Tratamiento quirúrgico para la enfermedad tubárica en mujeres a las que se les realizará fertilización in vitro
References
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
References to studies awaiting assessment
References to ongoing studies
Additional references
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial. Single‐centre, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology at a university hospital (Montpelier, France). Inclusion criteria: women with severe tubal infertility, not suitable for tubal repair. 60 women recruited, 60 randomised (30 to laparoscopic bilateral salpingectomy and adhesiolysis; 30 to laparoscopic adhesiolysis). Follow‐up duration 1‐5 years. Follow‐up scheme: not specified. | |
| Participants | Age </=40 years (range 27‐36). Characteristics of IVF treatment: | |
| Interventions | Laparoscopic bilateral salpingectomy and adhesiolysis VERSUS laparoscopic adhesiolysis. Criteria for surgical treatment prior to IVF: a communicating non‐draining hydrosalpinx with salpingitis isthmica nodosa. | |
| Outcomes | PRIMARY OUTCOMES SECONDARY OUTCOMES | |
| Notes | Subsequent publication of the cumulative results from this trial (Strandell 2001) were excluded from meta‐analysis (not intention to treat and too many protocol breached when intention to treat data was provided). | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | With sealed opaque envelopes. |
| Blinding? | High risk | No blinding. |
| Incomplete outcome data addressed? | Low risk | Intention to treat analysis is unclear; but number randomised is same as number analysed. |
| Free of selective reporting? | Low risk | No suggestion of selective reporting. |
| Detection adequate? | Low risk | Sufficient length of follow‐up: 1‐5 years. |
| Source of funding stated? | Unclear risk | Presence or absence of funding is not reported. |
| Powercalculation performed? | High risk | A power calculation was performed but not adhered to as the number calculated (322 patients in each group) would not be achieved in the setting of the trial. When the trial was ceased and the exact reasons for cessation are unknown. |
| Loss to Follow‐up explained? | Low risk | No withdrawals or losses to follow‐up. |
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial. Single centre, non academic, trial in the Assisted Conception Unit of Birmingham Women's Hospital, UK. Inclusion criteria: a uni‐ or bilateral hydrosalpinx diagnosed by ultrasound during ovarian stimulation in the IVF cycle or previous to the IVF cycle, or women with severe tubal pathology on the waiting list for salpingectomy for hydrosalpinges. 66 women recruited and randomised (32 to aspiration; 34 to no intervention). 1,154 exclusions prior to randomisation. No women withdrew or lost to follow up. 66 women were analysed. Follow‐up duration up to 1 IVF cycle. Type of follow‐up: biochemical pregnancy 14 days post ET; if positive ultrasound examination is performed 6 weeks post transfer. After diagnosis of viable pregnancy patients are referred to their GP. | |
| Participants | Age (years (SD)): aspiration group: 33.4±4.5 / no intervention group 33.9±4.7. Diagnosis of tubal pathology: by ultrasound and by DLS or HSG in 7 patients. Characteristics of IVF treatment: | |
| Interventions | Aspiration of hydrosalpinx or hydrosalpinges after collection of all eggs (covered with intravenous Augmentin followed by 3 days of oral Azithromycin antibiotic) VERSUS no aspiration. Criteria for surgical treatment prior to IVF ‐ Ultrasound visible hydrosalpinges (uni‐ or bilateral) during ovarian stimulation phase of IVF treatment or severe tubal pathology. | |
| Outcomes | PRIMARY OUTCOMES SECONDARY OUTCOMES | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | Randomisation by computer algorithm using a third party administrator just prior to oocyte retrieval procedure. |
| Blinding? | High risk | Investigator nor the outcome assessor were blinded. |
| Incomplete outcome data addressed? | Low risk | 'Intention to treat' analysis performed (as there were no drop‐outs or losses). |
| Free of selective reporting? | Low risk | No suggestion of selective reporting. |
| Detection adequate? | Low risk | Follow‐up duration up to 1 IVF cycle. |
| Source of funding stated? | Low risk | No source of funding reported. |
| Powercalculation performed? | High risk | Power calculation performed ‐ sample size 158 not attained owing to decrease in recruitment rate by virtue of patient preference for salpingectomy, recruitment was stopped on advice of the Data Monitoring Committee after 4 years. |
| Loss to Follow‐up explained? | Low risk | Yes, no loss to follow‐up occurred. |
| Methods | Randomised Controlled Trial Study in two centres: a academic centre: Aretaieon University Hospital; a non‐academic centre: the Centre for Human Reproduction, Genesis Clinic; both in Athens, Greece. Patients recruited prospectively; patient sampling consecutively. Inclusion criteria: Women aged ≤41 with unilateral of bilateral hydrosalpinges; confirmed by HSG, suitability for IVF‐ICSI treatment, FSH on day 2/3 <12mIU/ml, no contraindications for laparoscopic surgery, no history of IVF attempts before recruitment, absence of other obvious pelvic pathology in females. 115 patients were recruited and randomised (50 to proximal tubal occlusion; 50 to salpingectomy; 15 to non‐intervention). 112 patients underwent IVF and were analysed. 3 women withdrew from IVF; 3 women didn't respond to ovarian stimulation and in 4 women IVF did not result in embryo's. Follow‐up scheme: up to the first IVF cycle after tubal surgery. Type: ultrasound 4 weeks after ET. | |
| Participants | Age (years (SD)): 31±4.5 vs 29.8±3.4 vs 3.4±5.3. Diagnosis of tubal pathology was confirmed with HSG. Characteristics and distribution of tubal pathology: all patients had hydrosalpinges; bilateral in 70/115 patients (70% vs 54% vs 54%). 70/115 women (58% vs 64% vs 60%) had ultrasound visible hydrosalpinges. Characteristics of IVF treatment: | |
| Interventions | Uni‐ or bilateral laparoscopic tubal occlusion by bipolar diathermy at two separate sites on the isthmic segment of the tube VERSUS uni‐ or bilateral salpingectomy; with transection 1 to 1.5 cm from the cornual section VERSUS no intervention. Criteria for surgery: unilateral of bilateral hydrosalpinges. | |
| Outcomes | PRIMARY OBJECTIVES SECONDARY OBJECTIVES: | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | Randomisation by computer generated randomisation in blocks. |
| Blinding? | High risk | The operator and the IVF performer were the same person in some cases. |
| Incomplete outcome data addressed? | High risk | 112 women analysed of 115 randomised. Intention to treat analysis not explicitly stated. |
| Free of selective reporting? | Low risk | No suggestions of selective outcome reporting. |
| Detection adequate? | Low risk | adequate detection of stated outcomes. |
| Source of funding stated? | Low risk | correspondence stated that there was no source of funding. |
| Powercalculation performed? | Unclear risk | Power calculation is performed and calculated sample sizes were achieved. However, power calculations in this trial were made with very large anticipated differences (46% vs73% comparing salpingectomy to tubal occlusion and 46% vs 14% comparing surgery to no surgery) and not performed correctly. It is quite unlikely that these anticipated differences would be achieved; and therefore it may be questioned whether the made power calculation was adhered to. |
| Loss to Follow‐up explained? | Low risk | Withdrawal and losses to follow‐up were explained. |
| Methods | Randomised Controlled Trial. Single academic centre, Center for Reproductive Health and Genetics, Chisinau, Moldova. Inclusion criteria: women with hydrosalpinges. 204 patients recruited and randomised (66 women randomised to no surgical treatment; 60 women randomised to salpingectomy; 78 randomised to proximal tubal occlusion) 204 women analysed. loss to follow‐up/withdrawal: none. Follow‐up duration: up to one IVF cycle. | |
| Participants | Age: similar in all groups; range: 22‐35 years Duration of infertility: >2 years (mean months (SD): salpingectomy group: 46.2 (27.2); tubal occlusion group: 47.4 (28.5); non‐intervention group: 46.9 (27.8)). Previous investigative work‐up: ovulatory cycles, hormonal tests, transvaginal ultrasound examination of the genitalia interna, male semen parameters. Diagnosis of tubal pathology: bilateral distal tubal occlusion diagnosed by HSG or ultrasound visible hydrosalpinges. IVF: | |
| Interventions | Salpingectomy VERSUS proximal tubal clamping of hydrosalpinges VERSUS No intervention . Criterium for intervention: ultrasound visible hydrosalpinges. Timing of intervention: minimally 2 months before IVF treatment. Timing to the IVF treatment cycle after randomisation in the control group: unclear. | |
| Outcomes | PRIMARY OUTCOMES: Clinical pregnancy ‐ gestational sac on ultrasound. | |
| Notes | As data extraction on the abstract was limited; queries were resolved by contacting the author. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | By opaque numbered envelopes |
| Blinding? | Unclear risk | Not stated. |
| Incomplete outcome data addressed? | Low risk | Not stated in abstract; but number of patients randomised is the same as numbers of patients analysed, correspondence clarified there was no loss to follow‐up or withdrawal. |
| Free of selective reporting? | Low risk | no suggestions of selective reporting. |
| Detection adequate? | Low risk | yes, adequate follow‐up after IVF. |
| Source of funding stated? | Low risk | Source of funding: the Academy of Science of the Republic of Moldova (clarified by correspondence) |
| Powercalculation performed? | Unclear risk | Not clear. As study sizes were small it may be presumed that they have not been adhered to if they where performed. |
| Loss to Follow‐up explained? | Low risk | No loss to Follow‐up/ withdrawal, clarified by correspondence. |
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial. Inclusion criteria: hydrosalpinges, laparoscopic acces ability, age<39 at time of randomisation. 204 women were recruited and randomised. Number of exclusions not known. 5 patients of the intervention group did not undergo surgery; 6 patients in the intervention group and 6 patients in the non‐intervention group did not undergo IVF. 204 women were analysed. | |
| Participants | Age <39 years (range 22‐38) Diagnosis of tubal pathology: by HSG or laparoscopy. 37(51%) had ultrasound visible hydrosalpinges compared to 42(57%). Characteristics and distribution of tubal pathology: Hydrosalpinges. Bilateral in 69(59%) and 36(41%); unilateral in 47(41%) and 52(59%). Characteristics of IVF treatment : | |
| Interventions | Laparoscopic bilateral or unilateral salpingectomy (or, if technical difficulties e.g. extensive adhesions, proximal ligation and distal fenestration recommended) VERSUS no surgery. Criteria for surgical treatment prior to IVF ‐ Uni‐ or bilateral hydrosalpinges (a distally occluded pathologically dilated tube or one which became pathologically dilated on patency testing by HSG/laparoscopy. | |
| Outcomes | PRIMARY OUTCOMES SECONDARY OUTCOMES | |
| Notes | ‐ | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | True randomisation ‐ sealed opaque envelopes in blocks of 10‐30. |
| Blinding? | High risk | No blinding. |
| Incomplete outcome data addressed? | Low risk | 'Intention to treat' analysis performed. |
| Free of selective reporting? | Low risk | No suggestions of selective reporting. |
| Detection adequate? | Low risk | Follow‐up duration up to 1 IVF cycle (further follow‐up data anticipated). |
| Source of funding stated? | Low risk | Study was funded by grants from the Goteborg Medical Society, the Hjalmar Svensson Foundation and the society 'ordensallskapet W:6' |
| Powercalculation performed? | High risk | Power calculation performed ‐ sample size 300 not adhered to due to decrease in recruitment rate. |
| Loss to Follow‐up explained? | Low risk | Withdrawal and loss to follow up explained. |
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Retrospective non‐randomised controlled study. | |
| Study design and whether randomisation has been performed is unclear. It appears that patients serve as there own control after surgical intervention. Correspondance was sought to resolve this issue, but not with success. | |
| This trial was excluded because this article compared proximal/distal tubal occlusion with clamping; however comparisons were between outcomes in different degrees of tubal pathology rather than different interventions. Comparative data was not obtained as correspondence was unsuccessful. | |
| This trial is not a randomised trial ‐ the 'control' group was historical (the same women prior to their salpingectomy) and biased by the fact that no pregnancies occurred. | |
| The primary outcome of this study is the continuation of spontaneous pregnancy; IVF is not performed after tubal surgery. |
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Trial name or title | Is there a role for hysteroscopic tubal occlusion of functionless hydrosalpinges prior to IVF/ICSI in modern practice? |
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial. Single academic centre in Egypt (women's Health University Center, Assiut University, Assiut Egypt) Inclusion criteria: women with uni‐ or bilaterally laparoscopically‐proven functionless hydrosalpinges (a large blocked tube with lost major and minor folds) scheduled for IVF. Follow‐up: HSG in the following cycle after the procedure; follow‐up procedure for pregnancy unclear. |
| Participants | Women with uni‐ or bilaterally laparoscopically‐proven functionless hydrosalpinges scheduled for IVF. Women with a frozen pelvis at laparoscopy or inaccessible tubes at lap or hysteroscopy were excluded. |
| Interventions | Laparoscopic occlusion by coagulation and incision of the isthmic part of the fallopian tube VERSUS Hysteroscopic tubal occlusion by electrocautery with a rollerball electrode (3mm) introduced by a resectoscope; after cervical priming with misoprostol 200mg. |
| Outcomes | PRIMARY OUTCOMES: SECONDARY OUTCOMES |
| Starting date | April 2004 |
| Contact information | Atef M.M. Darwish, dept of obstetrics and gynaecology, women's Health University, P.O. Box(1), 71111 Assiut Egypt. [email protected] |
| Notes | The objective of Darwish 2007 is mainly to conduct a safety study and a study to address the value of hysteroscopic tubal occlusion compared to laparoscopic tubal occlusion. This current study is stated to be only a preliminary study of which the follow‐up time was to short to detect pregnancy. Subsequent studies might report outcomes in terms of pregnancy. |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Ongoing pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 3 | 329 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.20 [1.26, 3.82] |
| Analysis 1.1 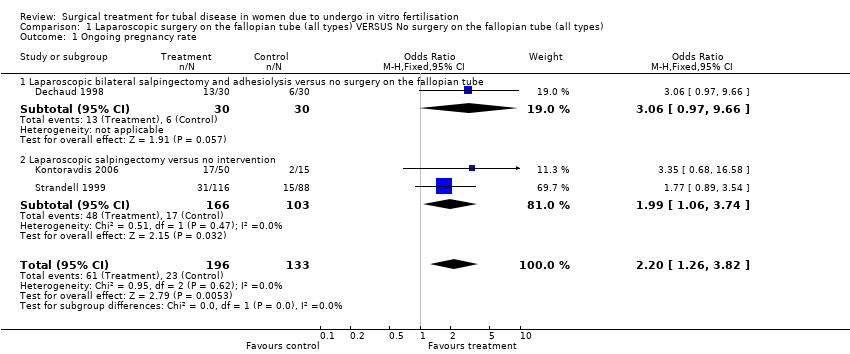 Comparison 1 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS No surgery on the fallopian tube (all types), Outcome 1 Ongoing pregnancy rate. | ||||
| 1.1 Laparoscopic bilateral salpingectomy and adhesiolysis versus no surgery on the fallopian tube | 1 | 60 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.06 [0.97, 9.66] |
| 1.2 Laparoscopic salpingectomy versus no intervention | 2 | 269 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.99 [1.06, 3.74] |
| 2 Clinical pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 3 | 395 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.31 [1.48, 3.62] |
| Analysis 1.2 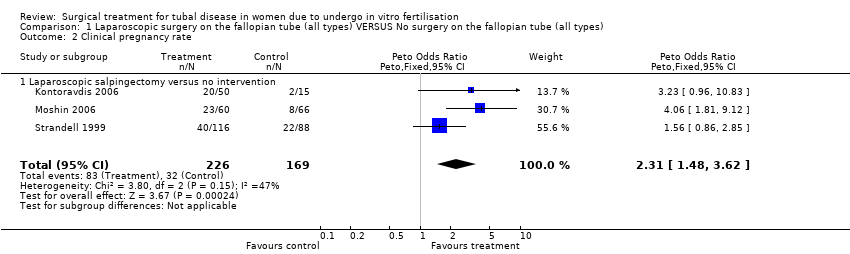 Comparison 1 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS No surgery on the fallopian tube (all types), Outcome 2 Clinical pregnancy rate. | ||||
| 2.1 Laparoscopic salpingectomy versus no intervention | 3 | 395 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.31 [1.48, 3.62] |
| 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition Show forest plot | 4 | 455 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.49 [1.60, 3.86] |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS No surgery on the fallopian tube (all types), Outcome 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition. | ||||
| 3.1 Laparoscopic bilateral salpingectomy and adhesiolysis versus no surgery on the fallopian tube | 1 | 60 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.06 [0.97, 9.66] |
| 3.2 Laparoscopic salpingectomy versus no intervention | 3 | 395 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.40 [1.49, 3.86] |
| 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 3 | 329 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.68 [0.13, 3.56] |
| Analysis 1.4  Comparison 1 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS No surgery on the fallopian tube (all types), Outcome 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate. | ||||
| 4.1 Laparoscopic bilateral salpingectomy and adhesiolysis versus laparoscopic adhesiolysis | 1 | 60 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.00, 6.82] |
| 4.2 Laparoscopic salpingectomy versus no intervention | 2 | 269 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.15, 6.01] |
| 5 Miscarriage rate Show forest plot | 3 | 115 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.38 [0.11, 1.28] |
| Analysis 1.5  Comparison 1 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS No surgery on the fallopian tube (all types), Outcome 5 Miscarriage rate. | ||||
| 5.1 Laparoscopic bilateral salpingectomy and adhesiolysis versus laparoscopic adhesiolysis | 1 | 38 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.17 [0.01, 5.24] |
| 5.2 Laparoscopic salpingectomy versus no intervention | 2 | 77 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.42 [0.12, 1.57] |
| 6 Surgical complication rate Show forest plot | 1 | 204 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.86 [0.35, 96.79] |
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS No surgery on the fallopian tube (all types), Outcome 6 Surgical complication rate. | ||||
| 6.1 Laparoscopic salpingectomy versus no intervention | 1 | 204 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.86 [0.35, 96.79] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Ongoing pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 7.21 [0.87, 59.57] |
| Analysis 2.1 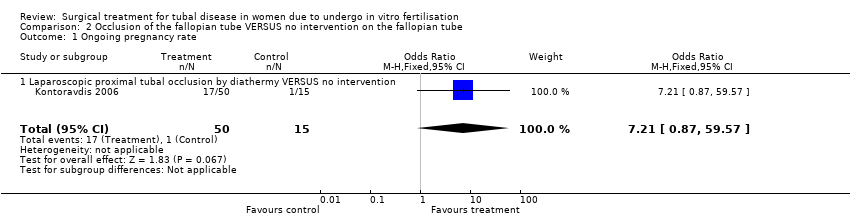 Comparison 2 Occlusion of the fallopian tube VERSUS no intervention on the fallopian tube, Outcome 1 Ongoing pregnancy rate. | ||||
| 1.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 7.21 [0.87, 59.57] |
| 2 Clinical pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 2 | 209 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.66 [2.17, 10.01] |
| Analysis 2.2  Comparison 2 Occlusion of the fallopian tube VERSUS no intervention on the fallopian tube, Outcome 2 Clinical pregnancy rate. | ||||
| 2.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.33 [0.88, 21.30] |
| 2.2 Proximal tubal clamping VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 144 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.78 [2.01, 11.38] |
| 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition Show forest plot | 2 | 209 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.66 [2.17, 10.01] |
| Analysis 2.3  Comparison 2 Occlusion of the fallopian tube VERSUS no intervention on the fallopian tube, Outcome 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition. | ||||
| 3.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.33 [0.88, 21.30] |
| 3.2 Laparoscopic proximal tubal clamping VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 144 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.78 [2.01, 11.38] |
| 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.04, 24.25] |
| Analysis 2.4  Comparison 2 Occlusion of the fallopian tube VERSUS no intervention on the fallopian tube, Outcome 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate. | ||||
| 4.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.04, 24.25] |
| 5 Miscarriage rate Show forest plot | 1 | 25 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.15 [0.01, 3.09] |
| Analysis 2.5  Comparison 2 Occlusion of the fallopian tube VERSUS no intervention on the fallopian tube, Outcome 5 Miscarriage rate. | ||||
| 5.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 25 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.15 [0.01, 3.09] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Clinical pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.97 [0.62, 6.29] |
| Analysis 3.1 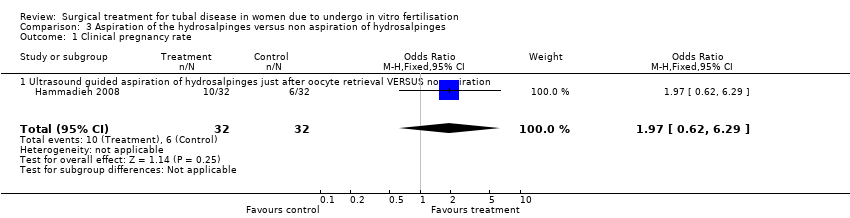 Comparison 3 Aspiration of the hydrosalpinges versus non aspiration of hydrosalpinges, Outcome 1 Clinical pregnancy rate. | ||||
| 1.1 Ultrasound guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges just after oocyte retrieval VERSUS no aspiration | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.97 [0.62, 6.29] |
| 2 Biochemical pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.78 [0.93, 8.27] |
| Analysis 3.2  Comparison 3 Aspiration of the hydrosalpinges versus non aspiration of hydrosalpinges, Outcome 2 Biochemical pregnancy rate. | ||||
| 2.1 Ultrasound guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges just after oocyte retrieval VERSUS no aspiration | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.78 [0.93, 8.27] |
| 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition Show forest plot | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.97 [0.62, 6.29] |
| Analysis 3.3  Comparison 3 Aspiration of the hydrosalpinges versus non aspiration of hydrosalpinges, Outcome 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition. | ||||
| 3.1 Ultrasound guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges just after oocyte retrieval VERSUS no aspiration | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.97 [0.62, 6.29] |
| 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 66 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 3.4  Comparison 3 Aspiration of the hydrosalpinges versus non aspiration of hydrosalpinges, Outcome 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate. | ||||
| 4.1 Ultrasound guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges just after oocyte retrieval VERSUS no aspiration | 1 | 66 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 5 Miscarriage rate Show forest plot | 1 | 16 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.09, 17.65] |
| Analysis 3.5 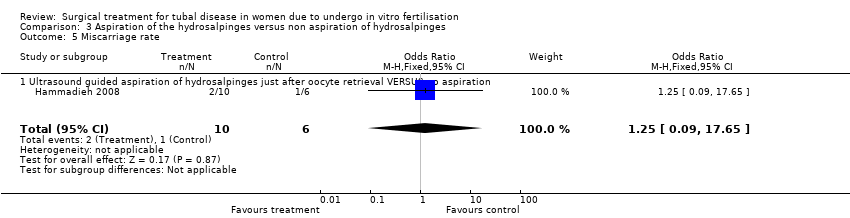 Comparison 3 Aspiration of the hydrosalpinges versus non aspiration of hydrosalpinges, Outcome 5 Miscarriage rate. | ||||
| 5.1 Ultrasound guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges just after oocyte retrieval VERSUS no aspiration | 1 | 16 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.09, 17.65] |
| 6 Surgical complication rate Show forest plot | 1 | 66 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 3.6  Comparison 3 Aspiration of the hydrosalpinges versus non aspiration of hydrosalpinges, Outcome 6 Surgical complication rate. | ||||
| 6.1 Ultrasound guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges just after oocyte retrieval VERSUS no aspiration | 1 | 66 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Ongoing pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.65 [0.74, 3.71] |
| Analysis 4.1  Comparison 4 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS (any other) laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube, Outcome 1 Ongoing pregnancy rate. | ||||
| 1.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.65 [0.74, 3.71] |
| 2 Clinical pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 2 | 238 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.28 [0.76, 2.14] |
| Analysis 4.2 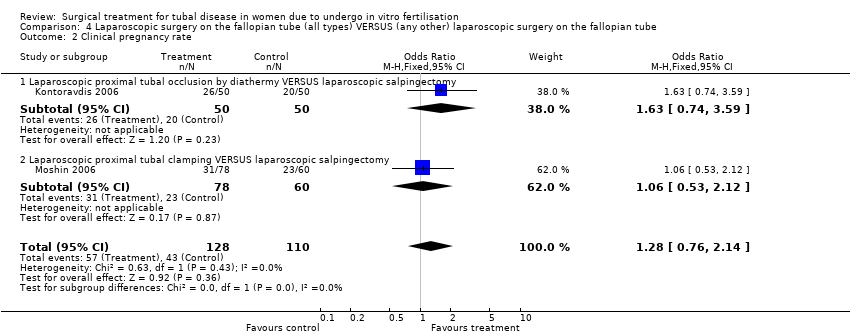 Comparison 4 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS (any other) laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube, Outcome 2 Clinical pregnancy rate. | ||||
| 2.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.63 [0.74, 3.59] |
| 2.2 Laparoscopic proximal tubal clamping VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 138 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.53, 2.12] |
| 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition Show forest plot | 2 | 238 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.28 [0.76, 2.14] |
| Analysis 4.3  Comparison 4 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS (any other) laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube, Outcome 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition. | ||||
| 3.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.63 [0.74, 3.59] |
| 3.2 Laparoscopic proximal tubal clamping VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 138 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.53, 2.12] |
| 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.06 [0.12, 76.95] |
| Analysis 4.4 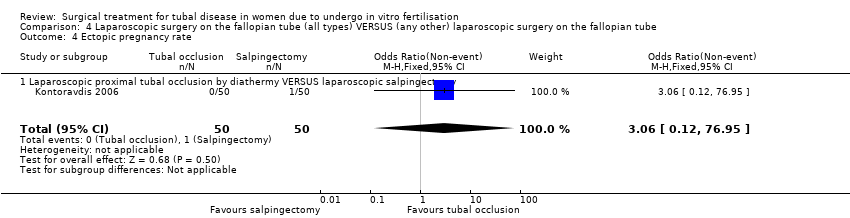 Comparison 4 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS (any other) laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube, Outcome 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate. | ||||
| 4.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.06 [0.12, 76.95] |
| 5 Miscarriage rate Show forest plot | 1 | 43 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.20, 9.02] |
| Analysis 4.5  Comparison 4 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS (any other) laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube, Outcome 5 Miscarriage rate. | ||||
| 5.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 43 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.20, 9.02] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Salpingectomy (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment Show forest plot | 4 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 5.1  Comparison 5 Surgical treatment (all types) VERSUS no surgical treatment, Outcome 1 Salpingectomy (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment. | ||||
| 1.1 Ongoing pregnancy rate | 3 | 329 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.20 [1.26, 3.82] |
| 1.2 Clinical pregnancy rate | 3 | 395 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.40 [1.49, 3.86] |
| 1.3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition | 4 | 455 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.49 [1.60, 3.86] |
| 1.4 Ectopic pregnancy rate | 3 | 329 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.64 [0.15, 2.75] |
| 1.5 Miscarriage rate | 3 | 329 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.31, 2.38] |
| 1.6 Surgical complication rate | 1 | 204 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.86 [0.18, 81.52] |
| 2 Tubal occlusion (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 5.2 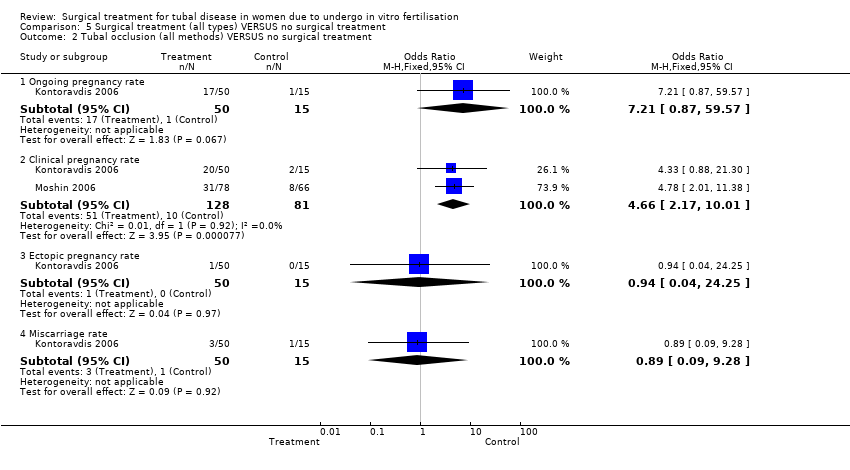 Comparison 5 Surgical treatment (all types) VERSUS no surgical treatment, Outcome 2 Tubal occlusion (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment. | ||||
| 2.1 Ongoing pregnancy rate | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 7.21 [0.87, 59.57] |
| 2.2 Clinical pregnancy rate | 2 | 209 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.66 [2.17, 10.01] |
| 2.3 Ectopic pregnancy rate | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.04, 24.25] |
| 2.4 Miscarriage rate | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.09, 9.28] |
| 3 Aspiration of hydro salpingeal fluid (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 5.3  Comparison 5 Surgical treatment (all types) VERSUS no surgical treatment, Outcome 3 Aspiration of hydro salpingeal fluid (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment. | ||||
| 3.1 Clinical pregnancy rate | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.97 [0.62, 6.29] |
| 3.2 Biochemical pregnancy rate | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.78 [0.93, 8.27] |
| 3.3 Ectopic pregnancy rate | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3.4 Miscarriage rate | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.07 [0.18, 24.01] |
| 3.5 Surgical complication rate | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Tubal occlusion (all methods) VERSUS Salpingectomy (all methods) Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 6.1  Comparison 6 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS (any other) laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube, Outcome 1 Tubal occlusion (all methods) VERSUS Salpingectomy (all methods). | ||||
| 1.1 Ongoing pregnancy rate | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.65 [0.74, 3.71] |
| 1.2 Clinical pregnancy rate | 2 | 238 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.28 [0.76, 2.14] |
| 1.3 Ectopic pregnancy rate | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.21] |
| 1.4 Miscarriage rate | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.53 [0.24, 9.59] |

Methodological quality graph: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item presented as percentages across all included studies.
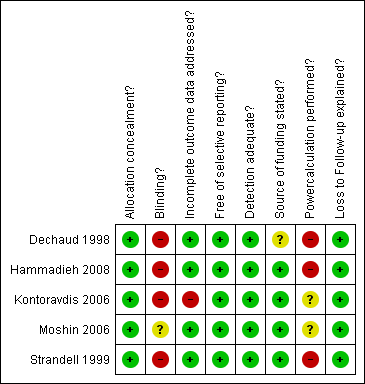
Methodological quality summary: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item for each included study.

Forest plot of comparison: Surgical treatment (all types) VERSUS no surgical treatment: Salpingectomy (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment. Outcomes: Ongoing pregnancy rate, Clinical pregnancy rate, Pregnancy rate according to any definition, Ectopic pregnancy rate, Miscarriage rate, Surgical complication rate.

Forest plot of comparison: Surgical treatment (all types) VERSUS no surgical treatment: Tubal occlusion (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment. Outcomes: Ongoing pregnancy rate, Clinical pregnancy rate, Ectopic pregnancy rate, Miscarriage rate, Surgical complication rate.
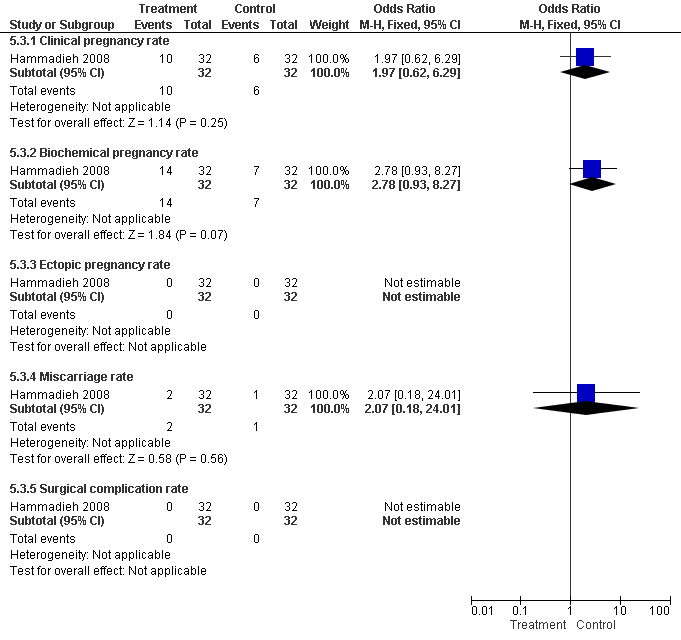
Forest plot of comparison: Surgical treatment (all types) VERSUS no surgical treatment: Aspiration of hydro salpingeal fluid (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment. Outcomes: Ongoing pregnancy rate, Clinical pregnancy rate, Ectopic pregnancy rate, Miscarriage rate, Surgical complication rate.

Forest plot of comparison: Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS (any other) laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube: Tubal occlusion (all methods) VERSUS Salpingectomy (all methods). Outcomes: Ongoing pregnancy rate, Clinical pregnancy rate, Ectopic pregnancy rate, Miscarriage rate.

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS No surgery on the fallopian tube (all types), Outcome 1 Ongoing pregnancy rate.

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS No surgery on the fallopian tube (all types), Outcome 2 Clinical pregnancy rate.

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS No surgery on the fallopian tube (all types), Outcome 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition.

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS No surgery on the fallopian tube (all types), Outcome 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate.

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS No surgery on the fallopian tube (all types), Outcome 5 Miscarriage rate.

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS No surgery on the fallopian tube (all types), Outcome 6 Surgical complication rate.

Comparison 2 Occlusion of the fallopian tube VERSUS no intervention on the fallopian tube, Outcome 1 Ongoing pregnancy rate.

Comparison 2 Occlusion of the fallopian tube VERSUS no intervention on the fallopian tube, Outcome 2 Clinical pregnancy rate.

Comparison 2 Occlusion of the fallopian tube VERSUS no intervention on the fallopian tube, Outcome 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition.

Comparison 2 Occlusion of the fallopian tube VERSUS no intervention on the fallopian tube, Outcome 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate.

Comparison 2 Occlusion of the fallopian tube VERSUS no intervention on the fallopian tube, Outcome 5 Miscarriage rate.

Comparison 3 Aspiration of the hydrosalpinges versus non aspiration of hydrosalpinges, Outcome 1 Clinical pregnancy rate.

Comparison 3 Aspiration of the hydrosalpinges versus non aspiration of hydrosalpinges, Outcome 2 Biochemical pregnancy rate.

Comparison 3 Aspiration of the hydrosalpinges versus non aspiration of hydrosalpinges, Outcome 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition.

Comparison 3 Aspiration of the hydrosalpinges versus non aspiration of hydrosalpinges, Outcome 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate.

Comparison 3 Aspiration of the hydrosalpinges versus non aspiration of hydrosalpinges, Outcome 5 Miscarriage rate.

Comparison 3 Aspiration of the hydrosalpinges versus non aspiration of hydrosalpinges, Outcome 6 Surgical complication rate.

Comparison 4 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS (any other) laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube, Outcome 1 Ongoing pregnancy rate.

Comparison 4 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS (any other) laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube, Outcome 2 Clinical pregnancy rate.

Comparison 4 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS (any other) laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube, Outcome 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition.

Comparison 4 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS (any other) laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube, Outcome 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate.

Comparison 4 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS (any other) laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube, Outcome 5 Miscarriage rate.

Comparison 5 Surgical treatment (all types) VERSUS no surgical treatment, Outcome 1 Salpingectomy (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment.

Comparison 5 Surgical treatment (all types) VERSUS no surgical treatment, Outcome 2 Tubal occlusion (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment.

Comparison 5 Surgical treatment (all types) VERSUS no surgical treatment, Outcome 3 Aspiration of hydro salpingeal fluid (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment.

Comparison 6 Laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube (all types) VERSUS (any other) laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tube, Outcome 1 Tubal occlusion (all methods) VERSUS Salpingectomy (all methods).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Ongoing pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 3 | 329 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.20 [1.26, 3.82] |
| 1.1 Laparoscopic bilateral salpingectomy and adhesiolysis versus no surgery on the fallopian tube | 1 | 60 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.06 [0.97, 9.66] |
| 1.2 Laparoscopic salpingectomy versus no intervention | 2 | 269 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.99 [1.06, 3.74] |
| 2 Clinical pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 3 | 395 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.31 [1.48, 3.62] |
| 2.1 Laparoscopic salpingectomy versus no intervention | 3 | 395 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.31 [1.48, 3.62] |
| 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition Show forest plot | 4 | 455 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.49 [1.60, 3.86] |
| 3.1 Laparoscopic bilateral salpingectomy and adhesiolysis versus no surgery on the fallopian tube | 1 | 60 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.06 [0.97, 9.66] |
| 3.2 Laparoscopic salpingectomy versus no intervention | 3 | 395 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.40 [1.49, 3.86] |
| 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 3 | 329 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.68 [0.13, 3.56] |
| 4.1 Laparoscopic bilateral salpingectomy and adhesiolysis versus laparoscopic adhesiolysis | 1 | 60 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.00, 6.82] |
| 4.2 Laparoscopic salpingectomy versus no intervention | 2 | 269 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.15, 6.01] |
| 5 Miscarriage rate Show forest plot | 3 | 115 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.38 [0.11, 1.28] |
| 5.1 Laparoscopic bilateral salpingectomy and adhesiolysis versus laparoscopic adhesiolysis | 1 | 38 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.17 [0.01, 5.24] |
| 5.2 Laparoscopic salpingectomy versus no intervention | 2 | 77 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.42 [0.12, 1.57] |
| 6 Surgical complication rate Show forest plot | 1 | 204 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.86 [0.35, 96.79] |
| 6.1 Laparoscopic salpingectomy versus no intervention | 1 | 204 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.86 [0.35, 96.79] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Ongoing pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 7.21 [0.87, 59.57] |
| 1.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 7.21 [0.87, 59.57] |
| 2 Clinical pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 2 | 209 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.66 [2.17, 10.01] |
| 2.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.33 [0.88, 21.30] |
| 2.2 Proximal tubal clamping VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 144 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.78 [2.01, 11.38] |
| 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition Show forest plot | 2 | 209 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.66 [2.17, 10.01] |
| 3.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.33 [0.88, 21.30] |
| 3.2 Laparoscopic proximal tubal clamping VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 144 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.78 [2.01, 11.38] |
| 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.04, 24.25] |
| 4.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.04, 24.25] |
| 5 Miscarriage rate Show forest plot | 1 | 25 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.15 [0.01, 3.09] |
| 5.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS no intervention | 1 | 25 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.15 [0.01, 3.09] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Clinical pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.97 [0.62, 6.29] |
| 1.1 Ultrasound guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges just after oocyte retrieval VERSUS no aspiration | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.97 [0.62, 6.29] |
| 2 Biochemical pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.78 [0.93, 8.27] |
| 2.1 Ultrasound guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges just after oocyte retrieval VERSUS no aspiration | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.78 [0.93, 8.27] |
| 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition Show forest plot | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.97 [0.62, 6.29] |
| 3.1 Ultrasound guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges just after oocyte retrieval VERSUS no aspiration | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.97 [0.62, 6.29] |
| 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 66 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4.1 Ultrasound guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges just after oocyte retrieval VERSUS no aspiration | 1 | 66 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 5 Miscarriage rate Show forest plot | 1 | 16 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.09, 17.65] |
| 5.1 Ultrasound guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges just after oocyte retrieval VERSUS no aspiration | 1 | 16 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.09, 17.65] |
| 6 Surgical complication rate Show forest plot | 1 | 66 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 6.1 Ultrasound guided aspiration of hydrosalpinges just after oocyte retrieval VERSUS no aspiration | 1 | 66 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Ongoing pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.65 [0.74, 3.71] |
| 1.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.65 [0.74, 3.71] |
| 2 Clinical pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 2 | 238 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.28 [0.76, 2.14] |
| 2.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.63 [0.74, 3.59] |
| 2.2 Laparoscopic proximal tubal clamping VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 138 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.53, 2.12] |
| 3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition Show forest plot | 2 | 238 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.28 [0.76, 2.14] |
| 3.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.63 [0.74, 3.59] |
| 3.2 Laparoscopic proximal tubal clamping VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 138 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.53, 2.12] |
| 4 Ectopic pregnancy rate Show forest plot | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.06 [0.12, 76.95] |
| 4.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.06 [0.12, 76.95] |
| 5 Miscarriage rate Show forest plot | 1 | 43 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.20, 9.02] |
| 5.1 Laparoscopic proximal tubal occlusion by diathermy VERSUS laparoscopic salpingectomy | 1 | 43 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.20, 9.02] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Salpingectomy (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment Show forest plot | 4 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 Ongoing pregnancy rate | 3 | 329 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.20 [1.26, 3.82] |
| 1.2 Clinical pregnancy rate | 3 | 395 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.40 [1.49, 3.86] |
| 1.3 Pregnancy rate ‐ any definition | 4 | 455 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.49 [1.60, 3.86] |
| 1.4 Ectopic pregnancy rate | 3 | 329 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.64 [0.15, 2.75] |
| 1.5 Miscarriage rate | 3 | 329 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.31, 2.38] |
| 1.6 Surgical complication rate | 1 | 204 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.86 [0.18, 81.52] |
| 2 Tubal occlusion (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 Ongoing pregnancy rate | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 7.21 [0.87, 59.57] |
| 2.2 Clinical pregnancy rate | 2 | 209 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.66 [2.17, 10.01] |
| 2.3 Ectopic pregnancy rate | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.04, 24.25] |
| 2.4 Miscarriage rate | 1 | 65 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.09, 9.28] |
| 3 Aspiration of hydro salpingeal fluid (all methods) VERSUS no surgical treatment Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.1 Clinical pregnancy rate | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.97 [0.62, 6.29] |
| 3.2 Biochemical pregnancy rate | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.78 [0.93, 8.27] |
| 3.3 Ectopic pregnancy rate | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3.4 Miscarriage rate | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.07 [0.18, 24.01] |
| 3.5 Surgical complication rate | 1 | 64 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Tubal occlusion (all methods) VERSUS Salpingectomy (all methods) Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 Ongoing pregnancy rate | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.65 [0.74, 3.71] |
| 1.2 Clinical pregnancy rate | 2 | 238 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.28 [0.76, 2.14] |
| 1.3 Ectopic pregnancy rate | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.21] |
| 1.4 Miscarriage rate | 1 | 100 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.53 [0.24, 9.59] |

