 | ||
| QOL ‐ bothered scores | Patient reported | No significant differences at any time point (baseline, 1st postoperative, 3, 6, 9, 12, 18 and 24 months) | |||
| QOL ‐ arm movement scores | Patient reported | At 1st postoperative surgery alone, reported less restriction in use of their arm than ALND (P < .0001). Otherwise, no significant differences | |||
| QOL ‐ numbness scores | Patient reported | At 1st postoperative surgery alone, reported less severe postsurgery numbness than ALND (P < .0001). Otherwise, no significant differences | |||
| QOL ‐ coping scores | Patient reported | No significant differences at any time point (baseline, 1st postoperative, 3, 6, 9, 12, 18 and 24 months) | |||
| Postoperative infection | Physician assessed | Surgery alone: 0/467 ALND: 1/464 | |||
| Sensory neuropathy | Physician assessed | Any: Surgery alone: 55/453 ALND: 82/447 Grade 3‐4: Surgery alone: 0/453 ALND: 1/447 | |||
| Lymphoedema | Physician assessed | Defined as long term: Any: Surgery alone: 15/453 ALND: 59/447 Grade 3‐4: Surgery alone: 0/453 ALND: 3/447 | |||
| Motor neuropathy | Physician assessed | Any: Surgery alone: 13/453 ALND: 37/447 Grade 3‐4: Surgery alone: 1/453 ALND: 3/447 | |||
| Arm fatigue | Unclear | Moderate/severe: no ALND: N = 4/258; ALND: N = 24/273 | |||
| Shoulder mobility | Unclear | Restricted somewhat or severely: no ALND: N = 5/257; ALND: N = 21/271 | |||
| Parasthesia | Unclear | Moderate/severe: no ALND: N = 6/258; ALND: N = 41/274 | |||
| Lymphoedema | Unclear | Minor/major difference: no ALND: N = 3/258; ALND: N = 29/275 | |||
| Other functional impairments | Unclear | Minor/major: no ALND: N = 12/263; ALND: N = 16/276 | |||
| Number of patients with functional impairments | Unclear | Minor: no ALND: N = 23/265; ALND: N = 78/278 | |||
| Upper limb circumference > 2 cm | Measured as per definition | 6 months: Obs: 6/57; ALND: 10/49 12 months: Obs: 8/57; ALND: 15/49 | 24 months: Obs: 8/57; ALND: 14/49 48 months: Obs: 4/57; ALND: 19/49 | ||
| Pain at rest | Patient reported | 6 months: Obs: 9/57; ALND: 9/49 12 months: Obs: 11/57; ALND: 14/49 | 24 months: Obs: 9/57; ALND: 10/49 48 months: Obs: 3/57; ALND: 7/49 | ||
| Parasthesias | Patient reported? | 6 months: Obs: 10/57; ALND: 28/49 12 months: Obs: 6/57; ALND: 29/49 | 24 months: Obs: 5/57; ALND: 34/49 48 months: Obs: 6/57; ALND: 30/49 | ||
| Shoulder dysfunction | Measured as per definition | 6 months: Obs: 5/57; ALND: 5/49 12 months: Obs: 4/57; ALND: 8/49 | 24 months: Obs: 0/57; ALND: 6/49 48 months: Obs: 2/57; ALND: 11/49 | ||
| Morbidity | Axillary pain (sporadic/continuous) | 6 months: ALND: 91/100; SNLB = 16/100 | 24 months: ALND: 39/100; SNLB = 8/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Numbness/Parasthesia on operated side | 6 months: ALND: 85/100; SNLB = 2/100 | 24 months: ALND: 68/100; SNLB = 1/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm mobility, 80%‐100% | 6 months: ALND: 73/100; SNLB = 100/100 | 24 months: ALND: 79/100; SNLB = 100/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm mobility, 60%‐79% | 6 months: ALND: 22/100; SNLB = 0/100 | 24 months: ALND: 18/100; SNLB = 0/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm mobility, 40%‐59% | 6 months: ALND: 5/100; SNLB = 0/100 | 24 months: ALND: 2/100; SNLB = 0/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm mobility, 20%‐39% | 6 months: ALND: 0/100; SNLB = 0/100 | 24 months: ALND: 1/100; SNLB = 0/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm mobility, < 20% | 6 months: ALND: 0/100; SNLB = 0/100 | 24 months: ALND: 0/100; SNLB = 0/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Aesthetic appearance of axillary scar: bad | 6 months: ALND: 9/100; SNLB = 2/100 | 24 months: ALND: 15/100; SNLB = 0/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm swelling < 1 cm difference in circumference | 6 months: ALND: 44/100; SNLB = 11/100 | 24 months: ALND: 38/100; SNLB = 6/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm swelling 1‐2 cm difference in circumference | 6 months: ALND: 17/100; SNLB = 0/100 | 24 months: ALND: 25/100; SNLB = 1/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm swelling >2 cm difference in circumference | 6 months: ALND: 8/100; SNLB = 0/100 | 24 months: ALND: 12/100; SNLB = 0/100 | ||
| Morbidity | Arm swelling, any | 6 months: ALND: 69/100; SNLB = 11/100 | 24 months: ALND: 75/100; SNLB = 7/100 | ||
| Arm oedema | Arm swelling ≥ 2 cm difference in circumference | No. of patients with data: ALND: N = 577; no ALND + RT: N = 568 no ALND: N = 312 both node + and node‐ patients. Final measurement was 2 to 5 years after surgery Arm oedema recorded at least once: ALND: 58.1%; no ALND + RT: 38.2%; no ALND: 39.1% (P < 0.001) Oedema always: ALND: 3.6%; no ALND + RT: 0.9%; no ALND: 1% No measurement after first oedema: ALND: 9.2%; no ALND + RT: 5.8%; no ALND: 3.2% Oedema always after first oedema: ALND: 6.1%; no ALND + RT: 3.2%; no ALND: 2.6% Intermittent, final measurement oedema: ALND: 11.8%; no ALND + RT: 4.9%; no ALND: 8.6%; Total with oedema on final measurement: ALND: 30.7%; no ALND + RT: 14.8%; no ALND: 15.4% (P < 0.001) | Oedema once, then resolution: ALND: 15.9%; no ALND + RT: 15.3%; no ALND: 16.7% Intermittent, final measurement no oedema: ALND: 11.4%; no ALND + RT: 8.1%; no ALND: 7.1% Total with no oedema on final measurement (after at least 1 measurement of oedema): ALND: 27.3%; no ALND + RT: 23.4%; no ALND: 23.8 Arm oedema ≥ 4 cm difference in circumference recorded at least once: ALND: 21.5%; no ALND + RT: 11.4%; no ALND: 13.1% | ||
| Adverse events (grade 3 or greater surgery related) | No details reported | ALND: 14/2788 SLN: 12/2800 Must include most of SLN positive and negative patients | Peri‐surgery | ||
| Arm mobility/shoulder abduction deficit (objective) | Physician assessed | 6 months: < 5%: ALND: 1299/1667; SLN: 1468/1744 5%‐10%: ALND: 218/1667; SLN: 176/1744 ≥ 10%: ALND: 150/1667; SLN: 99/1744 | |||
| Arm volume difference (objective) | Physician assessed | 6 months: < 5%: ALND: 1187/1677; SLN: 1363/1759 5%‐10%: ALND: 277/1677; SLN: 236/1759 ≥ 10%: ALND: 211/1677; SLN: 158/1759 | 12 months: < 5%: ALND: 1170/1639; SLN: 1345/1705 5%‐10%: ALND: 252/1639; SLN: 215/1705 ≥ 10%: ALND: 216/1639; SLN: 147/1705 | These data are also available for 18 and 30 months | |
| Arm volume difference (objective) | Physician assessed | 24 months: < 5%: ALND: 1062/1517; SLN: 1184/1504 5%‐10%: ALND: 243/1517; SLN: 197/1504 ≥ 10%: ALND: 212/1517; SLN: 123/1504 | 36 months: < 5%: ALND: 990/1421; SLN: 1156/1459 5%‐10%: ALND: 227/1421; SLN: 194/1459 ≥ 10%: ALND: 203/1421; SLN: 109/1459 | These data are also available for 18 and 30 months | |
| Tingling (subjective) | Self‐reported | 6 months: ALND (N = 388/1693), SLN (N = 184/1766) 12 months: ALND (N = 305/1640), SLN (N = 158/1713) 18 months: ALND (N = 272/1566), SLN (N = 138/1638) | 24 months: ALND (N = 236/1521), SLN (N = 137/1588) 30 months: ALND (N = 219/1448), SLN (N = 116/1502) 36 months: ALND (N = 193/1431), SLN (N = 110/1463) | ||
| Numbness (subjective) | Self‐reported | 6 months: ALND (N = 821/1693), SLN (N = 257/1769) 12 months: ALND (N = 679/1641), SLN (N = 216/1713) 18 months: ALND (N = 592/1567), SLN (N = 174/1638) | 24 months: ALND (N = 554/1523), SLN (N = 157/1587) 30 months: ALND (N = 473/1450), SLN (N = 137/1504) 36 months: ALND (N = 445/1430), SLN (N = 119/1463) | ||
| Shoulder abduction deficit ≥ 5% (in those with < 5% at baseline) | Physician assessed | 6 months: ALND (N = 275/1449), SLN (N = 201/1519) | |||
| Shoulder abduction deficit ≥ 5% (in those with < 5% at baseline) | Physician assessed | 36 months: ALND (N = 314/1136), SLN (N = 192/1151) | |||
| Numbness (in those with none at baseline) | Self‐reported | 36 months: ALND (N = 407/1336), SLN (N = 103/1371) | |||
| Tingling (in those with none at baseline) | Self‐reported | 36 months: ALND (N = 175/1329), SLN (N = 90/1343) | |||
| Seroma | Patients with percutaneous aspiration in outpatient department | ALND: 17/50; sampling: 10/50 | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for N = 100/200 | ||
| Postoperative discharge (mL), median (range) | ALND: 250 (25‐1610); sampling: 130 (0‐1785) | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for N = 100/200 | |||
| Duration of postop drainage (days) (median, range) | ALND: 4 (1‐11); sampling: 2.1 (1 ‐11) | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for N = 100/200 | |||
| Arm volume increase | ≥ 10% | ALND: 14/47; sampling: 0/48 | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for ca N = 100/200 | ||
| Subjective sensation of swelling in women without objective increase in arm volume | Any | ALND: 12/33; sampling: 9/48 | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for ca N = 100/200 | ||
| Shoulder mobility (mean decrease compared with baseline) | 7.5° decrease for whole sample of 95 patients | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for ca N = 100/200 | |||
| Axillary paraesthesia (impairment of sensibility in the axilla) | ALND: 17/48; sampling: 19/48 | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for ca N = 100/200 | |||
| Inner upper arm paraesthesia (impairment of sensibility in the inner upper arm) | ALND: 24/48; sampling: 4/48 | Adverse events reported only for the 1987‐89 sample; i.e. for ca N = 100/200 | |||
| Delayed healing | ALND: 27/100; Simple + RT: 8/100 | ||||
| Haematoma | ALND: 24/100; Simple + RT: 6/100 | ||||
| Infection | ALND: 9/100; Simple + RT: 6/100 | ||||
| DVT | ALND: 4/100; Simple + RT: 1/100 | ||||
| Pulmonary embolism | ALND: 1/100; Simple + RT: 1/100 | ||||
| Chest infection | ALND: 6/100; Simple + RT: 3/100 | ||||
| Severe skin reaction | ALND: 0/100; Simple + RT: 5/100 | ||||
| Nausea and vomiting | ALND: 0/100; Simple + RT: 2/100 | ||||
| Tracheitis | ALND: 0/100; Simple + RT: 2/100 | ||||
| Skin grafts | ALND: 10/100; Simple + RT: 0/100 | ||||
| Arm oedema | ALND: 10/100; Simple + RT: 5/100 | ||||
| Limitation of shoulder movement | ALND: 4/100; Simple + RT: 14/100 | ||||
| Haematoma | Any | ALND: 30/539; SLNB: 38/544 | |||
| Seroma | Any | ALND: 195/539; SLNB: 93/544 | |||
| Infection | Any | ALND: 73/539; SLNB: 48/544 | |||
| Arm morbidity | Mean changes in arm morbidity (patient reported, overall summary average score of 15 items; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported) from baseline | Node+ and node‐ patients: average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months: ALND: 7 (N = 457); SLNB: 4.4 (N = 456) 1 month: ALND: 2.2 (0.2); SLNB: 1.4 (0.15) 6 months: ALND: 1.1 (0.2); SLNB: 0.8 (0.15) 12 months: ALND: 1.05 (0.2); SLNB: 0.8 (0.15) | 24 months: ALND: 1.05 (0.2); SLNB: 0.75 (0.15) 36 months: ALND: 1.05 (0.2); SLNB: 0.7 (0.15) | ||
| Arm symptoms | Mean changes in arm symptoms (patient reported, average of 7 items; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported) from baseline | Node+ and node‐ patients: average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months: ALND: 9.7 (N = 457); SLNB: 5.5 (N = 456) 1 month: ALND: 2.1 (0.2); SLNB: 1.2 (0.1) 6 months: ALND: 1.3 (0.15); SLNB: 0.8 (0.1) 12 months: ALND: 1.25 (0.15); SLNB: 0.7 (0.1) | 24 months: ALND: 1.25 (0.15); SLNB: 0.7 (0.1) 36 months: ALND: 1.2 (0.2); SLNB: 0.65 (0.15) | ||
| Arm swelling | Mean changes in arm swelling (patient reported, 1 item; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported) from baseline | Node+ and node‐ patients: average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months: ALND: 7.3 (N = 457); SLNB: 3.4 (N = 456) 1 month: ALND: 1.25 (0.2); SLNB: 0.75 (0.15) 6 months: ALND: 0.9 (0.15); SLNB: 0.55 (0.1) 12 months: ALND: 0.95 (0.15); SLNB: 0.45 (0.1) | 24 months: ALND: 1 (0.2); SLNB: 0.55 (0.15) 36 months: ALND: 1 (0.2); SLNB: 0.55 (0.15) | ||
| Arm dysfunctions | Mean arm dysfunctions change (patient reported, average of 3 items; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported) from baseline | Node+ and node‐ patients: average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months: ALND: 5.5 (N = 457); SLNB: 3.6 (N = 456) 1 month: ALND: 1.9 (0.15); SLNB: 1.35 (0.15) 6 months: ALND: 0.8 (0.1); SLNB: 0.65 (0.1) 12 months: ALND: 0.75 (0.1); SLNB: 0.6 (0.1) | 24 months: ALND: 0.7 (0.1); SLNB: 0.55 (0.1) 36 months: ALND: 0.8 (0.1); SLNB: 0.5 (0.1) | ||
| Arm disabilities | Mean arm disabilities (patient‐reported change, average of 4 items; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported) from baseline | Node+ and node‐ patients: average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months: ALND: 3.4 (N = 457); SLNB: 2.9 (N = 456) 1 month: ALND: 2.2 (0.2); SLNB: 1.4 (0.15) 6 months: ALND: 0.75 (0.1); SLNB: 0.55 (0.1) 12 months: ALND: 0.65 (0.1); SLNB: 0.45 (0.1) | 24 months: ALND: 0.6 (0.1); SLNB: 0.5 (0.1) 36 months: ALND: 0.7 (0.1); SLNB: 0.45 (0.1) | ||
| Arm volume | Increase in arm volume (percentage change from clinician ratings from baseline; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported) | Average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months: ALND: 4.2% (N = 509); SLNB: 2.8% (N = 519) All patients: 1 month: ALND: 0.8% (0.4); SLNB: 0.9% (0.4), P = 0.67 6 months: ALND: 3.5% (0.8); SLNB: 2.4% (0.7), P = 0.02 12 months: ALND: 4.6% (0.8); SLNB: 3% (0.8), P = 0.001 Node‐negative patients: 1 month: ALND: 0.8% (0.4); SLNB: 0.3% (0.4), P = 0.16 6 months: ALND: 3.5% (0.8); SLNB: 1.9% (0.5), P = 0.004 12 months: ALND: 4.6% (0.8); SLNB: 2.2% (0.7), P = 0.001 | All patients: 24 months: ALND: 5.8% (1); SLNB: 3.9% (0.7), P = 0.006 36 months: ALND: 5.8% (1); SLNB: 4.0% (1), P = 0.02 Node‐negative patients: 24 months: ALND: 5.8% (1); SLNB: 3% (0.7), P = 0.001 36 months: ALND: 5.8% (1); SLNB: 3.1% (1), P= 0.004 | ||
| Arm volume | Number with an increase in arm volume ≥ 15% (percentage change from clinician ratings from baseline) | All patients: 1 month: ALND: 5/544; SLNB: 3/544 6 months: ALND: 29/544; SLNB:21/544 12 months: ALND: 47/544; SLNB: 29/544 (P = 0.02) Node‐negative patients only: 1 month: ALND: 4/363; SLNB: 1/356 6 months: ALND: 16/363; SLNB: 9/356 12 months: ALND: 28/363; SLNB: 13/356 (P = 0.02) | All patients: 24 months: ALND: 81/544; SLNB: /544 (P = 0.001) 36 months: ALND: 82/544; SLNB: /544 (P = 0.01) Node‐negative patients only: 24 months: ALND: 47/363; SLNB: 25/356 (P = 0.01) 36 months: ALND: 49/363; SLNB: 25/356 (P = 0.006) | ||
| Lateral abduction | Lateral abduction (change from clinician ratings from baseline; degrees; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported ‐ have assumed it is SEM for calculations) | Average of measures taken at 6 and 12 months (percentage change from baseline: ALND: 4.4% (N = 509); SLNB: 2.5% (N = 519) Node+ and node‐ patients (read off graph): Baseline: ALND: 158 (1); SLNB: 157 (1) 1 month: ALND: 131 (2); SLNB: 144 (2) 6 months: ALND: 150 (1); SLNB: 151 (1) 12 months: ALND: 150 (1); SLNB: 151 (1) | Node+ and node‐ patients (read off graph): 24 months: ALND: 151 (1); SLNB: 152 (1) 36 months: ALND: 150 (1); SLNB: 151 (1) | ||
| Forward flexion | Forward flexion (degrees; unclear if it is SEM or SD reported ‐ have assumed it is SEM for calculations) | Node+ and node‐ patients (read off graph): Baseline: ALND: 157 (1); SLNB: 158 (1) 1 month: ALND: 137 (2); SLNB: 148 (1.5) 6 months: ALND: 150 (1); SLNB: 152 (1) 12 months: ALND: 151 (1); SLNB: 151 (1) | Node+ and node‐ patients (read off graph): 24 months: ALND: 152 (1); SLNB: 152 (1) 36 months: ALND: 152 (1); SLNB: 151 (1) | ||
| Postoperative swelling (oedema) | Measurement of arm diameter | Level I clearance: 3/93 ALND: 7/88 | |||
| Involved upper limb disorder | Unclear | Level I clearance: 0/93 ALND: 0/88 | |||
| Cerebrovascular accident | Unclear | Level I clearance: 0/93 ALND: 2/88 | |||
| Cardiovascular events | Unclear | Level I clearance: 2/93 ALND: 1/88 |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 All‐cause mortality (radiotherapy subgroups) Show forest plot | 10 | 3849 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.06 [0.96, 1.17] |
| 1.1 no radiotherapy | 1 | 773 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.96 [0.80, 1.15] |
| 1.2 radiotherapy | 9 | 3076 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.11 [0.98, 1.25] |
| 2 All‐cause mortality (extra treatment for positive node subgroups) Show forest plot | 10 | 3849 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.06 [0.96, 1.17] |
| 2.1 additional treatment for node‐positive patients | 3 | 1174 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.51 [1.09, 2.09] |
| 2.2 no specific additional treatment for node‐positive patients | 7 | 2675 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.02 [0.92, 1.13] |
| 3 Locoregional recurrence (radiotherapy subgroups) Show forest plot | 4 | 20863 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 2.35 [1.91, 2.89] |
| 3.1 no radiotherapy | 1 | 7284 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 2.94 [2.05, 4.23] |
| 3.2 radiotherapy | 3 | 13579 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 2.11 [1.64, 2.72] |
| 4 Locoregional recurrence (extra treatment for positive‐node subgroups) Show forest plot | 4 | 20863 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 2.35 [1.91, 2.89] |
| 4.1 additional treatment for node‐positive patients | 1 | 4171 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.10 [0.69, 1.75] |
| 4.2 no specific additional treatment for node‐positive patients | 3 | 16692 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 2.83 [2.25, 3.57] |
| 5 Distant metastasis Show forest plot | 2 | 946 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.06 [0.87, 1.30] |
| 5.1 no radiotherapy | 1 | 727 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.10 [0.89, 1.35] |
| 5.2 radiotherapy | 1 | 219 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.64 [0.28, 1.42] |
| 6 Lymphoedema (≥ 12 months postop) ‐ fixed‐effect model Show forest plot | 4 | 1714 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.31 [0.23, 0.43] |
| 6.1 additional treatment for node‐positive patients | 1 | 532 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.02, 0.22] |
| 6.2 no additional treatment for node‐positive patients | 3 | 1182 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.39 [0.28, 0.54] |
| 7 Lymphoedema (≥ 12 months postop) ‐ random‐effects model Show forest plot | 4 | 1714 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.22 [0.08, 0.57] |
| 7.1 additional treatment for node‐positive patients | 1 | 532 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.02, 0.22] |
| 7.2 no additional treatment for node‐positive patients | 3 | 1182 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.40 [0.28, 0.55] |
| 8 Arm or shoulder movement impairment (≥ 12 months postop) Show forest plot | 5 | 1495 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.72 [0.49, 1.05] |
| 8.1 radiotherapy | 5 | 1495 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.72 [0.49, 1.05] |
| 9 Pain (≥ 12 months postop) Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 10 Paraesthesia (≥ 12 months postop) Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 10.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 11 Delayed healing Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 11.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 12 Skin graft Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 12.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 13 All‐cause mortality (allocation concealment subgroups) Show forest plot | 10 | 3849 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.06 [0.96, 1.17] |
| 13.1 adequate allocation concealment | 4 | 1442 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.98 [0.81, 1.18] |
| 13.2 unclear or inadequate allocation concealment | 6 | 2407 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.09 [0.97, 1.23] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 All‐cause mortality Show forest plot | 3 | 967 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.94 [0.73, 1.21] |
| 1.1 radiotherapy | 2 | 872 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.84 [0.64, 1.11] |
| 1.2 no radiotherapy | 1 | 95 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.47 [0.84, 2.56] |
| 2 Local recurrence Show forest plot | 3 | 1404 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.41 [0.94, 2.12] |
| 2.1 radiotherapy | 2 | 659 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.40 [0.89, 2.19] |
| 2.2 no radiotherapy | 1 | 745 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.48 [0.58, 3.82] |
| 3 Axillary recurrence Show forest plot | 1 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4 Locoregional recurrence Show forest plot | 1 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.2 no radiotherapy | 0 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5 Distant metastasis Show forest plot | 1 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5.2 no radiotherapy | 0 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 6 Lymphoedema. Increase in arm circumference (≥ 12 months postop) Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 6.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 7 Shoulder lateral rotation (12 months postop) Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 8 Seroma Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 8.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 All‐cause mortality Show forest plot | 3 | 6352 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.05 [0.89, 1.25] |
| 1.1 radiotherapy | 2 | 6127 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.05 [0.88, 1.25] |
| 1.2 no radiotherapy | 1 | 225 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.30 [0.35, 4.84] |
| 2 Local recurrence Show forest plot | 1 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 no radiotherapy | 0 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Axillary recurrence Show forest plot | 1 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Locoregional recurrence Show forest plot | 1 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.2 no radiotherapy | 0 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5 Distant metastasis Show forest plot | 1 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5.2 no radiotherapy | 0 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 6 Lymphoedema. Increase in arm circumference (≥ 12 months postop) Show forest plot | 3 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 6.1 radiotherapy | 3 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 7 Lymphoedema. Patient reported (at 12 or more months postop) Show forest plot | 3 | Odds Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.23, 0.47] | |
| 7.1 adequate allocation concealment | 2 | Odds Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.22, 0.48] | |
| 7.2 unclear allocation concealment | 1 | Odds Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.36 [0.15, 0.86] | |
| 8 Shoulder flexion (12 months postop) Show forest plot | 3 | 2257 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.55 [‐0.19, 3.29] |
| 8.1 radiotherapy | 3 | 2257 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.55 [‐0.19, 3.29] |
| 9 Shoulder abduction (12 months postop) Show forest plot | 3 | 2252 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.02 [‐2.79, 0.75] |
| 9.1 radiotherapy | 3 | 2252 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.02 [‐2.79, 0.75] |
| 10 Shoulder internal rotation (12 months postop) Show forest plot | 2 | 1227 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.50 [‐1.10, 2.09] |
| 10.1 radiotherapy | 2 | 1227 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.50 [‐1.10, 2.09] |
| 11 Shoulder external rotation (12 months postop) Show forest plot | 2 | 1227 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.56 [‐2.21, 1.09] |
| 11.1 radiotherapy | 2 | 1227 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.56 [‐2.21, 1.09] |
| 12 Subjective arm movement impairment (≥ 12 months postop) Show forest plot | 2 | 877 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.38 [0.22, 0.67] |
| 12.1 radiotherapy | 2 | 877 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.38 [0.22, 0.67] |
| 13 Pain (≥ 12 months postop) Show forest plot | 2 | 877 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.44 [0.30, 0.67] |
| 13.1 radiotherapy | 2 | 877 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.44 [0.30, 0.67] |
| 14 Paraesthesia (≥ 12 months postop) Show forest plot | 2 | 495 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.15 [0.09, 0.23] |
| 14.1 radiotherapy | 2 | 495 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.15 [0.09, 0.23] |
| 15 Numbness (≥ 12 months postop) Show forest plot | 3 | 1799 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.43 [0.34, 0.54] |
| 15.1 radiotherapy | 3 | 1799 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.43 [0.34, 0.54] |
| 16 Seroma Show forest plot | 2 | 1381 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.40 [0.31, 0.51] |
| 16.1 radiotherapy | 2 | 1381 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.40 [0.31, 0.51] |
| 17 Wound infection Show forest plot | 2 | 2074 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.65 [0.50, 0.85] |
| 17.1 radiotherapy | 2 | 2074 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.65 [0.50, 0.85] |
| 18 Brachial plexus injury at 6 months postop Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 18.1 radiotherapy | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 All‐cause mortality Show forest plot | 4 | 2469 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.10 [1.00, 1.21] |
| 2 Local recurrence Show forest plot | 4 | 22256 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.80 [0.64, 0.99] |
| 3 Distant metastasis Show forest plot | 1 | 1313 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.07 [0.93, 1.25] |
| 4 Lymphoedema. Increase in arm circumference (≥ 12 months postop) Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5 Delayed healing Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 6 Wound infection Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7 Skin graft Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 8 Haematoma Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 All‐cause mortality Show forest plot | 19 | 12864 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.08 [1.01, 1.16] |
| 1.1 no axillary surgery vs ALND | 9 | 3076 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.11 [0.98, 1.25] |
| 1.2 axillary sampling vs ALND | 3 | 967 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.94 [0.73, 1.21] |
| 1.3 SLNB vs ALND | 3 | 6352 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.05 [0.89, 1.25] |
| 1.4 radiotherapy vs ALND | 4 | 2469 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.10 [1.00, 1.21] |
| 2 All‐cause mortality (radiotherapy subgroups) Show forest plot | 19 | 13637 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.07 [1.00, 1.14] |
| 2.1 radiotherapy (same in both groups) | 13 | 10075 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.06 [0.96, 1.16] |
| 2.2 radiotherapy (in less surgery group only) | 4 | 2469 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.10 [1.00, 1.21] |
| 2.3 no radiotherapy | 3 | 1093 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.00 [0.85, 1.19] |
| 3 All‐cause mortality (additional treatment for histologically positive nodes) Show forest plot | 5 | 1708 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.90 [0.72, 1.14] |
| 3.1 additional treatment for histologically positive nodes | 4 | 1613 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.82 [0.64, 1.05] |
| 3.2 no additional treatment for histologically positive nodes | 1 | 95 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.47 [0.84, 2.56] |
| 4 Local recurrence Show forest plot | 8 | 24176 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.90 [0.75, 1.09] |
| 4.1 axillary sampling vs ALND | 3 | 1404 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.41 [0.94, 2.12] |
| 4.2 SLNB vs ALND | 1 | 516 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.94 [0.24, 3.77] |
| 4.3 radiotherapy vs ALND | 4 | 22256 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.80 [0.64, 0.99] |
| 5 Locoregional recurrence Show forest plot | 6 | 26880 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.53 [1.31, 1.78] |
| 5.1 no axillary surgery vs ALND | 4 | 20863 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 2.35 [1.91, 2.89] |
| 5.2 axillary sampling vs ALND | 1 | 406 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.74 [0.46, 1.20] |
| 5.3 SLNB vs ALND | 1 | 5611 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.96 [0.74, 1.24] |
| 6 Distant metastasis Show forest plot | 3 | 2665 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.07 [0.95, 1.20] |
| 6.1 no axillary surgery vs ALND | 2 | 946 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.06 [0.87, 1.30] |
| 6.2 axillary sampling vs ALND | 1 | 406 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.05 [0.74, 1.49] |
| 6.3 radiotherapy vs ALND | 1 | 1313 | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 1.07 [0.93, 1.25] |
| 7 Lymphoedema. Increase in arm volume at 12 months postop Show forest plot | 9 | 3964 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.37 [0.29, 0.46] |
| 7.1 no axillary surgery vs ALND | 4 | 1714 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.31 [0.23, 0.43] |
| 7.2 axillary sampling vs ALND | 1 | 85 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.32 [0.13, 0.81] |
| 7.3 SLNB vs ALND | 3 | 1965 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.48 [0.33, 0.69] |
| 7.4 radiotherapy vs ALND | 1 | 200 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.47 [0.16, 1.44] |
| 8 Paraesthesia (≥ 12 months postop) Show forest plot | 3 | 1027 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.10, 0.21] |
| 8.1 no axillary surgery vs ALND | 1 | 532 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.06, 0.32] |
| 8.2 SLNB vs ALND | 2 | 495 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.15 [0.09, 0.23] |
| 9 Pain (≥ 12 months postop) Show forest plot | 3 | 1256 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.47 [0.32, 0.68] |
| 9.1 no axillary surgery vs ALND | 1 | 379 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.60 [0.24, 1.47] |
| 9.2 SLNB vs ALND | 2 | 877 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.44 [0.30, 0.67] |
| 10 Delayed healing Show forest plot | 2 | 404 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.25 [0.13, 0.46] |
| 10.1 no axillary surgery vs ALND | 1 | 204 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.27 [0.11, 0.67] |
| 10.2 radiotherapy vs ALND | 1 | 200 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.24 [0.10, 0.55] |
| 11 Seroma Show forest plot | 3 | 1481 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.40 [0.32, 0.52] |
| 11.1 SLNB vs ALND | 2 | 1381 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.40 [0.31, 0.51] |
| 11.2 axillary sampling vs ALND | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.49 [0.20, 1.20] |
| 12 Wound infection Show forest plot | 3 | 2274 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.65 [0.50, 0.84] |
| 12.1 SLNB vs ALND | 2 | 2074 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.65 [0.50, 0.85] |
| 12.2 radiotherapy vs ALND | 1 | 200 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.65 [0.22, 1.89] |
| 13 Skin graft Show forest plot | 2 | 404 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.15 [0.04, 0.57] |
| 13.1 no axillary surgery vs ALND | 1 | 204 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.39 [0.07, 2.19] |
| 13.2 radiotherapy vs ALND | 1 | 200 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.04 [0.00, 0.74] |
| 14 Haematoma Show forest plot | 2 | 1283 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.80 [0.53, 1.20] |
| 14.1 SLNB vs ALND | 1 | 1083 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.27 [0.78, 2.09] |
| 14.2 radiotherapy vs ALND | 1 | 200 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.20 [0.08, 0.52] |


