Quimioterapia para el cáncer gástrico avanzado
References
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
References to ongoing studies
Additional references
References to other published versions of this review
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Methods | Multicentre RCT 2 arms Quality score: D | |
| Participants | n = 158 (68% with tumour location in the stomach; and 32 % with tumour location at the GE‐junction) Median age: 57 years ECOG 2‐3: 0% (Karnofsky performance status KPS was ≥70% for all patients) Metastatic disease: 95% | |
| Interventions | DCF: docetaxel (75 mg/m2d1) + cisplatin (75 mg/m2 d1) + FU (750 mg/m2/d d1‐5), repeated at d 21 versus DC: docetaxel (85 mg/m2) + cisplatin (75 mg/m2) d 1, repeated at d 21 | |
| Outcomes | Response rates Time to progression Overall survival Toxicities | |
| Notes | This is the phase II to chose the investigational arm in Van Cutsem 2006. A similar proportion of patients received second‐line chemotherapy (DCF 39%; DC 45%). | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomisation was centralised (Aventis, Antony, France) and was stratified for centre, liver and/or peritoneal metastases, prior gastrectomy, and measurable versus assessable disease. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomisation was centralised (Aventis, Antony, France) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Modified ITT (randomised and treated patients) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Modified ITT |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | All treated patients were included in the safety analyses. The primary efficacy end point was initially the CR rate in the per‐protocol population. However, because CRs were infrequent in this study, the IDMC based its decision regarding treatment selection on the best ORR. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Number of diffuse adenocarcinoma is lower in the DC arm (22% vs. 38%). The protocol required that the IDMC review data on at least 70 patients (minimum of 60 assessable patients) to make their decision; however, by the time mature data on 70 patients were verified, the study had accrued 158 patients |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | All pertinent imaging studies (except for those of four patients) were reviewed by an External Response Review Committee (ERRC) |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT 2 arms Quality score: A | |
| Participants | n = 1053 Median age: 59 years ECOG 2‐3: 0% Metastatic disease: 96% | |
| Interventions | S‐1+Cisplatin: S‐1 (50 mg/m2) in two daily doses d1‐21orally + cisplatin (75 mg/m2) repeated at d 28 versus FU+Cisplatin: fluorouracil (1000 mg/m2/24 hrs as 120‐hour infusion) + cisplatin (100 mg/m2), repeated at d 28 Cisplatin was discontinued after 6 cycles; provision to continue S‐1 or FU until progression of disease or unacceptable toxicities | |
| Outcomes | Overall survival Progression‐free survival Time to treatment failure Tumour response Toxicity | |
| Notes | Second‐line therapy in 31.4% of patients, most frequently with fluoropyrimidine | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated dynamic randomisation |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Centralised randomisation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Full analysis set of all treated patients (98.8% in S‐1+cisplatin arm and 94.6% in FU+cisplatin arm) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Full analysis set of all treated patients |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | PEP: OS SEP: ORR, PFS, TTF, safety |
| Other bias | Low risk | None |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | Radiographic evidence of response to treatment was also independently reviewed. An independent data monitoring committee oversaw the safety and efficacy data along with other aspects of the conduct of the study. |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 220 | |
| Interventions | FLO: oxaliplatin 85 mg/m²; leucovorin 200 mg/m² and FU 2.600 mg/m² as 24‐hour continuous infusion every 14 days | |
| Outcomes | Median overall survival | |
| Notes | A pre‐planned interim analysis of toxicity and response was conducted after 80 patients were included in the study | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT analysis of all randomised patients (n = 220) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis of all treated patients (n = 214) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Report includes all expected outcomes (OS, RR and toxicity) |
| Other bias | High risk | Differences in baseline distribution of sex (42.9% versus 25% female) and metastatic disease (97.3% versus 90.7%). Preplanned interim analysis. |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 143 | |
| Interventions | FLOT: oxaliplatin 85 mg/m2 + leucovorin 200 mg/m2 + docetaxel 50 mg/m2, followed by 5‐FU 2600 mg/m2 as a 24‐hour continuous infusion d 1, repeated at 2 weeks FLO: oxaliplatin 85 mg/m2 + leucovorin 200 mg/m2, each as infusion followed by 5‐FU 2600 mg/m2 as a 24‐hour continuous infusion d 1, repeated at 2 weeks until disease progression, or for a total of 8, maximum 12 cycles | |
| Outcomes | Tolerabiliby and feasibility, defined as per group differences in toxicity, serious adverse events, treatment duration, treatment withdrawal, discontinuation for toxicity or patient's request, proportion of patients with a > 10 point change of QoL global health status (EORTC QLQ C‐30 questionnaires) at eight weeks, compared to baseline Response rates Overall survival Progression‐free survival | |
| Notes | Study included older adult patients (age ≥ 65 years). Second line therapy was permitted (FLOT: 61% vs. FLO: 42.7%) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer random generator |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Centralised randomisation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All 143 patients (FLOT, 72; FLO, 71) were eligible for the efficacy analysis on an ITT basis |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Only 1 patient was excluded from the safety analysis because of consent withdrawal before study treatment |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | ITT analysis Expected endpoints (ORR, OS, PFS, safety by NCI‐CTC etc) were included. QoL also assessed |
| Other bias | Low risk | The treatment arms were well balanced for pretreatment characteristics |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | No blinded external radiologist |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 72 | |
| Interventions | 5‐FU/Lv: Lv 100 mg/m²; 5‐FU 370 mg/m² d 1‐5, repeated at d 29 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | No standard error can be assessed for TTP | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Patients were randomised by a sealed envelope method, using random permutated blocks unknown to the clinicians, to receive either the 5‐FU/6S‐LV (Study A) or EEP‐L combination (Study B). Patients also were stratified into four groups based on a resected or nonresected primary tumor and an ECOG PS ≤ 1 or > 1. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sealed envelope method, using random permutated blocks unknown to the clinicians |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | One patient refused further treatment after the first cycle and was excluded from the response analysis, but not from the tolerance and survival analysis. Two patients refused chemotherapy after randomisation and were excluded completely from the analysis. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | One patient refused further treatment after the first cycle and was excluded from the response analysis, but not from the tolerance and survival analysis. Two patients refused chemotherapy after randomisation and were excluded completely from the analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | High risk | 1 participant who died after the second cycle of therapy has not been included in the survival analysis = no ITT |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | High risk. Likely unblinded |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT Quality score: A | |
| Participants | n = 704 Median age: 63.5 years ECOG 2‐3: 1.4% The study was conducted in Japan. | |
| Interventions | 5‐FU: 800 mg/m²/d, ci, d 1‐5, repeated at 4 w versus IP: irinotecan 70 mg/m² d 1 +15 + cisplatin 80 mg/m² d 1, repeated at 4 w versus S‐1: 40 mg/m² twice a day, d 1‐28, repeated at 6 w | |
| Outcomes | Overall survival Response rates Time to treatment failure Progression‐free survival Non‐hospitalised survival Toxicity | |
| Notes | This study was conducted in Japan. Aim of this study was to investigate superiority of CP and non‐inferiority of S‐1 to 5‐FU. Second‐line therapy in 78% of patients, cross‐over of 39% (from 5‐FU to IP), 57% (from IP to S‐1) and 30% (from S‐1 to IP) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Minimisation method |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Extremely low rate of withdrawals |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Extremely low rate of withdrawals |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected endpoints reported |
| Other bias | Low risk | None |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | Reviewed centrally at a trial group meeting; reviewers were unaware of treatment allocations at this time |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 134 | |
| Interventions | LV5FU2: LV 200 mg/m² ; FU 400 mg/m² bolus; FU 600 mg/m² d 1 + 2 ,repeated at 15 d LV5FU2‐cisplatin: cisplatin 50 mg/m² d 1+ 2 + LV5FU2, repeated at d 15 LV5FU2‐irinotecan: irinotecan 180 mg/m² d 1 + LV5FU2 ,repeated at d 15 | |
| Outcomes | Tumour response | |
| Notes | Adjuvant chemotherapy without cisplatin or irinotecan was allowed if completed at least 6 months before randomisation. Prior radiotherapy was allowed if completed more than 4 weeks before randomisation. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | One hundred thirty‐six patients were enrolled between January 1999 and October 2001 in 41 centres in France. Two patients were considered ineligible; one had a lymphoma and the other had no metastatic disease. No arm was closed after the two interim analyses. Thus, the analyses were carried out on an ITT basis with the remaining 134 enrolled patients. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | One hundred thirty‐six patients were enrolled between January 1999 and October 2001 in 41 centres in France. Two patients were considered ineligible; one had a lymphoma and the other had no metastatic disease. No arm was closed after the two interim analyses. Thus, the analyses were carried out on an ITT basis with the remaining 134 enrolled patients. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Low QoL response (41% (n = 22) and 48% (n = 29) at the third evaluation in arms A and C can bias longitudinal QoL analysis. Prior chemotherapy and radiotherapy were allowed under certain circumstances. |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | All objective tumor responses and cases of disease stabilisation were reviewed retrospectively |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 78 Median age: 63 years ECOG 2‐3: 6.3% Metastatic disease: 89.7% | |
| Interventions | Arm A (LdCF): 5‐FU (400 mg/m2 bolus +600 mg/m2 22 h continuous infusion d 1‐2) + cisplatin (50 mg/m2 d 1) + pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (20 mg/m2 d1), repeated at d 14 versus Arm B (MCF) : 5‐FU (400 mg/m2 bolus +600 mg/m2 22 h continuous infusion d 1‐2) + cisplatin (50 mg/m2 d 1, repeated at d 15) + mitomycin‐C (7 mg/m2, repeated at d 42) | |
| Outcomes | Response rates Time to progression Overall survival Toxicity | |
| Notes | second‐line treatment in 38.5% and 25.6 % of patients | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Random sequence generated by a computer programme |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Seventy‐seven of 78 patients were assessable for response; one patient in arm B was not assessable but was included in the ITT analysis and kept in the denominator of the response rate. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Seventy‐seven of 78 patients were assessable for response; one patient in arm B was not assessable but was included in the ITT analysis and kept in the denominator of the response rate. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Expected endpoints reported |
| Other bias | Low risk | Patients characteristics resulted well balanced between the treatment groups |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | Tumour response was assessed by an independent radiologist as central reviewer. |
| Methods | 60 AGC participants randomly divided into 2 groups by "random number table" ‐ 30 vs 30 | |
| Participants | Age range 18‐75 years Males:Females ratio was 18:12 in the DSOX group and 14:16 in the DCF group | |
| Interventions | Docetaxel plus S1 plus oxaliplatin (DSOX) vs Docetaxel plus fluorouracil plus cisplatin (DCF) | |
| Outcomes | OS TTP Tumour response | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Random number table" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 2 patients lost to follow‐up, reasons not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 2 patients lost to follow‐up, reasons not stated |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Not clear how many were screened for eligibility and randomised. Only the number of evaluable patients are provided. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Nothing to comment on |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 130 | |
| Interventions | FAM: 5‐FU 600 mg/m² d 1, 8, 29, 36; adriamycin 30 mg/m² d 1, 29 and mitomycin 10 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 57 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | — | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Centralised |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All eligible pts include din survival evaluation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All eligible pts included |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Low risk | Baseline characteristics well‐balanced |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | Extramural review |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 200 | |
| Interventions | FAMTX: MTX 1500 mg/m² d1; 5‐FU 1500 mg/m²; Lv 7.5 mg/m² p.o. every 6 hrs d 1‐3, adriamycin 30 mg/m² d 15, repeated at d 29 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | — | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Eligible patients were centrally randomised by the operational office of GOIRC (Parma, Italy) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Thirteen of the 200 randomised patients (six in the PELF and seven in the FAMTX group) did not begin the assigned chemotherapy and were not evaluated for toxicity. Reasons were not provided, and it is possible that this proportion could have an impact on analysis. The response of 15 patients in the PELF group and 14 in the FAMTX group were unevaluable or not evaluated for the following reasons: the treatment was never started (five versus five), protocol violations (zero versus one), insufficient treatment due to early death (five versus three), refusal (four versus two), early discontinuation due to toxicity (zero versus three) or severe medical events (one versus zero) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Thirteen of the 200 randomised patients (six in the PELF and seven in the FAMTX group) did not begin the assigned chemotherapy and were not evaluated for toxicity. Reasons were not provided, and it is possible that this proportion could have an impact on analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Toxicity was evaluated in all of the patients receiving at least one dose of chemotherapy whether they were eligible or not |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Response was assessed by the clinical investigators at each participating unit, and centrally reviewed in the case of CR, PR, no change for more than 6 months, or in the case of patients who underwent gastric resection at the end of the chemotherapy programme. |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 71 | |
| Interventions | 5‐FU/Lv: Lv 200 mg/m²; 5‐FU 375 mg/m² d 1‐5, repeated at d 22 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | — | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Reasons for exclusion clearly documented and valid |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Reasons for exclusion clearly documented and valid |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | No ITT, missing information about type and schedule of follow‐up between groups |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | Not stated, likely unblinded/by investigators |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 151 Metastatic disease: 62% | |
| Interventions | 5‐FU included 5‐FU 500 mg/m² on dayS 1‐5, repeated at 4 weeks, 8 weeks and every 5 weeks thereafter FAM included 5‐FU at 600 mg/m² on days 1, 8, 29 and 36; doxorubicin 30 mg/m² on days 1 and 29, and mitomycin 10 mg/m² on day 1 FA included 5‐FU 400 mg/m² with 40 mg of doxorubicin on day 1 every 4 weeks | |
| Outcomes | Overall survival, response rates, toxicity (not classified according to WHO or CTC) | |
| Notes | Study included participants with pancreatic and gastric cancer. Patients were stratified within institution according to the primary tumour. Separate results were given for participants with gastric cancer. Results only for participants with gastric cancer are included in this analysis. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT analysis with 3.3% exclusion from analysis |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | High risk | 5‐FU/doxorubicin(FA) and FAM arm will be combined in the analysis |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | High risk ‐ likely unblinded |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 252 | |
| Interventions | FAMe: 5‐FU 325 mg/m² d1‐5; adriamycin 40 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 36; methyl‐CCNU 110 mg/m² p.o. d 1, repeated at d 71 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | Three combination chemotherapy arms combined in the analysis. The single‐agent 5‐FU arm was opened after 56 participants were randomised. FAMe and FAP were closed after a planned interim analysis because of slightly higher death rate. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Low attrition rate with long follow‐up (only 7 of 252 patients remain alive at the time of analysis) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | n = 69 + 51 + 53 + 79 |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Missing response rates only a small minority of patients had measurable disease so regression rate was not used as a study endpoint |
| Other bias | High risk | Missing information to type and follow‐up in the treatment groups, combination of 3 combination treatment arms in the analysis, 2 arms were closed after a planned interim analysis |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 337 | |
| Interventions | IF: irinotecan 80 mg/m² i.v.; FA 500 mg/m² i.v.; 5‐FU 2000 mg/m² as a 22‐hour continuous infusion on d 1 weekly for 6 weeks, followed by 1 week rest | |
| Outcomes | Hazard ratios and median survival for overall survival and time to progression, tumour response, toxicity, QoL | |
| Notes | The trial was planned to establish superiority or non‐inferiority of IF over CF. Patients have finished prior radiotherapy and surgery 6 and 3 weeks, respectively, before randomisation. Previous adjuvant or neo‐adjuvant chemotherapy was allowed if completed 12 months before first relapse. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Biased coin method |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis of the full‐analysis population of treated patients |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis of the full‐analysis population of treated patients |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | High risk | Rate of non‐evaluable response was imbalanced between arms (IF 9.4% versus CF 16.8%), largely due to the higher rate of early discontinuations for toxicity in the CF arm. This difference may result from closer follow‐up in IF. Prior radiotherapy and chemotherapy were allowed under certain circumstances. |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | An External Radiological Review Committee (ERRC), blinded to treatment arm, reviewed all disease assessments and determined evaluability for response and date of progression. |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 85 | |
| Interventions | Arm A: 5‐FU 13.5 mg/kg/day for 5 days, every 5 weeks Arm B: carmustine 50 mg/m² on days 1 and 29; doxorubicine 25 mg/m² on days 1, 8, 15, 29 and 36 and mitomycin C 10 mg/m² on day 15 | |
| Outcomes | Overall survival, response rate, haematological toxicity | |
| Notes | — | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Centralised |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | n = 82 |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Only haematological toxicity given (in table format ‐ but nonhaematologic side effects were also mentioned) |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | High risk |
| Methods | Single‐centre, randomised | |
| Participants | Total of 60 patients: 30 each received TIROX or DCF | |
| Interventions | "In the TIROX group, patients received 40 mg/m2 S‐1 orally twice daily after a meal on days 1–14; 150 mg/m2 irinotecan intravenously (i.v.) infused over 90 min on the first day; 85 mg/m2 oxaliplatin i.v. infused over 2 h on the first day. This treatment regimen was repeated every 21 days and a 21‐day treatment period was defined as one chemotherapy cycle. In the DCF group, patients received 75 mg/m2 docetaxel i.v. and 75 mg/m2 cisplatin i.v. on the first day; 750 mg/m2 5‐FU via continuous i.v. infusion once a day from the first day to the fifth day." | |
| Outcomes | Response rates | |
| Notes | No registration number found but "All of the study methods were approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (no. 2010‐003854)" | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Low |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | None stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Number screened for eligibility and excluded not provided. Only number of evaluable patients stated. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Number screened for eligibility and excluded not provided. Only number of evaluable patients stated. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Only response rates and certain safety data were presented. "The rates of long‐term progression‐free survival and overall survival were not measured". Not clear if any of these endpoints were prespecified. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 249 | |
| Interventions | FAP: 5‐FU 300 mg/m² d 1,8,15,22; adriamycin 30 mg/m² d 1; cisplatin 100 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 29 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | — | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Not clear how many screened for eligibility and excluded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Not clear how many screened for eligibility and excluded |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Toxicity not classified according to WHO or NCI |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Multicentre, randomised, open‐label, 3‐armed, phase 2 trial | |
| Participants | Median (IQR) age in the 3 arms was 65 (60–70), 65 (58–71), 65 (59–69) years | |
| Interventions | S‐1 plus leucovorin (S‐1 40–60 mg orally plus oral leucovorin 25 mg twice a day for 1 week, every 2 weeks), S‐1 plus leucovorin and oxaliplatin (S‐1 plus leucovorin and intravenous oxaliplatin 85 mg/m2 on day 1, every 2 weeks), or S‐1 plus cisplatin (S‐1 40–60 mg orally twice a day for 3 weeks, plus intravenous cisplatin 60 mg/m2 on day 8, every 5 weeks) 49 patients were randomly assigned to the S‐1 plus leucovorin group, 47 to the S‐1 plus leucovorin and oxaliplatin group, and 49 to the S‐1 plus cisplatin group | |
| Outcomes | Primary endpoint was overall response as assessed by an independent review committee, defined as a confirmed complete response or partial response. Secondary endpoints were overall survival, progression‐free survival, time to treatment failure, disease control, duration of response, and toxic effects | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomisation was done centrally with the minimisation method using performance status (0 vs 1) and tumour stage (stage IV vs recurrent) as stratification factors |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomisation sequence was generated by EPS Corporation (Tokyo, Japan) independently from the study sponsor |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | After randomisation, one patient did not receive treatment because of aspiration pneumonia. †Two patients who were judged to have no measurable lesions by the independent review committee after enrolment were excluded from the efficacy analyses |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | After randomisation, one patient did not receive treatment because of aspiration pneumonia. †Two patients who were judged to have no measurable lesions by the independent review committee after enrolment were excluded from the efficacy analyses |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All prespecified outcomes were reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | independent data monitoring committee (but not stated review committee was blinded) |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 240 Metastatic disease: 93% | |
| Interventions | Paclitaxel+S‐1: Paclitaxel 60 mg/m2 d 1,8,15, S‐1 depending on body surface area (BSA < 1.25 m2: 80 mg/d; BSA 1.25 to <1.5 m2: 100 mg/d; BSA > 1.5 m2, 120 mg/d twice daily) twice daily d 1‐14, repeated at d 29 versus Paclitaxel+5‐FU: Paclitaxel 60 mg/m2 d 1,8,15, 5‐FU 500mg/m2 d 1‐5, leucovorin 20 mg/m2 d 1‐5 repeated at d 29 | |
| Outcomes | Response rates Progression‐free survival Time to treatment failure Toxicity | |
| Notes | 6% of patients had no adenocarconoma | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central randomisation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 229/240 included in full analysis set: One patient was not eligible for the current analysis due to a lack of measurable lesions, 11 patients withdrew informed consent |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 229/240 included in full analysis set: One patient was not eligible for the current analysis due to a lack of measurable lesions, 11 patients withdrew informed consent |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected outcomes except OS analysed |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | OS not analysed |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 316 | |
| Interventions | XP: capecitabine 1000 mg/m² twice daily d 1–14; cisplatin 80 mg/m² d 1 every 3 weeks | |
| Outcomes | Progression‐free‐survival, overall survival | |
| Notes | — | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Random permuted block design |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis of ITT population (n = 316) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis of all treated patients (n = 311) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Low risk | Patients followed up for OS till end of study regardless of withdrawal + ITT vs PP, and unadjusted vs adjusted analyses performed |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | An independent review committee (IRC) reviewed patients’ radiological images and assessed tumour responses without knowledge of treatment assignment |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 77 | |
| Interventions | FA: 5‐FU 270 to 300 mg/m² CI d 1‐ 5; adriamycin 25 mg/m² d 5, repeated at d 22 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | Translated from Japanese | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sequential opaque envelopes |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All evaluable pts analysed |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All evaluable pts analysed |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | Evaluated during group meetings |
| Methods | Single‐centre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 121 | |
| Interventions | FP: 5‐FU 1000 mg/m² over 6 hours d 1‐5; cisplatin 60 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 29 versus | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | Study currently published as abstract only. Final results were provided by the first author. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Abstract / supplement only |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Abstract / supplement only |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Abstract / supplement only |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Abstract / supplement only |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Abstract / supplement only |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | Per first author |
| Methods | Single‐centre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 77 Median age: 57 years | |
| Interventions | wDP: docetaxel (35 mg/m2) d 1, 8, cisplatin versus wDO: docetaxel (35 mg/m2) d 1, 8, oxaliplatin | |
| Outcomes | Response rates Overall survival Progression‐free survival Toxicity | |
| Notes | Second‐line treatment in 63 % (wDP) and 77% (wDO): irinotecan monotherapy or irinotecan plus 5‐fluorouracil/ leucovorin in 67% and 70 % of the wDP and wDO arms | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT analysis |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected endpoints included |
| Other bias | Low risk | Patients in the wDP arm received 85% and 82 % of the planned dose intensities of docetaxel and cisplatin, respectively. In the wDO arm, the mean relative dose intensity was 83 % for docetaxel and 80 % for oxaliplatin. |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT The study was conducted in Japan. | |
| Participants | n = 305 | |
| Interventions | S‐1 + cisplatin: S‐1 twice daily d 1‐20 repeated at d 36, dose of S‐1 according to the patient’s body surface area (< 1.25 m²: 40 mg; 1.25–1.5 m²: 50 mg; > 1.5 m²: 60 mg) + cisplatin 60 mg/m² d 8, repeated at d 36 versus S‐1 : S‐1 twice daily d 1‐27 repeated at d 41, dose of S‐1 according to the patient’s body surface area (< 1.25 m²: 40 mg; 1.25–1.5 m²: 50 mg; > 1.5 m²: 60 mg) | |
| Outcomes | Hazard ratio for overall survival | |
| Notes | This study was conducted in Japan. Due to polymorphic differences in the CYP2A6 gene in Asians and whites, the tolerability of S‐1 is different in whites (Ajani 2006). The dose of S‐1, which was used in this trial may not be used in non‐Asian populations for this reason. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Minimisation by use of biased coin method |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 298/305 patients included in analysis. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 298/305 patients included in analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Low risk | If second‐line treatment was started without progressive disease (i.e. due to adverse events), patients were censored |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | Images were assessed by an extramural review committee |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT Quality score: D The study was conducted in Japan and Korea. | |
| Participants | n = 639, 635 eligible (ITT) | |
| Interventions | S‐1+docetaxel: docetaxel (40mg/m2 d1) + S‐1 (40‐60mg/m2 ‐according to BSA‐ twice daily d 1‐14), repeated at d 21 versus S‐1: S‐1 (40‐60mg/m2 ‐according to BSA‐ twice daily d 1‐28), repeated at d 42 | |
| Outcomes | Overall survival, progression‐free survival, response rate, safety | |
| Notes | The study was conducted in Japan and Korea. The dose of S‐1 which was used in this trial may not be valid for non‐Asian populations for this reason. This study was registered (NCT00287768). | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 4 (0.6%) patients were ineligible (no measurable or non‐measurable lesions) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All treated patients were included (98%) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | High risk | Second‐line treatment was given to 69.7% of patients in the S‐1+docetaxel group and 76% in the S‐1 group, planned interim analysis |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Images were reviewed by a central review board. |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 95 | |
| Interventions | irinotecan/S‐1: irinotecan 75 mg/m2 as iv infusion d 1, 15 repeated at d 29 + S‐1 initial 40–60 mg/m2 orally twice daily d 1‐14, repeated at 4 weeks versus S‐1: S‐1 initial 40–60 mg/m2 orally twice daily d 1‐28, repeated at 6 weeks In subsequent cycles doses were varied according to the most severe adverse events during the preceding cycle | |
| Outcomes | Response rates Time to treatment failure Time to progression Overall survival Toxicity | |
| Notes | This study was conducted in Japan. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Minimization |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 16.7 versus 9.4% were not evaluable for tumour response (RECIST) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Two untreated patients who were excluded from safety evaluation |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Response rates Time to treatment failure Time to progression Overall survival Toxicity |
| Other bias | High risk | Patients aged over 70 years were more frequent in the group treated with irinotecan and S‐1: 45.8% (irinotecan/S‐1) vs. 14.9% (S‐1). Median age was 70 years for patients treated with irinotecan/S‐1 and 63 years for patients treated with S‐1 alone. |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | High risk |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 60 Inoperable or metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma | |
| Interventions | FP: cisplatin 50 mg/m²; 5‐FU 250 mg/m² on day 1; 5‐FU 250 mg/m² days 2‐5 FPEPIR: cisplatin 50 mg/m²; 5‐FU 250 mg/m² days 2‐5; epirubicin 30 mg/m² day 2 | |
| Outcomes | Response rates Toxicity | |
| Notes | — | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sealed envelopes |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | 5 patients not evaluated: 3 death from PD with 4 weeks of treatment, 1 due to relocation, 1 due to absence of follow‐up exam |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Toxic reactions classified by "standardization of reporting of results of cancer treatment" grading |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | RR, OS, toxicity (but not CTCAE/WHO) |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 203 | |
| Interventions | A: adriamycin 60 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 22 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | — | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | 16 patients not included because of ?inadequate follow‐up, 3 = treatment cancellation, 2 = protocol violation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Not ITT |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | No information about type and schedule of follow‐up in the treatment groups |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Single‐centre | |
| Participants | n = 16 vs 16 | |
| Interventions | "Total of 32 patients with advanced gastric cancer proved pathologically were randomly divided into 2 groups: 16 patients received SOX regimen [oxaliplatin 1.30 mg/m2 as a 2‐hour infusion on day 1, S‐1 capsules 80 mg/m2·d) twice a day per oral from day 1 to day 14 every 3 weeks], the other 16 patients received FOLFOX4 regimen [oxaliplatin 85 mg/m2 as a 2 hour infusion on day 1 and a 2 hour infusion of LV 200/(m2·d) followed by a 5‐Fu bolus 400/(m2·d) and 22 hour infusion 600/(m 2·d) for 2 consecutive days every 2 weeks]. Efficacy was evaluated at least 2 cycles" | |
| Outcomes | Response rates | |
| Notes | PFS and OS were not analysed using Kaplan‐Meier methods. HR for PFS could be estimated from summary data but HR for OS could not. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Simple random assignment |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Time‐to‐event analysed not analysed using Kaplan‐Meier methods. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quantitative comparison only made for grade 3 or higher haematological toxicity |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | "prospectively recruited AGC patients all over China" (did not state number of centres involved) 2 arms: "randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive S1 plus cisplatin (CS group) or fluorouracil plus cisplatin (CF group)" | |
| Participants | 255 patients screened, 120 received at least one cycle of CS, 116 received at least one cycle of CF Mean age: CS group ‐ 53.3 years, CF group ‐ 55 years "About 50% of the patients had low differentiated cancer. Approximately 85% of the patients had more than one site of metastasis and over half of the patients received previous gastrectomy" | |
| Interventions | "S‐1 was given as 40mg/m2 twice daily on day 1‐21 and cisplatin was 20mg/m2 iv drip on day 1‐4, repeated every 5 weeks in the CS group. In the CF group, 5‐Fu was given as 800 mg/m2/d CI 120h, and the dosage of cisplatin was 20mg/m2 iv on day 1‐4, repeated every 4 weeks" | |
| Outcomes | PFS (although TTP was stated as the primary endpoint, the definition they used is more consistent with PFS) OS Safety | |
| Notes | "As a pilot study, there is no need for sample size calculation. We planned to enroll 270 patients" | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Randomized grouping information for each patient was generated by central randomization system. At randomization, patients were stratified by ECOG PS (0‐1 vs. 2), numbers of metastasis sites (1 vs. > 1) and gastrectomy (yes vs no)" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | "Neither patients nor investigators were masked to treatment assignment in this open‐label study" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Low rate of attrition but reasons not specified |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Low rate of attrition but reasons not specified |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Other bias | High risk | "As a pilot study, there is no need for sample size calculation. We planned to enroll 270 patients" |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | "Investigators assessed tumor response and progression" |
| Methods | SIngle‐centre Non‐inferiority comparison of mEOX vs FOLFIRI RCT 2 arms: modified EOX vs FOLFIRI | |
| Participants | 105 patients (55 received EOX, 50 received FOLFIRI) | |
| Interventions | "The EOX group was given epirubicin 50 mg/m2 iv on day one, oxaliplatin 85 mg/m2 iv on day 1 and capecitabine at a twice‐daily dose of 625 mg/m2 po for 2 wk, which was repeated every 3 wk" | |
| Outcomes | OS PFS (separately for both first‐ and second‐line) Objective response rate Disease control rate Adverse events | |
| Notes | Second‐line chemo allowed | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Patient disposition/CONSORT flow diagram not provided; unclear how many were screened and excluded, and for what reasons |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Patient disposition/CONSORT flow diagram not provided; unclear how many were screened and excluded, and for what reasons |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Adverse effects (NCI‐CTC) categorised and analysed as grades 1‐4 and 3‐4 |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 165 | |
| Interventions | 5‐FU: 5‐FU 500 mg/m² d 1‐5 repeated at d 29 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | — | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Random number tables |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Analysis for all randomised and screened patients |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Analysis for all randomised, screened and treated patients |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | No response rates are given |
| Other bias | Low risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | High risk |
| Methods | "randomized phase II clinical trial conducted at Guizhou Cancer Hospital, China" | |
| Participants | "a total of 94 consecutive patients were enrolled to Guizhou Cancer Hospital and randomly divided into two arms: OXS group (47 cases) and S‐1 group (47 cases)" In both arms, about 3/4 of participants were males Median age was 63 and 65 years in the OXS and S‐1 groups | |
| Interventions | "Advanced gastric cancer patients were treated with S‐1 daily for first 2 weeks of a 3‐week cycle, or S‐1 daily for first 2 weeks plus 130 mg/m2 of oxaliplatin administered as a 2‐hour intravenous infusion on day 1 of a 3‐week cycle. S‐1 was orally administered in a fixed quantity according to body surface area (BSA) as follows: BSA less than 1.25 m2, 40 mg two times daily; 1.25,BSA,1.5 m2, 50 mg two times daily; and BSA more than 1.5 m2, 60 mg two times daily" | |
| Outcomes | "The primary endpoint was OS, defined as time from date of randomization to date of death from any cause. The secondary endpoints included PFS, RR, and safety profile." | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Randomization was generated using a computer‐generated random sequence concealed in consecutively numbered opaque sealed envelopes" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | "Randomization was generated using a computer‐generated random sequence concealed in consecutively numbered opaque sealed envelopes" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No patient was lost to follow‐up |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No patient was lost to follow‐up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | OS, PFS, RR and safety included; possible loss of information because of the way the adverse events were categorised and analysed |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 90 | |
| Interventions | HD‐FU: weekly FU 3.000 mg/m² as 24‐hour infusion | |
| Outcomes | Tumour response | |
| Notes | After stage 1 (21 patients in each arm) of the trial, the HD‐FU (single agent‐arm) arm was closed because only 2 responses had been observed. Total number of patients in this arm was 37 because inclusion was not interrupted before interim analysis. The results of the 2 combination arms were combined in the analysis. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Minimisation technique |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central randomisation at the EORTC data centre |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 127/145 eligible, reasons for exclusions provided and valid |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 127/145 eligible, reasons for exclusions provided and valid |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | High risk | Single‐therapy arm was closed earlier (Simon 2‐stage minimax design). The results of the 2 combination arms were combined in the analysis. |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | Computed tomography scans were reviewed centrally by the study co‐ordinators. |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 120 | |
| Interventions | ILF: irinotecan 80 mg/m² + LV 500 mg/m² + 5‐FU 2000 mg/m² days 1, 8, 15, 22, 29, 36, repeated at 8 weeks | |
| Outcomes | Tumour response | |
| Notes | — | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central allocation by the Co‐ordination Centre for Clinical trials Mainz |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis of the full‐analysis set of all treated patients |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis of the full‐analysis set of all treated patients |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Low risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 118 | |
| Interventions | XI: capecitabine 1000 mg/m² twice daily d 1‐14 + irinotecan 250 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 22 | |
| Outcomes | Median overall survival | |
| Notes | The reported results are from the first stage of the study (design with adaptive interim analysis) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis of the full‐analysis set of all treated patients with at least one efficacy assessment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis of the full‐analysis set of all treated patients |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | High risk | Results are from the first stage of the study (design with adaptive interim analysis) |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Single‐centre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 41 | |
| Interventions | FAMTX: Mtx 1000 mg/m² d1; 5‐FU 1500 mg/m² d 1; Lv 15 mg p.o. every 6 hours d 1 + 2 ,repeated at d 29 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | After 21 patients were randomised, further participants were directly assigned to the chemotherapy arm because of "strong evidence for benefit in the treated participants" | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | No ITT |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | No ITT |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | After 21 participants were randomised, further participants were directly assigned to the chemotherapy arm because of "strong evidence for benefit in the treated participants" |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT Quality score: D The study was conducted in Japan. | |
| Participants | n = 326 Median age: 63 years | |
| Interventions | S‐1: oral S‐1 80 mg/m²/day d 1‐28, repeated at 6 weeks S‐1 + irinotecan: oral S‐1 80 mg/m²/d d 1‐21 + irinotecan iv 80 mg/m² d 1 + 15, repeated at 6 weeks | |
| Outcomes | Overall survival Time to treatment failure Response rates Toxicity | |
| Notes | This study was conducted in Japan. Pre‐planned follow‐up of ≥ 1.5 years after registration of all patients was continued to 2.5 years because of a unexpectedly high survival rate of 22% at the cut‐off date after a follow‐up of 1.5 years. Second‐line chemotherapy was administered to 76% of patients. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Centralised dynamic allocation |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Centralised dynamic allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Full analysis set |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 4 patients found to be ineligible after starting treatment were excluded from safety analysis ‐ ?per‐protocol analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Expected endpoints reported |
| Other bias | High risk | Second‐line chemotherapy was administered to a total of 76% of patients. This is likely to dilute the effect of both treatments on overall survival, but not on progression‐free‐survival. |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Extramural review is described (does not neccessarily mean blinded) |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT Quality score: D The study was conducted in Japan. | |
| Participants | n = 161 Median age: 67 years | |
| Interventions | Group A (sequential 5‐FU + paclitaxel): 5‐FU 800 mg/m² c.i.v. d 1‐5, repeated at 4 weeks, followed by paclitaxel 80 mg/m² d.i.v. d 1, 8, 15, repeated at 4 weeks after progression | |
| Outcomes | Overall survival (10 months overall survival rate) Progression‐free survival Time to treatment failure Response rates Toxicity | |
| Notes | This study was conducted in Japan. After publication of the results of the SPIRITS trial (Koizumi 2008) candidates for accrual were informed about the new treatment standard in Japan and they were offered the alternative to receive the combination therapy instead of participating in the trial. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Centralised dynamic randomisation |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Centralised dynamic randomisation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Only two patients in arm A and two in arm C declined therapies before the start of the assigned treatment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Only two patients in arm A and two in arm C declined therapies before the start of the assigned treatment |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Expected endpoints are reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | An irinotecan‐containing regimen was recommended for use in case if further lines of treatment were given. No information about the percentage of patients receiving second line treatment is provided. |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | not stated |
| Methods | Randomised, single‐centre phase 3 study | |
| Participants | "Most patients had metastatic disease and more than 50 % of patients in each arm have undergone gastrectomy (primary tumor resection) as part of curative or palliative treatment. Significantly more patients in the mDCF arm presented with metastases in the liver (48.1 vs. 17.2 %; p = 0.029)" | |
| Interventions | "The EOX regimen was given every 3 weeks, initially for a maximum of eight cycles (24 weeks of treatment). It consisted of epirubicin 50 mg/m2 (intravenous bolus), followed by oxaliplatin 130 mg/m2 (2‐h intravenous infusion); capecitabine was administered orally, twice daily at the dose of 625 mg/m2 for 21 days. The mDCF regimen was administered every 2 weeks, initially for a maximum of 12 cycles (24 weeks of treatment), docetaxel 40 mg/m2 (intravenous infusion over 60 min) on day 1, followed by leucovorin 400 mg/m2 (intravenous infusion over 120 min) on day 1, followed by 5‐fluorouracil 400 mg/m2 (intravenous bolus) on day 1, and then 5‐fluorouracil 1000 mg/m2/day continuous intravenous infusion on day 1 and day 2, followed by cisplatin 40 mg/m2 (intravenous infusion over 60 min) on day 3." | |
| Outcomes | OS PFS ‐ the definition of PFS was not clearly stated Safety | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No loss to follow‐up |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Only one patient from mDCF arm excluded due to rapid disease progression |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | RR not provided |
| Other bias | High risk | "Significantly more patients in the mDCF arm presented with metastases in the liver (48.1 vs. 17.2 %; p = 0.029)" ‐ no statistical adjustment was made for baseline imbalance CT scans every 8–12 weeks; and disease progression could also be evaluated based on clinical symptoms and urgent CT was requested whenever needed |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Single‐centre RCT Quality score: D | |
| Participants | n = 85 Median age: 55 years | |
| Interventions | ECF: epirubicin 50 mg/m² i.v. d 1 + cisplatin 60 mg/m² i.v. d 1 i.v.+ 5‐ FU 200 mg/m²/day continuous infusion d 1‐14, repeated at d 22 ECX: epirubicin 50 mg/m² i.v. d1+ cisplatin 60 mg/m² i.v. d 1 + capecitabine 825 mg/m² orally twice daily d 1‐14, repeated at d 22 Treatment was discontinued in case of disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or if the patient refused further treatment | |
| Outcomes | Overall survival Response rates Time to progression Toxicity | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | The method of sequence generation is not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | "Randomisation and allocation were done by a registration center" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All randomised patients were included in the ITT analysis |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All randomised patients were included in the ITT analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | N/A ‐ except that TTP rather than PFS reported |
| Other bias | High risk | Response assessment was done by abdominal ultrasound and/or abdominal CT (not CT of the thorax and abdomen). Both methods are insufficient. |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | Response assessment was done by abdominal ultrasound and/or abdominal CT (not CT of the thorax and abdomen). Both methods are insufficient. |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 280 | |
| Interventions | FU: 5‐FU 800 mg/m² CI d 1‐5, repeated at d 29 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | Full information about second‐line therapy given: 51% of participants in the combination therapy arms and 57% of participants in the single‐agent 5‐FU arm received a second‐line therapy | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Minimisation |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | JCOG data centre |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Low risk | Both combination chemotherapy arms (FP and UFTM) were combined in the analysis. High rates of second‐line therapy. |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | "objective responses confirmed by central review at regular group meetings" |
| Methods | Single‐centre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 60 | |
| Interventions | 5‐FU 2600 mg/m² over 24 hours d 1, repeated at d 15 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | Study published as abstract, information on final results provided by first author (Popov 2002). Final publication in Medical Oncology 2008. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Method of random numbers |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No excluded patients |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No excluded patients |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | Independent response review was performed by a joint interdisciplinary committee not involved in the study |
| Methods | RCT | |
| Participants | n = 72 | |
| Interventions | LV5‐FU2 oxaliplatin: oxaliplatin 85 mg/m² d 1+ folinic acid 200 mglm², as 2‐hour infusion, d 1‐2 + 5‐FU 400 mg/m², Lv. bolus d 1‐2, repeated at d 15 versus LV5‐FU2‐CDDP: cisplatin 50 mg/m², d1+ folinic acid 200 mg/m², as 2‐hour infusion, d 1‐2 + 5‐FU 400 mg/m², Lv. bolus d1‐2 + 5‐FU 600 mg/m² , 22‐hour continuous infusion d 1‐2, repeated at d 15 The maximum number of cycles foreseen was 12 | |
| Outcomes | Median overall survival | |
| Notes | — | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Patients receiving 4 or more cycles were evaluable for efficacy |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Patients receiving 1 cycle were evaluable for toxicity |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | "Independent response review was performed by members (surgeon, medical oncologist, radiologist and pathologist) of the joint interdisciplinary committee for gastrointestinal tumors of the Institute and the University Clinic for gastrointestinal diseases. The committee members were not involved in the study" |
| Methods | RCT | |
| Participants | n = 41 | |
| Interventions | FEMTX: methotrexate 1500 mg/m² d 1, 5‐FU 1500 mg/m² d 1, Lv 30 mg p.o. every 6 hours d 1, 2, epirubicin 60 mg/m² d 15, repeated at d 29 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | Study terminated after 6 years when 41 participants were randomised because of slow patient accrual and "conspicuous difference in survival" | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Random permutated blocks (length 10) were used. The block was not known by clinicians. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sealed envelopes, Random permutated blocks (length 10) were used. The block was not known by clinicians. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Only 1 patient in treatment group did not receive at least one course of chemo |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Only 1 patient in treatment group did not receive at least one course of chemo |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | High risk | Early termination of the study |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | High risk |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 273 | |
| Interventions | DC: docetaxel 75 mg/m² + cisplatin 75 mg/m² d 1, repeated at 3 w FLC: 5‐FU 2000 mg/m² + leucovorin 500 mg/m² d 1, 8, 15, 22, 29, 36, repeated at 7 w + cisplatin 50 mg/m² d 1, 15, 29, repeated at 7 w (cisplatin omitted in FLC in cycle 4) | |
| Outcomes | Median overall and hazard ratios for survival and time to progression | |
| Notes | Study currently published as abstract only. Information on final results provided by first author. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Random number tables |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis for all randomised and screened patients |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis for all randomised, screened and treated patients |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | Per first author |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 334 participants with adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastro‐oesophageal junction | |
| Interventions | ECF: epirubicin 50 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 22; cisplatin 60 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 22, 5‐FU CI 300 mg/m² continuously | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | The original study included 580 participants with inoperable adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, or undifferentiated carcinoma of the oesophagus, oesophagogastric junction or stomach. Information on participants with gastric and gastro‐oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma only was provided by the first author and is included in the meta‐analysis. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Query (correspondence) to first author was not answered |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Query (correspondence) to first author was not answered |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | Not done per first author correspondence |
| Methods | Single‐centre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 122 | |
| Interventions | FE: 5‐FU 1000 mg/m² CI d 1‐5, repeated at d 29; epirubicin 120 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 29 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | — | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 110/122 received treatment and were assessable |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 110/122 received treatment and were assessable |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected outcomes available |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | No information about type and schedule of follow‐up |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | High risk |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 121 | |
| Interventions | ECF: epirubicin 50 mg/m² d 1 + cisplatin 60 mg/m² d 1 + FU 200 mg/m²/d as 24‐hour continuous infusion on days 1‐21, repeated at d 22 TC: docetaxel 85 mg/m² d 1 + cisplatin 75 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 22 TCF: TC + FU 300 mg/m²/d as a 24‐hour continuous infusion d 1‐14, repeated at d 22 for up to 8 cycles | |
| Outcomes | Tumour response | |
| Notes | Because of the toxicity of this regimen, the dose of docetaxel was reduced to 75 mg/m² later in the trial. The results of two docetaxel arms were combined in the analysis. Second‐line therapy after disease progression in 56% of patients with docetaxel and 48% of patients without docetaxel. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central randomisation at the SAKK Co‐ordinating Center |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | "Of 121 patients randomly assigned between September 1999 and July 2003, two were not treated (renal failure, n = 1; and ineligibility, n = 1) and were excluded. Another patient received two cycles of TCF before being considered ineligible but was included in the analyses." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | "Of 121 patients randomly assigned between September 1999 and July 2003, two were not treated (renal failure, n = 1; and ineligibility, n = 1) and were excluded. Another patient received two cycles of TCF before being considered ineligible but was included in the analyses." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | All responses were confirmed by an independent panel of radiologists and an oncologist |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 86 | |
| Interventions | DI: docetaxel 60 mg/m2 + irinotecan 250 mg/m2 d1, repeated at d 22 DF: docetaxel 85 mg/m2 d 1 + 5‐FU 750 mg/m2 d 1‐5, repeated at d 22 | |
| Outcomes | Response rates Time to progression Time to treatment failure Overall survival Toxicities Clinical benefit (time to definitive worsening of KPS, time to definitive weight loss, time to definitive worsening of appetite and pain‐free survival) | |
| Notes | 43% patients in the DI group and 49% patients in the DF group received second‐line chemotherapy (mostly a platinum containing regimen) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT analysis with only 1 excluded because of jaundice in the DI group |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT analysis with only 1 excluded because of jaundice in the DI group |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected endpoints included |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Assessed by external response review committee |
| Methods | Single‐centre RCT | |
| Participants | n=86 | |
| Interventions | ECF: epirubicin 60 mg/m² + cisplatin 60 mg/m² + 5‐FU 750 mg/m²/day as 5 days continuous infusion; repeated at d 22 for 6 cycles TCF: docetaxel 60 mg/m² + cisplatin 60 mg/m² + 5‐FU 750 mg/m² as 5 days continuous infusion; repeated at d 22 for 6 cycles | |
| Outcomes | Response rate | |
| Notes | Extensive analysis of QoL data | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | No information regarding numbers of patients beside response rates (primary endpoint) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | For QoL evaluation, only 71 patients were included in the comparative analysis because 15 patients did not complete the QoL measurements at the beginning of the study |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Missing information regarding PFS as secondary endpoint |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 103 | |
| Interventions | FE: 5‐FU 400 mg/m² d 1‐5; Lv 200 mg/m² d 1‐5; epirubicin 50 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 29 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | Study published as abstract only; additional information provided by first author | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | |
| Other bias | Low risk | |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | High risk |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT The study was conducted in Japan . | |
| Participants | n = 237 | |
| Interventions | 5‐FU: 5‐FU 800 mg/m² d 1‐5, repeated at d 29 | |
| Outcomes | Overall survival, ingestion‐possible survival (=surviving days free from nutrition support in patients with sufficient ingestion aat baseline, ingestive improvement in patients without sufficient ingestion at baseline), safety | |
| Notes | The study was registered as NCT00149201 and UMIN‐CTR number C000000123. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Minimization |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Algorithm concealed to investigators |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 2 non‐treated patients were excluded in each group. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 2 non‐treated patients were excluded in each group. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | No response and PFS reported |
| Other bias | High risk | Second‐line treatment was given to 80.7% of patients in the 5‐FU group and 72.9 in the MF group, planned interim analysis |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | N/A (no response and PFS reported) |
| Methods | Multicentre, randomised phase 2 | |
| Participants | 102 patients with 51 patients each in SIri and SPac arms "no prior chemotherapy, except adjuvant chemotherapy completed four weeks or more before entry" | |
| Interventions | Schedule of S‐1 was not similar in both arms Arm A: SIri: Irinotecan (i.v.) over 1.5 h at 80 mg/m² on day 1 and 15, while 40 mg/m² S‐1 (Taiho Pharmaceutical, Tokyo, Japan) was orally administered twice daily for three weeks from days 1‐21 followed by a two‐week pause. | |
| Outcomes | Primary endpoint: Overall response rate | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | (All outcomes analysed for all patients) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | (All outcomes analysed for all patients) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Expected endpoints included in reporting |
| Other bias | High risk | High risk |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | ("All radiological assessments were confirmed by extratumoral review") |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 90 | |
| Interventions | DF: docetaxel 75 mg/m² d 1 + FU 200 mg/m²/day as a 24‐hour continuous infusion d 1‐21, repeated at d 22 | |
| Outcomes | Tumour response | |
| Notes | Phase II study The trial was not intended and not statistically powered to perform a head‐to‐head comparison of response rate and toxicity of the 2 treatment arms. ECF serves as an internal control arm to avoid selection bias. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Random numbers |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis of the full analysis set |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis of the full analysis set |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | High risk | The trial was not intended and not statistically powered to perform a head‐to‐head comparison of response rate and toxicity of the 2 treatment arms, ECF serves as an internal control arm to avoid selection bias. |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | Tumour response was assessed together with an independent radiologist |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 445 | |
| Interventions | DCF: docetaxel 75 mg/m² + cisplatin 75 mg/m² d 1 + 5‐FU 750 mg/m²/d as a 24‐hour continuous infusion d 1‐5, repeated at d 22 | |
| Outcomes | Median overall survival and time to progression | |
| Notes | — | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis of the full‐analysis set |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis of the full‐analysis set |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | All radiologic assessments were reviewed by an external response review committee and were assessed by WHO criteria |
| Methods | Prospective, multinational, randomised, phase II study Fifty‐two sites in the USA and 11 countries in Europe screened and randomised patients | |
| Participants | The majority (69%) of patients were male; mean age was 59 years | |
| Interventions | 3‐arm study: docetaxel/oxaliplatin (TE), docetaxel/oxaliplatin/5‐FU (TEF), and docetaxel/oxaliplatin/capecitabine (TEX) | |
| Outcomes | PFS OS ORR Safety | |
| Notes | "Tumour response was evaluated every 8 weeks and classified according to best overall response (World Health Organization criteria). Responses were confirmed by two evaluations conducted ≥4 weeks apart" | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not clear what method |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | RandomiSed centrally using an interactive voice response system |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | "primary efficacy population was the full analysis population (FAP: all randomized and treated patients analysed in the arm to which they were randomized), with supportive analyses conducted using the intent‐to‐treat (ITT: all randomized patients) and per protocol (PP: assessable patients [received study treatment and had ≥1 post‐baseline tumour assessment] without any major protocol violation) populations" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | "primary efficacy population was the full analysis population (FAP: all randomized and treated patients analysed in the arm to which they were randomized), with supportive analyses conducted using the intent‐to‐treat (ITT: all randomized patients) and per protocol (PP: assessable patients [received study treatment and had ≥1 post‐baseline tumour assessment] without any major protocol violation) populations" |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | PFS, OS, ORR, safety |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Single‐centre RCT 2 arms Quality score: B | |
| Participants | n = 82 participants with metastatic or locally recurrent gastric cancer ECOG 2: 8.5% | |
| Interventions | S‐1 +paclitaxel: S‐1 depending on body surface area (BSA < 1.25 m2: 80 mg/d; BSA 1.25 to < 1.5 m2: 100 mg/d; BSA > 1.5 m2, 120 mg/d twice daily) d 1‐14, paclitaxel 60mg/m2 d 1,8,15, repeated at d 29 versus S‐1: S‐1 depending on body surface area (BSA < 1.25 m2: 80 mg/d; BSA 1.25 to <1.5 m2: 100 mg/d; BSA > 1.5 m2, 120 mg/d twice daily) d 1‐14, repeated at d 29 | |
| Outcomes | Overall survival Progression‐free survival Response rate Toxicity | |
| Notes | Second‐line therapy with cisplatin or irinotecan in more than half of the patients | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated, random sequence |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Consecutively numbered opaque sealed envelopes |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No patients lost to follow‐up and all outcomes could be confirmed |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No patients lost to follow up and all outcomes could be confirmed |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | OS, PFS, ORR, safety |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | Tumor assessment was undertaken with CT or MRI consistently every 2 months by principal investigators |
| Methods | Multicentre, prospective, randomised, open‐label, phase III trial | |
| Participants | Histo: 15% Signet ring, 3% Others | |
| Interventions | "Untreated advanced gastric cancer patients randomly received docetaxel and cisplatin at 60 mg/m2 (day 1) followed by fluorouracil at 600 mg/m2/day (days 1–5; mDCF regimen) or cisplatin at 75 mg/m2 (day 1) followed by fluorouracil at 600 mg/m2/day (days 1–5; CF) every 3 weeks" | |
| Outcomes | "The primary end point was progression‐free survival (PFS). The secondary end points were OS, overall response rate (ORR), time‐to‐treatment failure (TTF), and safety" | |
| Notes | NCT00811447 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated what method was used. "Random assignment was centralized and stratified for center, liver metastases, prior gastrectomy, Karnofsky performance status (KPS) (80 or above vs below 80), and weight loss during the previous 3 months (5 % or less vs more than 5 %)" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Random assignment was centralised |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All patients who received treatment were included in full analysis set |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All patients who received treatment were included in full analysis set |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Endpoints were all reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | "Tumor response and PFS were evaluated by investigators, and although much effort has been done to limit the bias in the evaluation of these parameters..." |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 199 participants with adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastro‐oesophageal junction | |
| Interventions | ECF: epirubicin 50 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 22; cisplatin 60 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 22, 5‐FU CI 200 mg/m² d 1‐21, repeated at d 22 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | The entire study included 274 participants with inoperable adenocarcinoma or undifferentiated carcinoma of the oesophagus, oesophagogastric junction or stomach. Results for participants with adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastro‐oesophageal junction only were provided by the corresponding author and included in the meta‐analysis. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Query to first author was not answered |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Query to first author was not answered |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT per correspondence |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT per correspondence |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report includes all expected outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | N/A |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | High risk | Not done according to correspondence |
| Methods | Pilot randomiSed‐controlled study | |
| Participants | "158 participants were initially screened, of whom 86 were excluded. Of these 86 patients, 73 did not fulfill the study criteria and 13 declined to participate. The remaining 72 patients (36 treated with SC and 36 treated with C) were entered into the study" "The mean age of the patients was 64.1 years in the SC group and 62.7 years in the C group. The performance status was 0 for 41.7% of patients treated with SC and 44.4% of patients treated with C and it was 1 for 58.3% of patients treated with SC and 44.4% of patients treated with C. The primary lesion was 55.6% in the SC group and 50.0% in the C group. Histological types were intestinal (58.3% in the SC group and 61.1% in the C group), diffuse (36.1% in the SC group and 30.6% in the C group), and others (5.6% in the SC group and 8.3% in the C group). The diagnosis was AGC (86.1% in the SC group and 83.3% in the C group) and relapse gastric cancer (13.9% in the SC group and 16.7% in the C group)." | |
| Interventions | "Patients in the C group received cisplatin 75 mg/m2 intravenously over 1–3 h on day 1 and then at 4‐week intervals. In addition to receiving the same intervention as the C group, patients in the SC group were also administered S‐1 on days 1–14 of a 21‐day cycle. The daily dose of S‐1 was assigned according to the body surface area as follows: less than 1.25 m2, 40 mg two times daily; more than or equal to 1.25 m2 and less than 1.5 m2, 50 mg two times daily; and more than or equal to 1.5 m2, 60 mg two times daily." | |
| Outcomes | OS PFS Adverse events | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Patients were stratified using the block randomization method of the SAS package (version 8.2; SAS Institute Inc., Cary, North Carolina, USA) by a statistician with no clinical involvement in this study" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | "The allocation was concealed in sequentially numbered, opaque, sealed envelopes containing the randomization assignments" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All participants could undergo evaluations for efficacy and safety. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All participants could undergo evaluations for efficacy and safety. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Overall response rates were compared although it did not appear to be prespecified. Furthermore, details of how response was assessed were not provided. |
| Other bias | High risk | Study did not clearly specify minimum required sample size ‐ "Sample size was calculated on the basis of an expected 15% difference between the two groups, with 80% power and a two‐sided [alpha] value of 0.05" Comments from statistician BCT:The paper is not clear about how the sample size is being estimated. In particular, we do not have information on the HR or the survival probability of the control group. I assume the 15% difference refers to absolute difference. I try to work out this difference from the KM curve of Fig 2. If we assume a 1 year estimate, then the survival probability is approx. 25% vs 40% (HR approx. 0.66). If we assume a 0.5 year estimate, then the survival probability is 75% vs 90% (HR approx. 0.37). This corresponds to a total sample size of about 300 and 200 respectively, assuming a two‐sided test at 5% level and a power of 80%. If we estimate the HR from the median OS that is reported, the HR is approx. 0.8, and so we would expect an even larger sample size. |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | Randomised, open‐label, multicentre phase III study | |
| Participants | 685 patients were enrolled; 343 and 342 patients were randomly assigned to SOX or CS | |
| Interventions | "In CS, S‐1 was given orally twice daily for the first 3 weeks of a 5‐week cycle. The dose was 80 mg/day for body surface area (BSA) <1.25 m2, 100 mg/day for BSA ≥1.25 to <1.5 m2, and 120 mg/day for BSA ≥1.5 m2. Cisplatin was administered at 60 mg/m2 as an i.v. infusion with adequate hydration on day 8 of each cycle [9]. In SOX, S‐1 was given as the same way for the first 2 weeks of a 3‐week cycle. Oxaliplatin at 100 mg/m2 was infused for 2 h i.v. on day 1 of each cycle" | |
| Outcomes | The primary end points were noninferiority in progression‐free survival (PFS) and relative efficacy in overall survival (OS) for SOX using adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Minimisation method. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | The randomisation sequence was generated by an independent team from the trial sponsor and investigators |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | PFS, OS, tumor responses, Adverse events |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | "During the study period, we did not test HER2 expression in tumors and could not know its exact influence on our results. The proportion of patients who received trastuzumab after the study treatment was small (<10%) and similar in both groups. Therefore, trastuzumab treatment would not seem to impact on comparing OS between both groups." "Patients who were alive and free of progression (i.e. second‐line treatment was started due to any cause) were regarded as censored cases at the date of the last assessment" "In February 2011, it appeared to be difficult to achieve the required number of events within the preplanned timetable, and the target number of patients was revised to 680 according to the predefined procedure in the protocol" |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Low risk | "All images for PFS and tumor responses were reviewed by an independent review committee, according to the Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.0" |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT | |
| Participants | n = 71 | |
| Interventions | MTX/5‐FU/THP: methotrexate 50 mg/m², 5‐FU 650 mg/m², pirarubicin 20 mg/m² d 1, repeated at d 15 | |
| Outcomes | Median survival | |
| Notes | Study translated from Japanese | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Centralised. Phone call |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 71/74 evaluable |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 71/74 evaluable |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | No response rates available JCOG criteria for toxicity |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Study translated from Japanese |
| Blinded review of CT/MRI‐scans? | Unclear risk | N/A |
Abbreviations:
BSA: body surface area
BSC: best supportive care
CI: continuous infusion
CT: computed tomography
d: day
dFUR: 5‐Deoxyfluouridine
ECOG: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group
5‐FU: 5‐Fluorouracil
FA: folinic acid
h: hour
IQR: interquartile range
ITT: intention‐to‐treat
i.v.: intravenous
KI: Karnofsky‐Index
KPS: Karnofsky performance status
Lv: leucovorin
NCI‐CTC: National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria
OS: overall survival
p.o.: per os (orally)
PFS: progression‐free survival
QoL: quality of life
RCT: randomised controlled trial
RR: response rate
TTP: time to progression
UFT: uracil/ftorafur
w: week
WHO: World Health Organization
If not stated differently, all drugs were given as intravenous bolus or short infusion (duration max. 2 hours)
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| According to information provided by the first author about 2/3 of included participants had undergone gastric resection and were treated in adjuvant/additive intention. | |
| Article about study published elsewhere (Van Cutsem 2006). | |
| Non‐randomised phase II study. | |
| Other indication (patients underwent macroscopically curative resection). | |
| Study not randomised. | |
| Interventions not relevant for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Not all participants were randomised (some were directly assigned to 1 treatment arm according to their prior chemotherapy). Systematic cross‐over between treatment arms. | |
| Study began as three‐arm comparison of FAMe, FAMi and FIMe regimens. FMe was added to randomization later. ICRF‐159 =dexrazoxaneL None of the possible permutations between these regimens fit our study comparisons | |
| 18 of 82 included participants were crossed over (< 10 %) | |
| Compared FA, FAMe, and FAMi. None of the possible permutations between these regimens fit our study comparisons. | |
| Study not randomised | |
| Participants not randomised to different chemotherapy regimens, but to one regimen (FEP) with or without GM‐CSF | |
| Participants with different advanced gastrointestinal cancers were included in the study. No separate results given for gastric cancer participants. | |
| Preliminary publication. | |
| Final publication: Berenberg 1995 (excluded). | |
| Compares different single‐agent chemotherapy regimens. | |
| Published as abstract only. No further information obtained by contacting the first author. | |
| Published as abstract only. No further information obtained by contacting the first author. | |
| Other indications. | |
| Cross‐over study. | |
| Study included participants with different advanced gastrointestinal cancers. No separate results given for gastric cancer participants. | |
| Preliminary publication. | |
| Study published as abstract only with insufficient data available. According to information provided by the first author no further analysis was performed as the study was terminated early due to slow accrual. | |
| Secondary publication. | |
| Does not compare different intravenous combination chemotherapy regimens but 1 intravenous regimen with or without an additional oral chemotherapy (methyl‐CCNU). | |
| Not an RCT, retrospective analysis of an RCT. | |
| Final publication: Cascinu 1995 (excluded). | |
| Participants not randomised to different chemotherapy regimens but to reduced glutathione or placebo to prevent cisplatin‐induced neurotoxicity. | |
| Participants not randomised to different chemotherapy regimens but to different doses of G‐CSF as supportive therapy. | |
| Testing VEGF inhibitor (ramucirumab) as second‐line therapy. | |
| Gimeracil + oteracil, neither contains a 5‐FU prodrug nor is equivalent to S‐1. So this combination does not fit any comparison. | |
| One study arm was treated with oral 5‐FU. | |
| Insufficient information for calculation of HRs given in the publication or provided by the author. | |
| Missing information to calculate HRs for OS | |
| Not an RCT. | |
| Included 108 participants with advanced cancer (only 5 gastric cancer patients). | |
| Systematic cross‐over between study groups (< 10 % of included participants). | |
| Final publication: Cocconi 1994 (included). | |
| Final publication: Colucci 1995 (included). | |
| Study not randomised. | |
| Compares different single agents. | |
| Final publication: Cullinan 1994 (included). | |
| Wider indication (inclusion of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus as well). | |
| Final publication: De Lisi 1986 (included). | |
| Second publication to De Lisi 1986 (included). | |
| Preliminary publication. | |
| Final publication: Douglass 1984 (excluded). | |
| Not all participants were randomised. Some were directly assigned to 1 study arm according to their prior treatment. | |
| Interventions not relevant for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Study not randomised. Two consecutive regimens were compared. | |
| Second‐line CTX. | |
| Testing VEGF inhibitor (ramucirumab) as second‐line therapy. | |
| Study not randomised. | |
| Schizophyllan: mushroom polysaccharide with immunomodulatory properties (biologic therapy), no chemotherapy. | |
| Although described as advanced gastric cancer in the title, according to the text of the article the study compared different adjuvant chemotherapy regimens. | |
| inclusion pf patients with squamous epithelium carcinoma. | |
| Study not randomised. | |
| Final publication: Glimelius 1997 (excluded). | |
| Study includes participants with different inoperable cancers. Cross‐over from BSC to chemotherapy arm permitted. Primary aim: cost‐effectiveness. | |
| Study compares chemotherapy versus best supportive care. Provision of chemotherapy upon request in the best supportive care group was requested by the research ethics committee, and 12 of 30 participants (19.6%) randomised to best supportive care finally received chemotherapy (cross‐over). | |
| Participants were not randomised between different chemotherapy regimens but to methionine‐depleted total parenteral nutrition versus a conventional amino acid solution. | |
| All participants were treated with chemotherapy after resection (no advanced/metastatic disease). | |
| Study not randomised. | |
| Prescheduled cross‐over between study arms after four courses. | |
| Considerable use of second‐line therapy. | |
| Insufficient data on survival available. | |
| Cross‐over after failure was encouraged. | |
| Preliminary data. | |
| Retrospective analysis of clinical benefit and quality of life in participants with different inoperable gastrointestinal cancers. | |
| Study not randomised. | |
| Includes participants treated in adjuvant intention after curative resection of gastric cancer. | |
| Participants with ascites were treated with intraperitoneal chemotherapy. | |
| Interventions not relevant for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Interventions not relevant for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Preliminary publication. | |
| Not an RCT. | |
| Final publication: Kim 1993 (excluded). | |
| According to information provided by author (YSP) allocation was done by alternation (not truly randomised). | |
| Interventions not relevant for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Meta‐analysis is examining second‐line therapy vs BSC. | |
| Study compares the effect of different amino‐acid solutions (methionine‐free amino‐acid solution versus commercial amino‐acid solution) in addition to 5‐FU chemotherapy. | |
| Compares different dosages of cisplatin (60 mg and 80 mg) within the same chemotherapy regimen. | |
| Interventions not relevant for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Not an RCT. | |
| Testing irinotecan plus cisplatin versus irinotecan as second‐line therapy. | |
| Participants with stomach and rectosigmoid cancer included. No separate information about gastric cancer provided. | |
| Study uses oral 5‐FU (no intravenous chemotherapy, varying bioavailability). | |
| Study treatment: adoptive immunotherapy. | |
| Does not compare different chemotherapy regimens but the same chemotherapy with or without G‐CSF and/or erythropoietin. | |
| One group was treated with intra‐arterial chemotherapy. | |
| Insufficient data for calculation of HRs given (P value missing). | |
| Final publication: Pyrhönen 1995 (included). | |
| Compared: tegafur + mitomycin C (FTM), uracil‐tegafur + mitomycin C (UFTM), 5'deoxy‐flurorouridine + cisplatin (5'P), etoposide + doxorubicin + cisplatin (EAP), and 5‐fluorouracil + cisplatin (FP). Firstly, none of the possible permutations between these regimens fit our study comparisons. Secondly, the Ohkuwa 2000 paper resembles a “pooled ” analysis (of other RCTs such as Kurihara 1991) rather than an original RCT. | |
| Participants randomised to either methionine‐free or commercial amino‐acid solution, with the same (mitomycin C/fluorouracil) chemotherapy in both groups. | |
| Final publication: Koizumi 1996 (excluded). | |
| Final publication: Lacave 1987 (excluded). | |
| Does not compare different intravenous chemotherapy regimens but 1 intravenous chemotherapy with or without an additional oral chemotherapy (methyl‐CCNU). | |
| Interventions not relevant for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Gastrointestinal endoscopy. | |
| Participants had oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. | |
| Drug under investigation was never approved, and the regimen does not fit any of our 10 comparisons. Also their trial was not solely done in gastric cancer patients, but also included patients with colorectal, oesophageal, and liver cancer. | |
| Missing information to calculate HRs for OS. | |
| Not relevant for any of the comparisons. | |
| Testing second‐line apatinib. | |
| Not relevant for any of the comparisons. | |
| Radiochemotherapy is compared to systemic intravenous chemotherapy. | |
| Testing whether cetuximab (EGFR targeted mAB) should be included as first‐line in combination with capecitabine and cisplatin. | |
| Not a randomised trial. | |
| Interventions not relevant for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Study not randomised. Includes participants with gastric and colorectal cancer. | |
| Second‐line chemotherapy. | |
| Published as abstract only. No further information obtained by contact with the first author. | |
| Published as abstract only. No further information obtained by contact with the first author. | |
| Interventions not relevant for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Insufficient information for calculation of HRs given. | |
| The combination therapy arm consisted of only 1ne oral agent (methyl‐CCNU, no intravenous chemotherapy), in addition to 5‐FU which was used as single‐agent. | |
| Not all participants were randomised (some were directly assigned to 1 treatment arm according to their prior treatment). Systematic cross‐over between study groups. | |
| Secondary publication. | |
| Study included participants with different advanced cancers (only 3 patients with gastric cancer). | |
| Study compares different adjuvant chemotherapies. | |
| Study treatment included schizophyllan (mushroom polysaccharide with immunomodulatory effects, biological therapy). | |
| The treatment for each patient was decided by the patient’s choice or randomisation (not a randomised trial). | |
| Compares different modes of application of the same chemotherapy (continuous and intermittent oral administration of 5´deoxy‐5‐fluorouridine), not different chemotherapy regimens. | |
| Study presents different interpretations of quality of life data from a previously performed study (Glimelius 1997). The study included advanced gastric cancer participants, but was excluded because of cross‐over. | |
| Compares different single agents. | |
| Testing whether bevacizumab (VEGF targeted mAB) should be included in first‐line chemotherapy combinations. | |
| Not an RCT. | |
| Study treatment: adjuvant chemo‐immunotherapy. | |
| Compares 2 modes of application (sequential versus simultaneous) of 1 chemotherapy regimen (FAM). | |
| Interim analysis of Park 2006. | |
| Interventions not relevant for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Interventions not eligible for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Study treatment: chemo‐immunotherapy. | |
| Final publication: Popov 2000 (excluded). | |
| Compares different applications of doxorubicin (bolus versus 8‐hour infusion) in the same chemotherapy regimen (EAP), not different chemotherapy regimens. | |
| Interventions not relevant for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Final publication: Pyrhönen 1995 (included). | |
| Compared 5‐fluorouracil and carmustine with or without adriamycin. This does not fit our study comparisons. | |
| 39 of 77 included participants receiving chemotherapy as additive therapy after non‐curative resection with histological evidence of residual disease. | |
| Final publication: Roth 1999 (included). | |
| Final publication: Roth 1999 (included). | |
| Final publication: Roth 1999 (included). | |
| Participants were treated with OK‐432 (streptococcal preparation, biological response modifier). | |
| Study included participants with various gastrointestinal tumors, which were treated with a biological therapy. | |
| Study included participants with different adenocarcinomas. | |
| Insufficient information for calculation of HRs given. | |
| Publication presents only preliminary results of this study. No information about final results provided by the first author. | |
| Study not randomised. | |
| Study includes participants with colorectal and gastric cancer. Insufficient information given about results in gastric cancer. | |
| Study includes participants with colorectal and gastric cancer. Insufficient information given about results in gastric cancer. | |
| Study summarises the experience of angiotensin II‐induced hypertension to enhance drug delivery for chemotherapy. Participants were not randomised to different chemotherapy regimens. | |
| Participants were not randomised to different chemotherapy regimens but to angiotensin II‐induced hypertension to enhance chemotherapy effects or control. | |
| Text needed. | |
| Testing whether lapatinib (HER2 inhibitor) should be used in second‐line therapy in HER2‐amplified Asian population. | |
| Study not randomised. | |
| No information on overall survival. | |
| Interventions not relevant for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Reporting standards to be insufficient and/or the dose schedule to be different from other studies. | |
| Study compared the effect of intraperitoneal combined with intravenous to only intravenous chemotherapy. | |
| Insufficient information for calculation of HRs given. | |
| Study included various advanced adenocarcinomas of the gastrointestinal tract (only 5 participants with gastric cancer). | |
| Interventions not relevant for any of the comparisons specified (radiochemotherapy). | |
| A study in participants refractory to first‐line chemotherapy ‐ thus no first‐line treatment. | |
| Study not randomised. | |
| Study treatment includes lentinan (mushroom polysaccharide with immunomodulatory properties, biological therapy). | |
| Study participants had resectable tumours. One group received intraarterial chemotherapy. | |
| Not eligible for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Not relevant for any of the comparisons (docetaxel in both treatment arms). | |
| Included esophageal cancer patients. | |
| Second‐line therapy. | |
| Study treatment includes OK (streptococcal preparation, biologic response modifier). | |
| Targeted therapy. | |
| Compared methotrexate, fluorouracil, and doxorubicin versus etoposide, leucovorin, and fluorouracil versus infusional fluorouracil and cisplatin. None of the possible permutations between these regimens fit our study comparisons | |
| Study included participants with advanced gastrointestinal malignancies (only 11 participants with gastric cancer). | |
| Inconclusive data (time to progression and survival identical). | |
| Study included participants (13 of 46) with only microscopic disease in the resection margins. | |
| One study arm consisted only of oral chemotherapy (CCNU). Two other of 5 study arms differed from others only in the addition of oral CCNU (does not compare different intravenous chemotherapy regimens). | |
| Study treatment includes interferon and filgrastim (biological therapy). | |
| Participants had various gastrointestinal malignancies. Therapy includes levamisole (antihelmintic drug with immunomodulatory properties). | |
| Participants had various gastrointestinal malignancies. Therapy included levamisole (antihelmintic drug with immunomodulatory properties). | |
| Study treatment includes lentinan (mushroom polysaccharide with immunomodulatory properties, biological therapy). | |
| Not relevant for any of the comparisons. | |
| Paper reports long‐term follow‐up of the study published by Webb 1997 (included) | |
| Testing VEGF inhibitor (ramucirumab) as second‐line therapy. | |
| Compared 5‐fluorouracil, adriamycin and methotrexate vs 5‐fluorouracil, adriamycin and mitomycin‐C. This does not fit our study comparisons | |
| Published as abstract only, no further information about final results obtained by contacting the first author. | |
| Tested recombinant human endostatin, and regimen does not fit our comparisons. | |
| According to information provided by the first author the study was not randomised. | |
| Study treatment includes Elemene (product isolated from the Chinese medical herb Rhizoma zedoariae, biological therapy). | |
| Compares the feasibility of personalised chemotherapy (according to the expression of molecular markers) with standard therapy. | |
| Tested a chemoimmunotherapy combination. | |
| Intervention not eligible for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| Intervention not eligible for any of the comparisons specified. | |
| missing information to calculate HRs for OS. | |
| Final publication: Cocconi 1994 (included) |
5‐FU: 5‐Fluorouracil
A: adriamycin (also known as doxorubicin)
BSC: best supportive care
CTX: chemotherapy
FA: folinic acid
FAMe: 5‐FU 325mg/m² d 1‐5, A 40mg/m² d 1 until d 36, Me 110mg/m² orally at d 1 repeated at d 71
FAMi: 5‐FU 275mg/m² d 1‐5, A 30mg/m² d 1 until d 36, M 10mg/m² d1 repeated at d 71
FIMe: 5‐FU 325mg/m² d 1‐5 repeated at d 36, ICRF‐159 500mg/m² orally at d 2‐4 and d 36‐38, Me 110mg/m² orally at d 1 repeated at d 71
FMe: 5‐FU 300 mg/m² d 1‐5 repeated at d 36, Me 175 mg/m² orally at d 1 repeated at d 50
G‐CSF: granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor
HR: hazard ratio
ICRF: razoxane
M: mitomycin C
Me: semustine (also known as methyl‐CCNU)
OS: overall survival
RCT: randomised controlled trial
VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Trial name or title | Randomized phase III trial of docetaxel, carboplatin and 5FU versus epirubicin, cisplatin and 5FU for locally advanced gastric cancer (final publication not found) |
| Methods | RCT |
| Participants | N = 64 |
| Interventions | Arm A: docetaxel (75 mg/m² d 1) + carboplatin (AUC6 d2) + continuous infusion 5FU (1200 mg/m²/day d1‐3), repeated at d 21 versus Arm B: Epirubicin (50 mg/m² d 1) + cisplatin (60 mg/m² d1)+ continuous infusion 5FU (200 mg/m²/day d 1‐21) Prophylactically G‐CSF day 4‐9 to all participants |
| Outcomes | Toxicity, tumour response, progression‐free and overall survival |
| Starting date | 1999 |
| Contact information | Amr Abdelaziz Elsaid Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt |
| Notes | This study is currently published as abstract only. Participants were enrolled between 1999 and 2004. |
| Trial name or title | Randomized phase III study of S‐1 plus oxaliplatin versus S‐1 plus cisplatin for first‐line treatment of advanced gastric cancer |
| Methods | RCT 2 arms |
| Participants | N = 685 with unresectable advanced or recurrent gastric cancer, PS 0‐2, age ≥ 20 years |
| Interventions | Arm A (SOX): (oral S‐1 40 mg/m² twice a day d 1‐14 + oxaliplatin 100 mg/m² iv day 1, repeated at 3 weeks) versus Arm B (SP): (oral S‐1 40 mg/m² twice a day d 1‐ 21 + cisplatin 60 mg/m² iv day 8, repeated at 5 weeks) |
| Outcomes | Progression‐free survival, response rate (RR), safety, and length of hospital stay per cycle |
| Starting date | |
| Contact information | Yakult Honsha Co., Ltd., Clinical Development, Medical Development Department, Pharmaceutical Division, Tel 813‐5550‐8966 Fax 813‐3248‐5502 |
| Notes | The study is registered (JapicCTI‐101021) and has recruited 685 participants from January 2010 and October 2011. |
| Trial name or title | Isovorin: Phase III study |
| Methods | RCT 2 arms |
| Participants | Participants with histologically confirmed, advanced gastric adenocarcinoma without prior chemotherapy, PS 0‐2, age 20 to 70 years |
| Interventions | 5‐FU+ isovorin (active form of leucovorin) versus |
| Outcomes | Overall survival, response rates, time to progression, safety, quality of life |
| Starting date | — |
| Contact information | Minoru Kurihara, M.D., Showa University, Japan |
| Notes | Sponsor: Wyeth Pharmaceuticals. Final publication not found. |
| Trial name or title | Epirubicin (E) in combination with cisplatin (CDDP) and capecitabine (C) versus docetaxel (D) combined with 5‐fluorouracil (5‐FU) by continuous infusion as front‐line therapy in participants with advanced gastric cancer (AGC) |
| Methods | RCT 2 arms |
| Participants | N = 77 with advanced gastric cancer and measurable disease |
| Interventions | Arm A (ECX): epirubicin (50 mg/m² d 1) + cisplatin (60 mg/m² d 1) + capecitabine (625 mg/m² twice a day, d 1‐21) repeated at d 21 versus Arm B (DF): docetaxel (85 mg/m² d1)+ 5‐FU (750 mg/m² /day, d1‐5) qd 21 |
| Outcomes | Response rate, toxicity |
| Starting date | |
| Contact information | G.Colucci, Instituto Oncologici Bari, Bari, Italy |
| Notes | Preliminary results of this study are currently published as abstract only. Final publication not found. |
| Trial name or title | A randomized phase II pilot study prospectively evaluating treatment for participants based on ERCC1(excision repair cross‐complementing 1) for advanced/metastatic oesophageal, gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT 2 arms stratification according to ERCC1 |
| Participants | N = 225 with unresectable, advanced or recurrent gastric cancer, age ≥18 years, HER‐2 negative |
| Interventions | Arm A (FOLFOX): 4‐FU (bolus 400 mg/m², ci 2400 mg/m² )+ LV (400 mg/m²) + oxaliplatin (85 mg/m²) d 1, repeated at d 14. Arm B docetaxel (30 mg/m² on day 1 + 8 qd 21) + irinotecan (65 mg/m² on day 1 + 8 qd 21). |
| Outcomes | Progression‐free survival (PFS) between high‐ERCC1 and low‐ERCC1 participants treated with FOLFOX versus irinotecan hydrochloride plus docetaxel, overall survival, response rate, toxicity |
| Starting date | February 2012 |
| Contact information | Contact: Kimberly Kaberle: [email protected]; Dana Sparks: [email protected] Principal Investigator: Syma Iqbal |
| Notes | Sponsors: Southwest Oncology Group and National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
| Trial name or title | Peri‐operative chemotherapy with ECX (Epirubicin + Cisplatin + Capecitabine) or XP (Capecitabine + Cisplatin) in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer: a randomized, multicentre, parallel vontrol |
| Methods | Allocation: Randomised Intervention Model: Parallel assignment Masking: Single‐blind (participant) Primary Purpose: Treatment |
| Participants | Gastric cancer participants, ≥ T2 or N +; or staging II, IIIA, IIIB. |
| Interventions | Experimental: chemotherapy with ECX Preoperative chemotherapy of ECX for 3 cycles (Epirubicin 50 mg/m² on day 1; capecitabine 1000 mg/m², 2 times /day, 1 to 14 days; cisplatin 60 mg/m² on day 1, need hydration, 21 day/cycle), operation after 2˜4 weeks, and postoperative chemotherapy of ECX for 3 cycles 4˜6 weeks after surgery. Experimental: chemotherapy with XP Preoperative chemotherapy of XP for 3 cycles(capecitabine 1000 mg/m², 2 times / day, 1 to 14 days; cisplatin 60 mg/m² on day 1, need hydration, 21 day/cycle), operation after 2˜4 weeks, and postoperative chemotherapy of XP for 3 cycles 4˜6 weeks after surgery. Other Name: XP chemotherapy |
| Outcomes | Relapse‐free survival time/rate [ Time Frame: 3 years ] |
| Starting date | January 2011 |
| Contact information | Xiangdong Cheng, MD, Zhejiang Cancer Hospital |
| Notes |
| Trial name or title | A prospective, multi‐center, randomized controlled phase 2 trial of optimising platinum‐based chemotherapy based on ERCC1 expression as first‐line treatment in participants with locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT 3 arms |
| Participants | N = 180, advanced gastric cancer, 18‐65 years, KPS 70, measurable disease |
| Interventions | Active comparator: ERCC1 high expression‐group A: Cisplatin 75 mg/m², d 1; Capecitabine 1700 mg/m²/day to 2000 mg/m²/day d 1‐14 repeated at d 21 for 6 cycles.Capecitabine is to be continued until disease progression or intolerable toxicity. Experimental: ERCC1 high expression‐group B: Docetaxel 75 mg/m², d 1; Capecitabine 1700 mg/m²/day to 2000 mg/m²/day on days1‐14 every 21 days, 6 cycles. Capecitabine is to be continued until disease progression or intolerable toxicity. Active comparator: ERCC1 low expression group: Cisplatin 75 mg/m², d 1; Capecitabine 1700 mg/m²/day to 2000 mg/m²/day d 1‐14 repeated at d 21 for 6 cycles. Capecitabine is continued until disease progression or intolerable toxicity. |
| Outcomes | Progression‐free survival, overall survival, objective response rate, disease control rate, duration of response, safety, quality of life |
| Starting date | July 2013 |
| Contact information | Yunpeng Liu: [email protected], Jing Liu:[email protected] |
| Notes | Sponsor: China Medical University, China |
| Trial name or title | A randomized phase III study of low‐docetaxel oxaliplatin, capecitabine (low‐tox) vs epirubicin, oxaliplatin and capecitabine (Eox) In patients with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic gastric cancer |
| Methods | Phase 3 Allocation: Randomised Intervention Model: Parallel assignment Masking: Open‐label Primary Purpose: Treatment |
| Participants | N = 462 Age 18 to 69 years · Histologically proven diagnosis of adenocarcinoma of the stomach · HER2 negative tumour or HER2+ tumours not qualifying for herceptin therapy · Locally advanced (non resectable) or metastatic gastric cancer |
| Interventions | Experimental arm A: docetaxel & oxaliplatin & capecitabine Participants will receive cycles every 3 weeks of docetaxel (35 mg/m², intravenous at days 1 and 8 by 1‐hour infusion)and oxaliplatin (80 mg/m², intravenous at day 1 by 2‐hour infusion) and capecitabine (750 mg/ m², oral tablets of 500 mg and 150 mg, x2 daily for 2 weeks) Experimental arm B: epirubicin & oxaliplatin & capecitabine Participants will receive cycles every 3 weeks of epirubicin (50 mg/m², intravenous on day 1 by 2‐hour infusion)and oxaliplatin (130 mg/m², intravenous on day 1 by 2‐hour infusion) and capecitabine (625 mg/m²,oral tablets of 500 mg and 150 mg, x2 daily for 3 weeks) |
| Outcomes | Overall survival (OS) [Time frame: Measured as the time from randomisation to the date of death from any cause, assessed up to 18 months of follow‐up] Progression‐free survival (PFS) [Time frame: Measured as the time from randomisation to the date of local or regional progression, distant metastasis, second primary malignancy or death from any cause, whichever comes first, assessed up to 18 months of follow‐up] Objective Response Rate (CR + PR) according to RECIST 1.1 guideline [Time frame: Measured as the time from randomisation, assessed up to 18 months of follow‐up] Disease control rate: CR + PR + SD lasting > 12 weeks [Time frame: Measured as the time from randomisation, assessed up to 18 months of follow‐up] To assess tolerability of the treatments of participants with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic gastric cancer treated with docetaxel plus oxaliplatin plus capecitabine (Arm A) or with epirubicin plus oxaliplatin plus capecitabine (Arm B) |
| Starting date | January 2013 |
| Contact information | Contact: Roberto Labianca, MD +39 035 2673691 [email protected] |
| Notes |
| Trial name or title | Comparison of efficacy and tolerance between combination therapy and monotherapy as first line chemotherapy in elderly participants with advanced gastric cancer: a multicenter randomized phase 3 study |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT Phase 3 Allocation: Randomised Intervention Model: Parallel assignment Masking: Open‐label Primary Purpose: Treatment |
| Participants | N = 332, >70 years, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group 0‐2, Measurable or evaluable disease, HER‐2 negative |
| Interventions | Experimental: Platinum/fluoropyrimidine combination chemotherapy · Drug: Capecitabine/cisplatin Capecitabine/cisplatin (XP) : cisplatin 50 mg/m² (80% dose of 60 mg/²m) iv over 15 min D1, capecitabine 1000 mg/m² (80% dose of 1250 mg/m²) orally twice a day D1‐14, repeated at 3 weeks · Drug: S‐1/cisplatin S‐1/cisplatin (SP) : cisplatin 50 mg/m² (80% dose of 60 mg/²m) iv ov 15min D1, S‐1 30 mg/m² (80% dose of 40 mg/m²) orally twice a day D1‐14, repeated at 3 weeks · Drug: Capecitabine/oxaliplatin Capecitabine+oxaliplatin (XELOX): oxaliplatin 100 mg/m² (80% dose of 130 mg/m²)iv ov 120 min D1, capecitabine 800 mg/m² (80% dose of 1000 mg/m²) orally twice a day D1‐14, repeated at 3 weeks · Drug: 5‐fluorouracil/oxaliplatin 5‐fluorouracil/oxaliplatin (FOLFOX): oxaliplatin 80 mg/m² (80% dose of 100 mg/m²) iv ov 120 min, leucovorin 80 mg/m² (80% dose of 100 mg/m²) iv ov 120min, 5‐fluorouracil 1900 mg/m² (80% dose of 2400 mg/m²) iv ov 46h D1, repeated at 2 weeks Active Comparator: Fluoropyrimidine mono chemotherapy · Drug: Capecitabine Capecitabine : 1250 mg/m² orally twice a day D1‐14 repeated at 3 weeks (if Ccr < 60 mL/min, 1000 mg/m² orally twice a day) · Drug: S‐1 S‐1 : 40 mg/m² orally twice a day D1‐14 repeated at 3 weeks (if Ccr < 60 mL/min, 30 mg/m² orally twice a day) · Drug: 5‐fluorouracil 5‐fluorouracil (FL) : leucovorin 100 mg/m² iv ov 2h, 5‐fluorouracil 2400 mg/m² iv ov 46 h D1, repeated at 2 weeks Arm A (XP): cisplatin 50 mg/m² d1, capecitabine 1000 mg/m2 orally twice a day d 1‐14, repeated at day 21 Arm B (SP): cisplatin 50mg/m2 d1, S‐1 30mg/m2 orally twice a day d 1‐14, repeated at d 21 Arm C (XELOX): oxaliplatin 100 mg/m2d1, capecitabine 800 mg/² orally twice a day d1 ‐14, repeated at day 21 Arm D (FOLFOX): oxaliplatin 80 mg/m², leucovorin 80 mg/m², 5‐fluorouracil 1900 mg/m² ci 46 h d 1, repeated at day 14 |
| Outcomes | Comparison of overall survival [Time frame: up to 3 years] Comparison of progression‐free survival [Time frame: up to 2 years] Comparison of response rate [Time frame: up to 2 years] Comparison of adverse events [Time frame: up to 2 years] Comparison of quality of life [Time frame: up to 2 years] |
| Starting date | February 2014 |
| Contact information | In Sil Choi, M.D., Ph.D.; 82‐10‐9137‐3883; [email protected] |
| Notes | Sponsor and Collaborators: Seoul National University Hospital, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Korea, Korean Cancer Study Group |
| Trial name or title | Dose‐dense biweekly docetaxel, oxaliplatin and 5‐fluorouracil as first‐line treatment in advanced gastric cancer (DaeMon‐Plus) |
| Methods | Phase 2 Intervention Model: Single‐group assignment Masking: Open‐label Primary Purpose: Treatment |
| Participants | N = 30 Age 18‐75 years · Participants with histologically or cytologically confirmed unresectable gastric adenocarcinoma whose ECOG performance status are 0‐2 |
| Interventions | Experimental: docetaxel, oxaliplatin and 5‐Fu Docetaxel 50 mg/m² Oxaliplatin 85 mg/m² 5‐Fu 2800 mg/m² Repeated every two weeks |
| Outcomes | Progression‐free survival [Time frame: 2 years] |
| Starting date | November 2014 |
| Contact information | Ping Lan, MD The Sixth Affilated Hospital of Sun Yat‐sen University |
| Notes |
| Trial name or title | Randomized phase 3 study of XELOX (capecitabine plus oxaliplatin) followed by maintenance capecitabine or observation in participants with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT 2 arms Phase 3 Allocation: Randomised Intervention Model: Parallel assignment Masking: Open‐label Primary Purpose: Treatment |
| Participants | N = 184 advanced or recurrent gastric cancer, age ≥18 years, HER‐2 negative, with more than stable disease after 6 cycles 1st line of XELOX chemotherapy (objective response, non‐complete response/non‐progressive disease in cases of non‐measurable disease before XELOX chemotherapy) |
| Interventions | Arm A : Capecitabine: capecitabine 1000 mg/m² twice a day D1‐14, repeated at 3 weeks Arm B : Observation |
| Outcomes | Progression‐free survival, overall survival, quality of life (as measured by QLQ‐c30 and STO‐22), Toxicity profile |
| Starting date | January 2015 |
| Contact information | Byoungyong Shim: [email protected]; Ho Jung An: |
| Notes | Sponsor: The Catholic University of Korea |
| Trial name or title | Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy, intravenous chemotherapy combined with surgery for the treatment of advanced gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis |
| Methods | Phase 2 Intervention Model: Single‐group assignment Masking: Open‐label Primary Purpose: Treatment |
| Participants | N = 40 18‐75 years Gastric cancer confirmed by endoscopic biopsy , and enhanced CT suspected to have peritoneal metastasis, including ascites, ovarian metastasis, omentum or peritoneal metastasis. |
| Interventions | Experimental: HIPEC,Chemotherapy AND surgery
Intervention: Other: HIPEC, chemotherapy AND surgery |
| Outcomes | R0 resection [Time frame: 3 months] Adverse events [Time frame: 6 months] Overall survival time [Time Frame: 3 years] |
| Starting date | September 2015 |
| Contact information | Yian Du, MD; [email protected]; 86‐571‐88128031 |
| Notes |
| Trial name or title | The first‐line combined chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer: A prospective observational clinical study |
| Methods | Observational Model: Cohort Time Perspective: Prospective |
| Participants | N = 250 Histopathology or cytopathology confirmed unresectable locally advanced, or recurrent, or metastatic chemotherapy‐naive gastric cancer and gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma participants |
| Interventions | Observational Model: Cohort Time Perspective: Prospective |
| Outcomes | Overall survival (OS) [Time frame: From date of enrolment until the date of death from any cause, assessed up to 60 months] Progression‐free survival (PFS) [Time frame: From date of enrolment until the date of first documented progression or date of death from any cause, whichever came first, assessed up to 60 months] Objective response rate (ORR) [Time frame: The sum of complete remission (CR) rate and partial remission (PR) rate. Response will be measured through first‐line treatment completion, up to 1 year] Disease control rate (DCR) [Time frame: The sum of CR rate, PR rate and stable disease (SD) rate. Response will be measured through first‐line treatment completion, up to 1 year] Number of participants with treatment‐related adverse events as assessed by CTCAE v4.0 [Time frame: Through first‐line treatment completion, up to 24 weeks.] |
| Starting date | January 2013 |
| Contact information | Xianglin Yuan, MD,PHD Tongji hospital of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology |
| Notes |
| Trial name or title | Phase II study of weekly metronomic chemotherapy using weekly aclitaxel, Oxaliplatin, Leucovorin and 5‐FU (POLF) in participants with advanced gastric cancer |
| Methods | Phase 2 Intervention Model: Single‐group assignment Masking: Open‐label Primary Purpose: Treatment |
| Participants | N = 40 18‐70 years AJCC stage 3 or 4 gastric cancer |
| Interventions | Experimental: POLF regimen Paclitaxel 60 mg/m² , oxaliplatin 50 mg/m² , leucovorin 20 mg/m² , and 5‐FU 425 mg/m² IV weekly Intervention: Drug: paclitaxel 60 mg/m² , oxaliplatin 50 mg/m² , leucovorin 20 mg/m² , and 5‐FU 425 mg/m² IV weekly |
| Outcomes | Response rate [Time frame: 3 months] ‐based on Recist 1.1 Adverse events [Time frame: 2 years] ‐based on NCI‐CTC v.2 Progression‐free survival [Time frame: 2 years] Overall survival [Time frame: 2 years] |
| Starting date | May 2015 |
| Contact information | Contact: Nick N Chen, M.D., Ph.D. 206‐588‐1722 [email protected] Contact: Jie Liu, M.D. 021‐5288236 [email protected] |
| Notes |
| Trial name or title | ASE III randomised trial to evaluate folfox with or without docetaxel (TFOX) as 1st line chemotherapy for locally advanced or metastatic oesophago‐gastric carcinoma (GASTFOX) |
| Methods | Phase 3 Allocation: Randomised Intervention Model: Parallel assignment Masking: No masking Primary Purpose: Treatment |
| Participants | N = 506 Gastric or gastro‐oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (all Siewert), histologically proven (on primary tumour or metastatic lesion), HER2 negative (positive HER2 status is defined by a positive IHC test of 3+ or IHC of 2+ with positive FISH) Metastatic or non‐resectable (locally advanced) disease |
| Interventions | Active Comparator: FOLFOX Cycles every 15 days until progression disease Experimental: TFOX Cycles every 15 days until progression disease Interventions: Drug: oxaliplatin
|
| Outcomes | Progression‐free survival [Time frame: 12 months after last randomisation] Overall survival toxicity events (adverse events) according to NCI‐CTC v4.0 [Time frame: 12 months after last randomisation] Objective response rate [Time frame: 12 months after last randomisation] Toxicity events according to NCI‐CTC v4.0 [Time frame: 12 months after last randomisation] |
| Starting date | December 2016 |
| Contact information | Contact: Marie MOREAU +33 (0)380393404 marie.moreau@u‐bourgogne.fr |
| Notes | PRODIGE 51 |
| Trial name or title | A randomized phase II trial to elucidate the efficacy of capecitabine plus cisplatin (XP) and S‐1 plus cisplatin (SP) as a first‐line treatment for advanced gastric cancer: XP ascertainment vs. SP randomized PII trial (XParTS II) |
| Methods | Multicentre RCT |
| Participants | N = 100 (planned) |
| Interventions | Arm A: S‐1 (40 mg/m² twice a day d1‐21) + cisplatin (60 mg/m² d 8) repeated at d 35 versus Arm B: capecitabine (1000 mg/² d1‐14) + cisplatin (80 mg/m² d 1) repeated at d 21 |
| Outcomes | Progression‐free survival, overall survival, time to treatment failure, tumour response, safety |
| Starting date | August 2011 |
| Contact information | Akira Tsuburaya, Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Kanagawa Cancer Center, 1‐1‐2, Nakao, 241‐0815, Yokohama, Asahi‐ku, Japan, [email protected] |
| Notes | The study is registered (NCT01406249), the study protocol is published. Estimated study completion date is June 2015. The study is not yet published. |
5‐FU: 5‐fluorouracil
ci: continuous infusion
d: day
E: epirubicin
G‐CSF: granulocyte colony stimulating factor
PFS: progression‐free survival
RCT: randomised controlled trial
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 3 | 184 | Hazard ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.37 [0.24, 0.55] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Chemotherapy versus best supportive care, Outcome 1 Overall survival. | ||||
| 2 Time to progression Show forest plot | 2 | 144 | Hazard ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.31 [0.22, 0.43] |
| Analysis 1.2 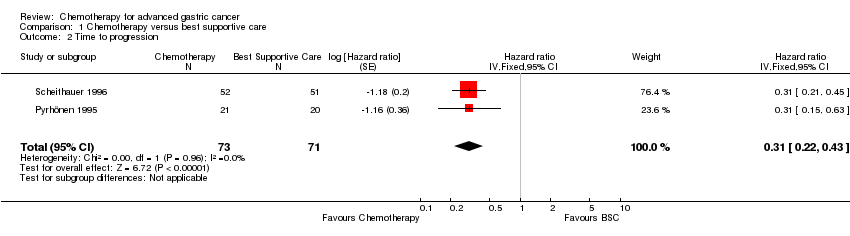 Comparison 1 Chemotherapy versus best supportive care, Outcome 2 Time to progression. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 23 | 4447 | Hazard ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.84 [0.79, 0.89] |
| Analysis 2.1  Comparison 2 Combination versus single‐agent chemotherapy, Outcome 1 Overall survival. | ||||
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 18 | 2833 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.30 [1.94, 2.72] |
| Analysis 2.2 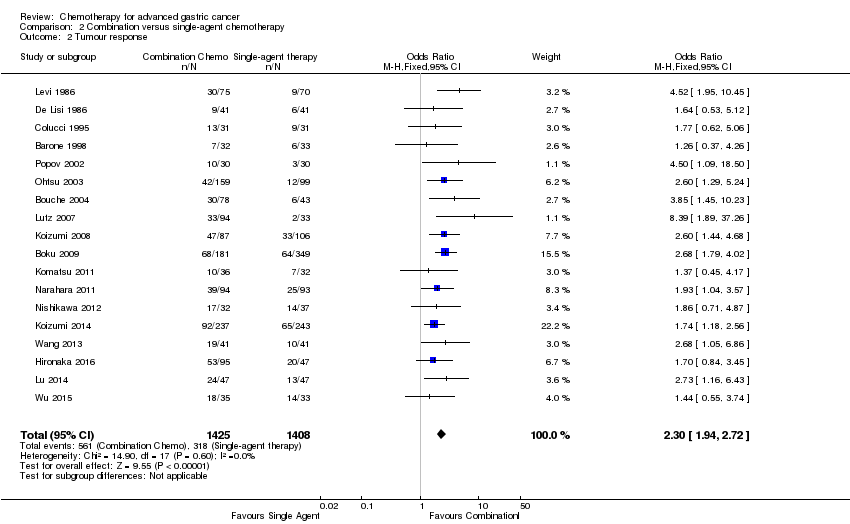 Comparison 2 Combination versus single‐agent chemotherapy, Outcome 2 Tumour response. | ||||
| 3 Time to progression Show forest plot | 4 | 720 | Hazard ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.69 [0.55, 0.87] |
| Analysis 2.3 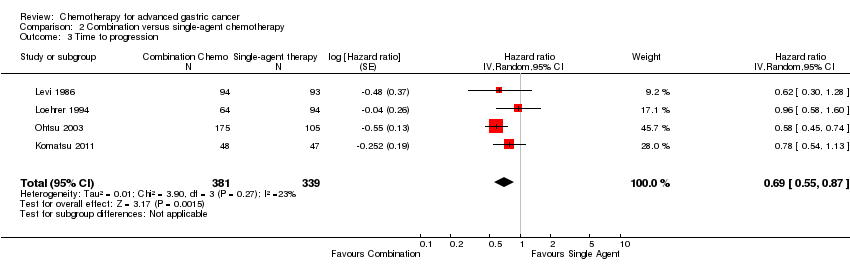 Comparison 2 Combination versus single‐agent chemotherapy, Outcome 3 Time to progression. | ||||
| 4 Treatment‐related death Show forest plot | 18 | 3876 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.64 [0.83, 3.24] |
| Analysis 2.4  Comparison 2 Combination versus single‐agent chemotherapy, Outcome 4 Treatment‐related death. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 4 | 579 | Hazard ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.61, 0.89] |
| Analysis 3.1  Comparison 3 5‐FU/cisplatin/anthracycline combinations versus 5‐FU/cisplatin combinations (without anthracyclines), Outcome 1 Overall survival. | ||||
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 3.2 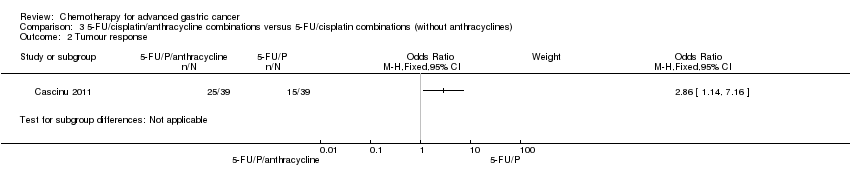 Comparison 3 5‐FU/cisplatin/anthracycline combinations versus 5‐FU/cisplatin combinations (without anthracyclines), Outcome 2 Tumour response. | ||||
| 3 Time to progression Show forest plot | 1 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 3.3  Comparison 3 5‐FU/cisplatin/anthracycline combinations versus 5‐FU/cisplatin combinations (without anthracyclines), Outcome 3 Time to progression. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 7 | 1147 | Hazard ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.73, 0.92] |
| Analysis 4.1  Comparison 4 5‐FU/cisplatin/anthracycline combinations versus 5‐FU/anthracycline combinations (without cisplatin), Outcome 1 Overall survival. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 10 | 2135 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.80, 0.95] |
| Analysis 5.1  Comparison 5 Chemotherapy with irinotecan versus non‐irinotecan‐containing regimes, Outcome 1 Overall survival. | ||||
| 1.1 Substitutive comparisons | 6 | 826 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.75, 1.00] |
| 1.2 Additive comparisons | 3 | 500 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.76, 1.03] |
| 1.3 Other comparisons | 2 | 809 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.76, 1.00] |
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 10 | 1266 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.72 [1.24, 2.40] |
| Analysis 5.2 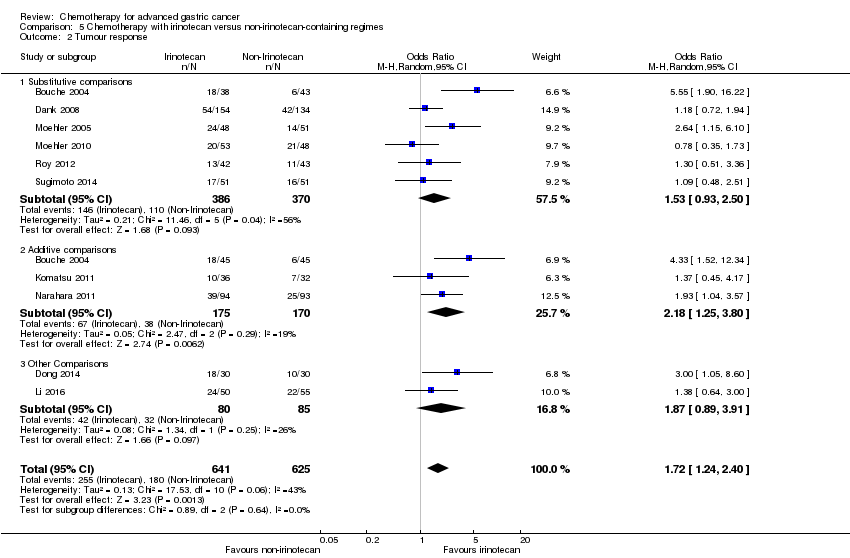 Comparison 5 Chemotherapy with irinotecan versus non‐irinotecan‐containing regimes, Outcome 2 Tumour response. | ||||
| 2.1 Substitutive comparisons | 6 | 756 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.53 [0.93, 2.50] |
| 2.2 Additive comparisons | 3 | 345 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.18 [1.25, 3.80] |
| 2.3 Other Comparisons | 2 | 165 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.87 [0.89, 3.91] |
| 3 Progression‐free survival Show forest plot | 7 | 1640 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.69, 0.84] |
| Analysis 5.3  Comparison 5 Chemotherapy with irinotecan versus non‐irinotecan‐containing regimes, Outcome 3 Progression‐free survival. | ||||
| 3.1 Substitutive comparison | 5 | 741 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.72, 1.00] |
| 3.2 Additive comparisons | 1 | 90 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.51 [0.33, 0.77] |
| 3.3 Other comparisons | 2 | 809 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.66, 0.84] |
| 4 Treatment‐related death Show forest plot | 9 | 1979 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.23, 3.32] |
| Analysis 5.4  Comparison 5 Chemotherapy with irinotecan versus non‐irinotecan‐containing regimes, Outcome 4 Treatment‐related death. | ||||
| 5 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity Show forest plot | 9 | 1979 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.46, 2.20] |
| Analysis 5.5 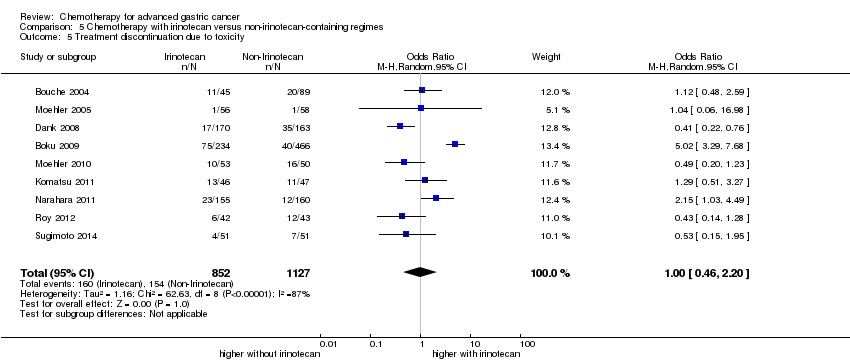 Comparison 5 Chemotherapy with irinotecan versus non‐irinotecan‐containing regimes, Outcome 5 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 8 | 2001 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.78, 0.95] |
| Analysis 6.1  Comparison 6 Chemotherapy with docetaxel versus non‐docetaxel‐containing regimes, Outcome 1 Overall survival. | ||||
| 1.1 Substitutive comparisons | 3 | 479 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.87, 1.27] |
| 1.2 Additive comparisons | 4 | 1466 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.80 [0.71, 0.91] |
| 1.3 Other comparisons | 1 | 56 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.80 [0.46, 1.39] |
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 9 | 1820 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.37 [1.03, 1.83] |
| Analysis 6.2  Comparison 6 Chemotherapy with docetaxel versus non‐docetaxel‐containing regimes, Outcome 2 Tumour response. | ||||
| 2.1 Substitutive comparison | 4 | 525 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.71, 1.50] |
| 2.2 Additive comparison | 4 | 1235 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.83 [1.45, 2.32] |
| 2.3 Other comparisons | 1 | 60 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.12, 0.96] |
| 3 Time to progression Show forest plot | 2 | 360 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.85, 1.32] |
| Analysis 6.3  Comparison 6 Chemotherapy with docetaxel versus non‐docetaxel‐containing regimes, Outcome 3 Time to progression. | ||||
| 4 Progression‐free survival Show forest plot | 5 | 1498 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.63, 0.91] |
| Analysis 6.4  Comparison 6 Chemotherapy with docetaxel versus non‐docetaxel‐containing regimes, Outcome 4 Progression‐free survival. | ||||
| 4.1 Substitutive comparisons | 1 | 119 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 1.15 [0.77, 1.72] |
| 4.2 Additive comparison (PFS) | 3 | 1323 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.70 [0.61, 0.81] |
| 4.3 Other comparisons | 1 | 56 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.55, 1.60] |
| 5 Treatment‐related death Show forest plot | 7 | 2113 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.55, 2.20] |
| Analysis 6.5  Comparison 6 Chemotherapy with docetaxel versus non‐docetaxel‐containing regimes, Outcome 5 Treatment‐related death. | ||||
| 6 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity Show forest plot | 5 | 1066 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.53, 1.25] |
| Analysis 6.6  Comparison 6 Chemotherapy with docetaxel versus non‐docetaxel‐containing regimes, Outcome 6 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall Survival Show forest plot | 5 | 732 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.79, 1.11] |
| Analysis 7.1 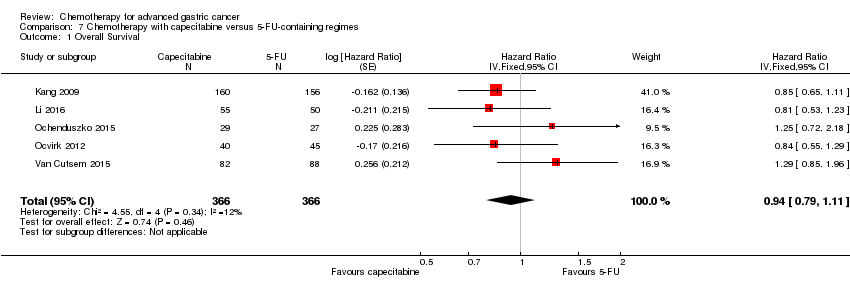 Comparison 7 Chemotherapy with capecitabine versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 1 Overall Survival. | ||||
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 4 | 636 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.40, 1.79] |
| Analysis 7.2 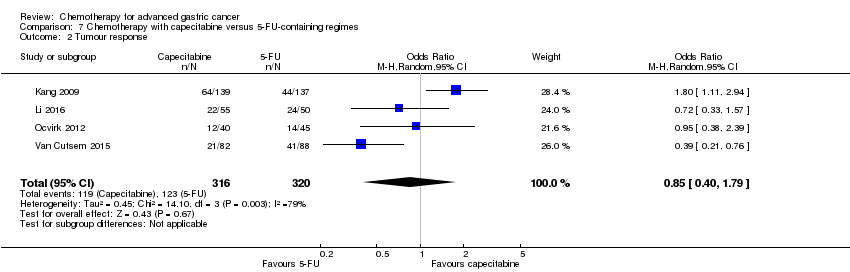 Comparison 7 Chemotherapy with capecitabine versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 2 Tumour response. | ||||
| 3 Time to progression Show forest plot | 1 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 7.3  Comparison 7 Chemotherapy with capecitabine versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 3 Time to progression. | ||||
| 4 Progression‐free survival Show forest plot | 4 | 647 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.98 [0.77, 1.23] |
| Analysis 7.4 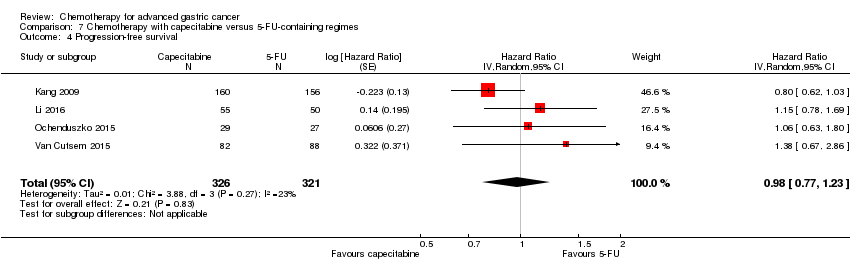 Comparison 7 Chemotherapy with capecitabine versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 4 Progression‐free survival. | ||||
| 5 Treatment‐related death Show forest plot | 2 | 481 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.88 [0.23, 15.15] |
| Analysis 7.5  Comparison 7 Chemotherapy with capecitabine versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 5 Treatment‐related death. | ||||
| 6 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 7.6  Comparison 7 Chemotherapy with capecitabine versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 6 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall Survival Show forest plot | 5 | 1105 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.67, 0.98] |
| Analysis 8.1  Comparison 8 Chemotherapy with oxaliplatin versus the same regime including cisplatin, Outcome 1 Overall Survival. | ||||
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 5 | 1081 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.38 [1.08, 1.76] |
| Analysis 8.2  Comparison 8 Chemotherapy with oxaliplatin versus the same regime including cisplatin, Outcome 2 Tumour response. | ||||
| 3 Progression‐free survival Show forest plot | 4 | 1034 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.66, 1.19] |
| Analysis 8.3  Comparison 8 Chemotherapy with oxaliplatin versus the same regime including cisplatin, Outcome 3 Progression‐free survival. | ||||
| 4 Treatment‐related death Show forest plot | 5 | 1132 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.47 [0.17, 1.30] |
| Analysis 8.4 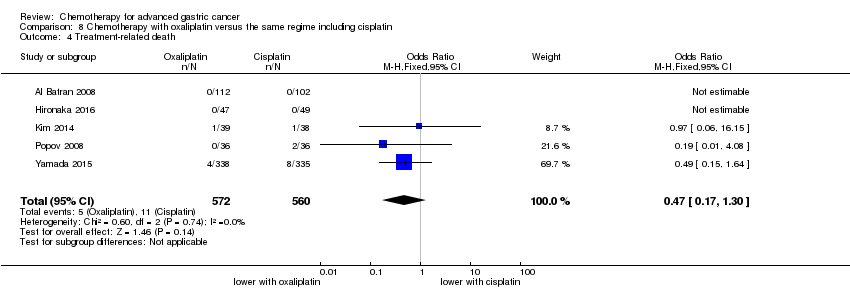 Comparison 8 Chemotherapy with oxaliplatin versus the same regime including cisplatin, Outcome 4 Treatment‐related death. | ||||
| 5 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity Show forest plot | 3 | 970 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.44, 2.13] |
| Analysis 8.5 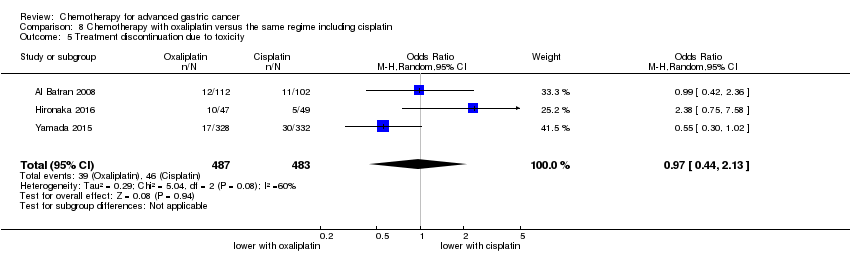 Comparison 8 Chemotherapy with oxaliplatin versus the same regime including cisplatin, Outcome 5 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 3 | 482 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.71, 1.06] |
| Analysis 9.1  Comparison 9 Taxane‐platinum‐fluoropyrimidine combinations versus taxane‐platinum (without fluoropyrimidine), Outcome 1 Overall survival. | ||||
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 3 | 482 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.08 [1.37, 3.15] |
| Analysis 9.2  Comparison 9 Taxane‐platinum‐fluoropyrimidine combinations versus taxane‐platinum (without fluoropyrimidine), Outcome 2 Tumour response. | ||||
| 3 Progression‐free survival Show forest plot | 3 | 482 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.59, 0.93] |
| Analysis 9.3  Comparison 9 Taxane‐platinum‐fluoropyrimidine combinations versus taxane‐platinum (without fluoropyrimidine), Outcome 3 Progression‐free survival. | ||||
| 4 Treatment‐related death Show forest plot | 3 | 482 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.95 [0.73, 5.17] |
| Analysis 9.4 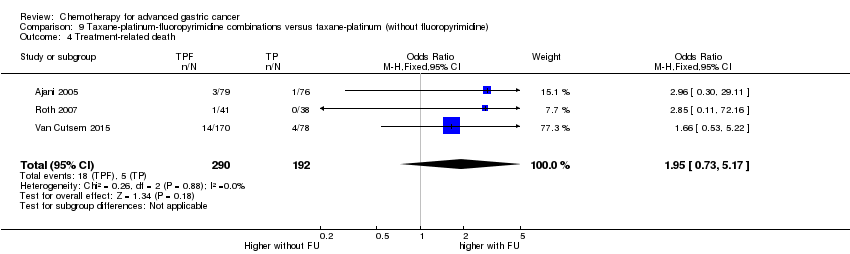 Comparison 9 Taxane‐platinum‐fluoropyrimidine combinations versus taxane‐platinum (without fluoropyrimidine), Outcome 4 Treatment‐related death. | ||||
| 5 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity Show forest plot | 2 | 234 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.71 [0.79, 3.69] |
| Analysis 9.5 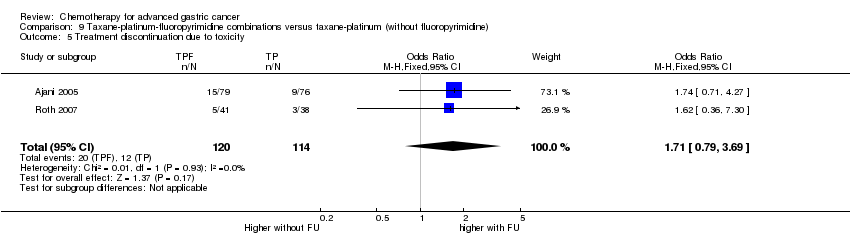 Comparison 9 Taxane‐platinum‐fluoropyrimidine combinations versus taxane‐platinum (without fluoropyrimidine), Outcome 5 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall Survival Show forest plot | 4 | 1793 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.83, 1.00] |
| Analysis 10.1  Comparison 10 S‐1 versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 1 Overall Survival. | ||||
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 7 | 1753 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.73 [1.01, 2.94] |
| Analysis 10.2  Comparison 10 S‐1 versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 2 Tumour response. | ||||
| 3 Progression‐free survival Show forest plot | 4 | 1942 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.70, 1.04] |
| Analysis 10.3 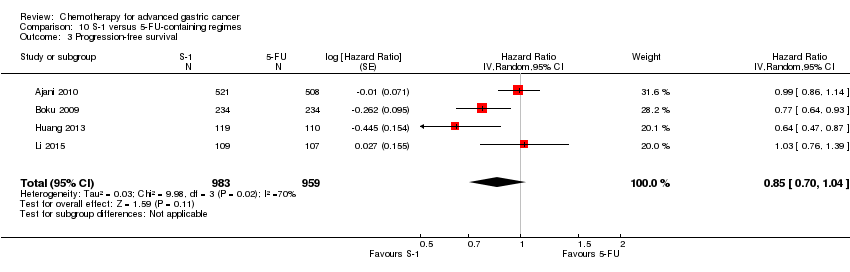 Comparison 10 S‐1 versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 3 Progression‐free survival. | ||||
| 4 Time‐to treatment failure Show forest plot | 5 | 1818 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.76, 1.01] |
| Analysis 10.4  Comparison 10 S‐1 versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 4 Time‐to treatment failure. | ||||
| 5 Treatment‐related deaths Show forest plot | 4 | 1962 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.56 [0.30, 1.06] |
| Analysis 10.5  Comparison 10 S‐1 versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 5 Treatment‐related deaths. | ||||
| 6 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity Show forest plot | 3 | 1726 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.63, 1.13] |
| Analysis 10.6  Comparison 10 S‐1 versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 6 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity. | ||||

Study flow diagram: review update
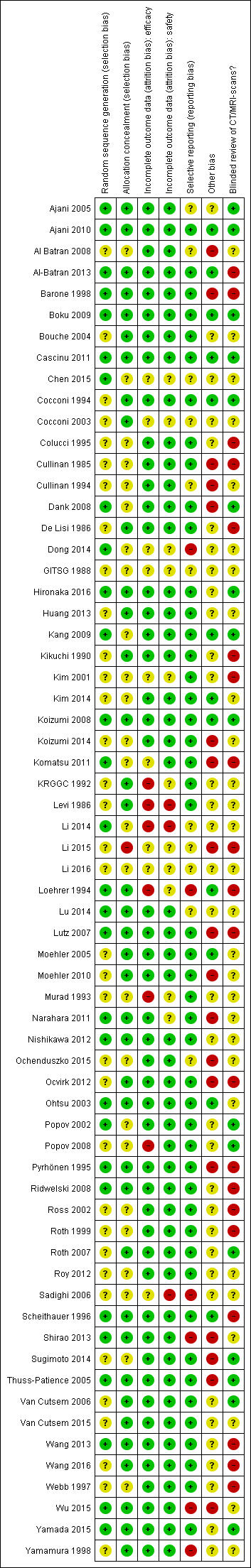
'Risk of bias' summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
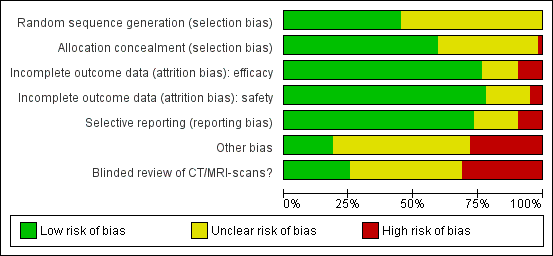
'Risk of bias' graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.

Comparison 1 Chemotherapy versus best supportive care, Outcome 1 Overall survival.

Comparison 1 Chemotherapy versus best supportive care, Outcome 2 Time to progression.

Comparison 2 Combination versus single‐agent chemotherapy, Outcome 1 Overall survival.

Comparison 2 Combination versus single‐agent chemotherapy, Outcome 2 Tumour response.

Comparison 2 Combination versus single‐agent chemotherapy, Outcome 3 Time to progression.

Comparison 2 Combination versus single‐agent chemotherapy, Outcome 4 Treatment‐related death.

Comparison 3 5‐FU/cisplatin/anthracycline combinations versus 5‐FU/cisplatin combinations (without anthracyclines), Outcome 1 Overall survival.

Comparison 3 5‐FU/cisplatin/anthracycline combinations versus 5‐FU/cisplatin combinations (without anthracyclines), Outcome 2 Tumour response.

Comparison 3 5‐FU/cisplatin/anthracycline combinations versus 5‐FU/cisplatin combinations (without anthracyclines), Outcome 3 Time to progression.

Comparison 4 5‐FU/cisplatin/anthracycline combinations versus 5‐FU/anthracycline combinations (without cisplatin), Outcome 1 Overall survival.

Comparison 5 Chemotherapy with irinotecan versus non‐irinotecan‐containing regimes, Outcome 1 Overall survival.

Comparison 5 Chemotherapy with irinotecan versus non‐irinotecan‐containing regimes, Outcome 2 Tumour response.

Comparison 5 Chemotherapy with irinotecan versus non‐irinotecan‐containing regimes, Outcome 3 Progression‐free survival.

Comparison 5 Chemotherapy with irinotecan versus non‐irinotecan‐containing regimes, Outcome 4 Treatment‐related death.

Comparison 5 Chemotherapy with irinotecan versus non‐irinotecan‐containing regimes, Outcome 5 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity.

Comparison 6 Chemotherapy with docetaxel versus non‐docetaxel‐containing regimes, Outcome 1 Overall survival.

Comparison 6 Chemotherapy with docetaxel versus non‐docetaxel‐containing regimes, Outcome 2 Tumour response.

Comparison 6 Chemotherapy with docetaxel versus non‐docetaxel‐containing regimes, Outcome 3 Time to progression.

Comparison 6 Chemotherapy with docetaxel versus non‐docetaxel‐containing regimes, Outcome 4 Progression‐free survival.

Comparison 6 Chemotherapy with docetaxel versus non‐docetaxel‐containing regimes, Outcome 5 Treatment‐related death.

Comparison 6 Chemotherapy with docetaxel versus non‐docetaxel‐containing regimes, Outcome 6 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity.

Comparison 7 Chemotherapy with capecitabine versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 1 Overall Survival.

Comparison 7 Chemotherapy with capecitabine versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 2 Tumour response.

Comparison 7 Chemotherapy with capecitabine versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 3 Time to progression.

Comparison 7 Chemotherapy with capecitabine versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 4 Progression‐free survival.

Comparison 7 Chemotherapy with capecitabine versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 5 Treatment‐related death.

Comparison 7 Chemotherapy with capecitabine versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 6 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity.

Comparison 8 Chemotherapy with oxaliplatin versus the same regime including cisplatin, Outcome 1 Overall Survival.

Comparison 8 Chemotherapy with oxaliplatin versus the same regime including cisplatin, Outcome 2 Tumour response.

Comparison 8 Chemotherapy with oxaliplatin versus the same regime including cisplatin, Outcome 3 Progression‐free survival.

Comparison 8 Chemotherapy with oxaliplatin versus the same regime including cisplatin, Outcome 4 Treatment‐related death.

Comparison 8 Chemotherapy with oxaliplatin versus the same regime including cisplatin, Outcome 5 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity.

Comparison 9 Taxane‐platinum‐fluoropyrimidine combinations versus taxane‐platinum (without fluoropyrimidine), Outcome 1 Overall survival.

Comparison 9 Taxane‐platinum‐fluoropyrimidine combinations versus taxane‐platinum (without fluoropyrimidine), Outcome 2 Tumour response.

Comparison 9 Taxane‐platinum‐fluoropyrimidine combinations versus taxane‐platinum (without fluoropyrimidine), Outcome 3 Progression‐free survival.

Comparison 9 Taxane‐platinum‐fluoropyrimidine combinations versus taxane‐platinum (without fluoropyrimidine), Outcome 4 Treatment‐related death.

Comparison 9 Taxane‐platinum‐fluoropyrimidine combinations versus taxane‐platinum (without fluoropyrimidine), Outcome 5 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity.

Comparison 10 S‐1 versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 1 Overall Survival.

Comparison 10 S‐1 versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 2 Tumour response.

Comparison 10 S‐1 versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 3 Progression‐free survival.

Comparison 10 S‐1 versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 4 Time‐to treatment failure.

Comparison 10 S‐1 versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 5 Treatment‐related deaths.

Comparison 10 S‐1 versus 5‐FU‐containing regimes, Outcome 6 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity.
| Chemotherapy versus best supportive care for advanced gastric cancer | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with advanced gastric cancer Control: best supportive care alone | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Best supportive care | Chemotherapy | |||||
| Overall survival | Study population | HR 0.37 | 184 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 4.3 months | 11.0 months | |||||
| Time to progression | Study population | HR 0.31 | 144 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 2.5 months | 7.4 months | |||||
| *For time‐to‐event outcomes, e.g. overall survival, the assumed and corresponding risks were obtained by calculating the weighted average of the median survival durations reported in included studies. For dichotomous outcomes, the assumed and corresponding risks (and their 95% confidence interval) are based on proportions of events in the control and intervention groups respectively. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Early termination of Pyrhönen 1995; downgraded by one level for risk of bias. Outcomes shown include those which were measured in the studies, or reported in a consistent fashion across included studies. Several critical outcomes (e.g. tumour response, treatment‐related death, and discontinuation due to toxicity) were not evaluated or reported in a consistent fashion in these studies, as they were mainly conducted before year 2000. | ||||||
| Combination versus single‐agent chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with advanced gastric cancer Control: single‐agent chemotherapy | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Single‐agent chemotherapy | Combination | |||||
| Overall survival | Study population | HR 0.84 | 4447 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
|
|
| |||||
| Tumour response | Study population | OR 2.30 | 2833 | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | ||
| 226 per 1000 | 402 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 231 per 1000 | 409 per 1000 | |||||
| Time to progression | Study population | HR 0.69 | 720 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 2.8 months | 4.1 months | |||||
| Treatment‐related death | Study population | OR 1.64 | 3876 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 5 per 1000 | 9 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 0 per 1000 | 0 per 1000 | |||||
| *For time‐to‐event outcomes, e.g. overall survival, the assumed and corresponding risks were obtained by calculating the weighted average of the median survival durations reported in included studies. For dichotomous outcomes, the assumed and corresponding risks (and their 95% confidence interval) are based on proportions of events in the control and intervention groups respectively. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Downgraded by one level for risk of bias. | ||||||
| 5‐FU/cisplatin/anthracycline combinations versus 5‐FU/cisplatin combinations (without anthracyclines) for advanced gastric cancer | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with advanced gastric cancer Control: 5‐FU/cisplatin combinations (without anthracyclines) | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| 5‐FU/cisplatin combinations (without anthracyclines) | 5‐FU/cisplatin/anthracycline combinations | |||||
| Overall survival | Study population | HR 0.74 | 579 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 8.6 months | 9.9 months | |||||
| Tumour response | Study population | OR 2.86 | 78 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 385 per 1000 | 641 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 385 per 1000 | 642 per 1000 | |||||
| Time to progression | Study population | HR 0.62 | 78 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Median survival durations from the only included study | |
| 7.9 months | 12.1 months | |||||
| *For time‐to‐event outcomes, e.g. overall survival, the assumed and corresponding risks were obtained by calculating the weighted average of the median survival durations reported in included studies. For dichotomous outcomes, the assumed and corresponding risks (and their 95% confidence interval) are based on proportions of events in the control and intervention groups respectively. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Downgraded by one level for risk of bias. Outcomes shown include those which were measured in the studies, or reported in a consistent fashion across included studies. Several critical outcomes (e.g. treatment‐related death and discontinuation due to toxicity) were not evaluated or reported in a consistent fashion in these studies, as they were mainly conducted before year 2000. | ||||||
| 5‐FU/cisplatin/anthracycline combinations versus 5‐FU/anthracycline combinations (without cisplatin) for advanced gastric cancer | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with advanced gastric cancer Control: 5‐FU/cisplatin combinations (without anthracyclines) | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| 5‐FU/anthracycline combinations (without cisplatin) | 5‐FU/cisplatin/anthracycline combinations | |||||
| Overall survival | Study population | HR 0.82 | 1147 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 6.2 months | 8.4 months | |||||
| *For time‐to‐event outcomes, e.g. overall survival, the assumed and corresponding risks were obtained by calculating the weighted average of the median survival durations reported in included studies. For dichotomous outcomes, the assumed and corresponding risks (and their 95% confidence interval) are based on proportions of events in the control and intervention groups respectively. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Downgraded by one level for risk of bias. Several critical outcomes (i.e. tumour response, progression‐free survival, treatment‐related death and discontinuation due to toxicity) were not evaluated or reported in a consistent fashion in these studies, most of which were conducted before year 2000. | ||||||
| Irinotecan versus non‐irinotecan‐containing regimens for advanced gastric cancer | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with advanced gastric cancer Control: non‐irinotecan‐containing regimens | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Non‐irinotecan‐containing regimens | Chemotherapy with Irinotecan | |||||
| Overall survival | Study population | HR 0.87 | 2135 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 9.7 months | 11.3 months | |||||
| Overall survival ‐ Substitutive comparisons | Study population | HR 0.87 (0.75 to 1.00) | 826 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 9.1 months | 9.9 months | |||||
| Overall survival ‐ Additive comparisons | Study population | HR 0.88 | 500 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 10.9 months | 11.9 months | |||||
| Overall survival ‐ Other comparisons | Study population | HR 0.87 | 809 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 11.4 months | 12.6 months | |||||
| Tumour response | Study population | OR 1.72 (1.24 to 2.40) | 1266 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 288 per 1000 | 410 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 275 per 1000 | 395 per 1000 | |||||
| Tumour response ‐ Substitutive comparisons | Study population | OR 1.53 (0.93 to 2.50) | 756 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 297 per 1000 | 393 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 294 per 1000 | 389 per 1000 | |||||
| Tumour response ‐ Additive comparisons | Study population | OR 2.18 (1.25 to 3.80) | 345 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 224 per 1000 | 386 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 219 per 1000 | 379 per 1000 | |||||
| Tumour response ‐ Other comparisons | Study population | OR 1.87 | 165 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 376 per 1000 | 530 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 367 per 1000 | 520 per 1000 | |||||
| Progression‐free survival | Study population | HR 0.76 (0.69 to 0.84) | 1640 | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 4.4 months | 5.9 months | |||||
| Progression‐free survival ‐ Substitutive comparison | Study population | HR 0.85 (0.72 to 1.00) | 741 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 4.2 months | 5.3 months | |||||
| Progression‐free survival ‐ Additive comparisons | Study population | HR 0.51 | 90 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Median survival durations from the only included study | |
| 3.2 months | 6.9 months | |||||
| Progression‐free survival ‐ Other comparisons | Study population | HR 0.74 (0.66 to 0.84) | 809 | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 5.4 months | 6.6 months | |||||
| Treatment‐related death | Study population | OR 0.88 (0.23 to 3.32) | 1979 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 10 per 1000 | 9 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 2 per 1000 | 2 per 1000 | |||||
| Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity | Study population | OR 1.00 (0.46 to 2.20) | 1979 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 137 per 1000 | 137 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 215 per 1000 | 215 per 1000 | |||||
| *For time‐to‐event outcomes, e.g. overall survival, the assumed and corresponding risks were obtained by calculating the weighted average of the median survival durations reported in included studies. For dichotomous outcomes, the assumed and corresponding risks (and their 95% confidence interval) are based on proportions of events in the control and intervention groups respectively. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Downgraded by one level for risk of bias. | ||||||
| Docetaxel versus non‐docetaxel‐containing regimens for advanced gastric cancer | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with advanced gastric cancer Control: non‐docetaxel‐containing regimens | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Non‐docetaxel‐containing regimens | Chemotherapy with docetaxel | |||||
| Overall survival | Study population | HR 0.86 (0.78 to 0.95) | 2001 | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 9.9 months | 11.2 months | |||||
| Overall survival ‐ Substitutive comparisons | Study population | HR 1.05 (0.87 to 1.27) | 479 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 9.4 months | 9.2 months | |||||
| Overall survival ‐ Additive comparisons | Study population | HR 0.80 (0.71 to 0.91) | 1466 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 10.6 months | 12.3 months | |||||
| Overall survival ‐ Other comparisons | Study population | HR 0.80 (0.46 to 1.39) | 56 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Median survival durations from the only included study | |
| 9.5 months | 11.9 months | |||||
| Tumour response | Study population | OR 1.37 (1.03 to 1.83) | 1820 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ||
| 311 per 1000 | 382 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 310 per 1000 | 381 per 1000 | |||||
| Tumour response ‐ Substitutive comparison | Study population | OR 1.03 (0.71 to 1.50) | 525 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ||
| 314 per 1000 | 320 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 327 per 1000 | 334 per 1000 | |||||
| Tumour response ‐ Additive comparison | Study population | OR 1.83 (1.45 to 2.32) | 1235 | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | ||
| 295 per 1000 | 434 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 296 per 1000 | 435 per 1000 | |||||
| Tumour response ‐ Other comparison | Study population | OR 0.33 (0.12 to 0.96) | 60 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 600 per 1000 | 331 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 600 per 1000 | 331 per 1000 | |||||
| Time to progression | Study population | HR 1.06 (0.85 to 1.32) | 360 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 6.0 months | 5.9 months | |||||
| Progression‐free survival | Study population | HR 0.76 (0.63 to 0.91) | 1498 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 4.8 months | 6.0 months | |||||
| Progression‐free survival ‐ Substitutive comparisons | Study population | HR 1.15 (0.77 to 1.72) | 119 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Median survival durations from the only included study | |
| 4.9 months | 4.6 months | |||||
| Progression‐free survival ‐ Additive comparison | Study population | HR 0.70 (0.61 to 0.81) | 1323 | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 4.3 months | 6.0 months | |||||
| Progression‐free survival ‐ Other comparison | Study population | HR 0.94 (0.55 to 1.60) | 56 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Median survival durations from the only included study | |
| 6.4 months | 6.8 months | |||||
| Treatment‐related death | Study population | OR 1.10 | 2113 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ||
| 12 per 1000 | 14 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 5 per 1000 | 5 per 1000 | |||||
| Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity | Study population | OR 0.81 (0.53 to 1.25) | 1066 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 211 per 1000 | 178 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 197 per 1000 | 166 per 1000 | |||||
| *For time‐to‐event outcomes, e.g. overall survival, the assumed and corresponding risks were obtained by calculating the weighted average of the median survival durations reported in included studies. For dichotomous outcomes, the assumed and corresponding risks (and their 95% confidence interval) are based on proportions of events in the control and intervention groups respectively. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Downgraded by one level for imprecision. | ||||||
| Capecitabine versus 5‐FU‐containing regimens for advanced gastric cancer | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with advanced gastric cancer Control: 5‐FU‐containing regimens | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| 5‐FU‐containing regimens | Capecitabine‐containing regimens | |||||
| Overall Survival | Study population | HR 0.94 (0.79 to 1.11) | 732 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 10.9 months | 10.8 months | |||||
| Tumour response | Study population | OR 0.85 (0.40 to 1.79) | 636 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 384 per 1000 | 347 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 394 per 1000 | 356 per 1000 | |||||
| Time to progression | Study population | HR 0.72 (0.47 to 1.12) | 85 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Median survival durations from the only included study | |
| 5.5 months | 6.8 months | |||||
| Progression‐free survival | Study population | HR 0.98 (0.77 to 1.23) | 647 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 6.7 months | 6.5 months | |||||
| Treatment‐related death | Study population | OR 1.88 (0.23 to 15.15) | 481 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 21 per 1000 | 38 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 24 per 1000 | 44 per 1000 | |||||
| Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity | Study population | OR 0.99 (0.56 to 1.77) | 311 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 181 per 1000 | 179 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 181 per 1000 | 180 per 1000 | |||||
| *For time‐to‐event outcomes, e.g. overall survival, the assumed and corresponding risks were obtained by calculating the weighted average of the median survival durations reported in included studies. For dichotomous outcomes, the assumed and corresponding risks (and their 95% confidence interval) are based on proportions of events in the control and intervention groups respectively. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Downgraded by one level for risk of bias. | ||||||
| Oxaliplatin versus the same regimen including cisplatin for advanced gastric cancer | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with advanced gastric cancer Control: the same regimen including cisplatin | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Cisplatin‐containing regimen | Oxaliplatin‐containing regimen | |||||
| Overall Survival | Study population | HR 0.81 (0.67 to 0.98) | 1105 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 11.3 months | 14.0 months | |||||
| Tumour response | Study population | OR 1.38 (1.08 to 1.76) | 1081 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ||
| 468 per 1000 | 548 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 458 per 1000 | 538 per 1000 | |||||
| Progression‐free survival | Study population | HR 0.88 (0.66 to 1.19) | 1034 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 4.9 months | 6.0 months | |||||
| Treatment‐related death | Study population | OR 0.47 (0.17 to 1.30) | 1132 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 20 per 1000 | 9 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 24 per 1000 | 11 per 1000 | |||||
| Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity | Study population | OR 0.97 (0.44 to 2.13) | 970 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 95 per 1000 | 93 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 102 per 1000 | 99 per 1000 | |||||
| *For time‐to‐event outcomes, e.g. overall survival, the assumed and corresponding risks were obtained by calculating the weighted average of the median survival durations reported in included studies. For dichotomous outcomes, the assumed and corresponding risks (and their 95% confidence interval) are based on proportions of events in the control and intervention groups respectively. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Downgraded by one level for risk of bias. | ||||||
| Taxane‐platinum‐fluoropyrimidine combinations versus taxane‐platinum (without fluoropyrimidine) for advanced gastric cancer | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with advanced gastric cancer Control: taxane‐platinum (without fluoropyrimidine) | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Taxane‐platinum (without fluoropyrimidine) | Taxane‐platinum‐fluoropyrimidine combination | |||||
| Overall survival | Study population | OR 0.86 | 482 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 10.0 months | 11.7 months | |||||
| Tumour response | Study population | OR 2.08 | 482 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 234 per 1000 | 389 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 231 per 1000 | 385 per 1000 | |||||
| Progression‐free survival | Study population | OR 0.74 | 482 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 4.4 months | 5.7 months | |||||
| Treatment‐related death | Study population | OR 1.95 | 482 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 26 per 1000 | 50 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 13 per 1000 | 25 per 1000 | |||||
| Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity | Study population | OR 1.71 | 234 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 105 per 1000 | 167 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 99 per 1000 | 158 per 1000 | |||||
| *For time‐to‐event outcomes, e.g. overall survival, the assumed and corresponding risks were obtained by calculating the weighted average of the median survival durations reported in included studies. For dichotomous outcomes, the assumed and corresponding risks (and their 95% confidence interval) are based on proportions of events in the control and intervention groups respectively. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Downgraded by one level for risk of bias. | ||||||
| S‐1 versus 5‐FU‐containing regimens for advanced gastric cancer | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with advanced gastric cancer Control: 5‐FU‐containing regimens | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| 5‐FU‐containing regimens | S‐1 containing regimens | |||||
| Overall Survival | Study population | HR 0.91 | 1793 | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 9.1 months | 9.6 months | |||||
| Tumour response | Study population | OR 1.73 | 1753 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 256 per 1000 | 374 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 320 per 1000 | 449 per 1000 | |||||
| Progression‐free survival | Study population | HR 0.85 | 1942 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 4.3 months | 5.0 months | |||||
| Time‐to treatment failure | Study population | HR 0.88 | 1818 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Weighted average of median survival durations from included studies | |
| 3.1 months | 3.9 months | |||||
| Treatment‐related deaths | Study population | OR 0.56 | 1962 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ||
| 27 per 1000 | 15 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 5 per 1000 | 3 per 1000 | |||||
| Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity | Study population | OR 0.85 | 1726 | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | ||
| 128 per 1000 | 111 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 144 per 1000 | 125 per 1000 | |||||
| *For time‐to‐event outcomes, e.g. overall survival, the assumed and corresponding risks were obtained by calculating the weighted average of the median survival durations reported in included studies. For dichotomous outcomes, the assumed and corresponding risks (and their 95% confidence interval) are based on proportions of events in the control and intervention groups respectively. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Downgraded by two levels for severe statistical heterogeneity. | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 3 | 184 | Hazard ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.37 [0.24, 0.55] |
| 2 Time to progression Show forest plot | 2 | 144 | Hazard ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.31 [0.22, 0.43] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 23 | 4447 | Hazard ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.84 [0.79, 0.89] |
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 18 | 2833 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.30 [1.94, 2.72] |
| 3 Time to progression Show forest plot | 4 | 720 | Hazard ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.69 [0.55, 0.87] |
| 4 Treatment‐related death Show forest plot | 18 | 3876 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.64 [0.83, 3.24] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 4 | 579 | Hazard ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.61, 0.89] |
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3 Time to progression Show forest plot | 1 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 7 | 1147 | Hazard ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.73, 0.92] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 10 | 2135 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.80, 0.95] |
| 1.1 Substitutive comparisons | 6 | 826 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.75, 1.00] |
| 1.2 Additive comparisons | 3 | 500 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.76, 1.03] |
| 1.3 Other comparisons | 2 | 809 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.76, 1.00] |
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 10 | 1266 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.72 [1.24, 2.40] |
| 2.1 Substitutive comparisons | 6 | 756 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.53 [0.93, 2.50] |
| 2.2 Additive comparisons | 3 | 345 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.18 [1.25, 3.80] |
| 2.3 Other Comparisons | 2 | 165 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.87 [0.89, 3.91] |
| 3 Progression‐free survival Show forest plot | 7 | 1640 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.69, 0.84] |
| 3.1 Substitutive comparison | 5 | 741 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.72, 1.00] |
| 3.2 Additive comparisons | 1 | 90 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.51 [0.33, 0.77] |
| 3.3 Other comparisons | 2 | 809 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.66, 0.84] |
| 4 Treatment‐related death Show forest plot | 9 | 1979 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.23, 3.32] |
| 5 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity Show forest plot | 9 | 1979 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.46, 2.20] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 8 | 2001 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.78, 0.95] |
| 1.1 Substitutive comparisons | 3 | 479 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.87, 1.27] |
| 1.2 Additive comparisons | 4 | 1466 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.80 [0.71, 0.91] |
| 1.3 Other comparisons | 1 | 56 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.80 [0.46, 1.39] |
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 9 | 1820 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.37 [1.03, 1.83] |
| 2.1 Substitutive comparison | 4 | 525 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.71, 1.50] |
| 2.2 Additive comparison | 4 | 1235 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.83 [1.45, 2.32] |
| 2.3 Other comparisons | 1 | 60 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.12, 0.96] |
| 3 Time to progression Show forest plot | 2 | 360 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.85, 1.32] |
| 4 Progression‐free survival Show forest plot | 5 | 1498 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.63, 0.91] |
| 4.1 Substitutive comparisons | 1 | 119 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 1.15 [0.77, 1.72] |
| 4.2 Additive comparison (PFS) | 3 | 1323 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.70 [0.61, 0.81] |
| 4.3 Other comparisons | 1 | 56 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.55, 1.60] |
| 5 Treatment‐related death Show forest plot | 7 | 2113 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.55, 2.20] |
| 6 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity Show forest plot | 5 | 1066 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.53, 1.25] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall Survival Show forest plot | 5 | 732 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.79, 1.11] |
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 4 | 636 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.40, 1.79] |
| 3 Time to progression Show forest plot | 1 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 4 Progression‐free survival Show forest plot | 4 | 647 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.98 [0.77, 1.23] |
| 5 Treatment‐related death Show forest plot | 2 | 481 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.88 [0.23, 15.15] |
| 6 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall Survival Show forest plot | 5 | 1105 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.67, 0.98] |
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 5 | 1081 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.38 [1.08, 1.76] |
| 3 Progression‐free survival Show forest plot | 4 | 1034 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.66, 1.19] |
| 4 Treatment‐related death Show forest plot | 5 | 1132 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.47 [0.17, 1.30] |
| 5 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity Show forest plot | 3 | 970 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.44, 2.13] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall survival Show forest plot | 3 | 482 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.71, 1.06] |
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 3 | 482 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.08 [1.37, 3.15] |
| 3 Progression‐free survival Show forest plot | 3 | 482 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.59, 0.93] |
| 4 Treatment‐related death Show forest plot | 3 | 482 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.95 [0.73, 5.17] |
| 5 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity Show forest plot | 2 | 234 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.71 [0.79, 3.69] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Overall Survival Show forest plot | 4 | 1793 | Hazard Ratio (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.83, 1.00] |
| 2 Tumour response Show forest plot | 7 | 1753 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.73 [1.01, 2.94] |
| 3 Progression‐free survival Show forest plot | 4 | 1942 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.70, 1.04] |
| 4 Time‐to treatment failure Show forest plot | 5 | 1818 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.76, 1.01] |
| 5 Treatment‐related deaths Show forest plot | 4 | 1962 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.56 [0.30, 1.06] |
| 6 Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity Show forest plot | 3 | 1726 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.63, 1.13] |

