Antagonistas opiáceos con sedación mínima para la abstinencia de opiáceos
Appendices
Appendix 1. CENTRAL search strategy
#1 (opiate or opioid or heroin or narcotic) near/2 (abuse or addiction or dependence):ti,ab,kw in Trials
#2 MeSH descriptor: [Opioid‐Related Disorders] explode all trees
#3 #1 or #2
#4 MeSH descriptor: [Substance Withdrawal Syndrome] explode all trees
#5 detoxification:ti,ab,kw in Trials
#6 #4 or #5
#7 #3 and #6
Appendix 2. MEDLINE search strategy via Ovid Online
-
exp Opioid‐Related Disorders/
-
((opiate$ or opioid$ or heroin$ of narcot$) adj2 (abus$ or depend$)).ti,ab
-
exp Substance Withdrawal Syndrome/
-
(detoxifi$ or desintoxi$ or disintoxi$ or disintossi$).ti,ab
-
1 or 2
-
3 or 4
-
5 and 6
-
exp clinical trial/ or exp comparative study/
-
random$.ti,ab
-
exp Double‐Blind Method/
-
(double adj2 blind).ti,ab
-
8 or 9 or 10 or 11
-
7 and 12
-
Limit 13 to humans
Appendix 3. Embase search strategy
#1 'opiate addiction'/exp
#2 'heroin dependence'/exp
#3 (opiate* or opioid* or heroin* or narcot*) NEAR/2 (abus* or depend*)
#4 'withdrawal syndrome'/exp
#5 detoxifi*.ab,ti or desintoxi*.ab,ti or disintoxi*.ab,ti or disintossi*.ab,ti
#6 'drug detoxification'/exp
#7 #1 or #2 or #3
#8 #4 or #5 or #6
#9 #7 and #8
#10 'clinical study'/exp
#11 random*.ab,ti
#12 'double blind procedure'
#13 double NEAR/1 blind
#14 #10 or #11 or #12 or #13
#15 #9 and #14 AND [humans]/lim
Appendix 4. PsycINFO search strategy via Ovid Online
-
exp drug dependency/
-
exp heroin addiction/
-
((opiate$ or opioid$ or heroin$ of narcot$) adj2 (abus$ or depend$)).ti,ab
-
exp drug withdrawal/ or exp detoxification/
-
(detoxifi$ or desintoxi$ or disintoxi$ or disintossi$).ti,ab
-
1 or 2 or 3
-
4 or 5
-
6 and 7
-
limit 8 to human
-
exp clinical trials/
-
random$.ti,ab
-
(double adj2 blind).ti,ab
-
10 or 11 or 12
-
9 and 13
Appendix 5. Web of Science search strategy
-
TS="opioid‐related disorders"
-
TS=opiate addiction
-
TS=opiate depend*
-
TS=heroin* depend*
-
TS=heroin* addict*
-
#5 or #4 or #3 or #2 or #!
-
TS="substance withdrawal syndrome"
-
TX=detox*
-
#8 or #7
-
#9 and #6
-
TS=clinical trial*
-
TS=random*
-
TS=double blind
-
#13 or #12 or #11
-
#14 and #10
Appendix 6. Criteria for 'Risk of bias' assessment
| Item | Judgement | Description |
| 1. Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | The investigators describe a random component in the sequence generation process such as: random number table; computer random number generator; coin tossing; shuffling cards or envelopes; throwing dice; drawing of lots; minimisation |
| High risk | The investigators describe a non‐random component in the sequence generation process such as: odd or even date of birth; date (or day) of admission; hospital or clinic record number; alternation; judgement of the clinician; results of a laboratory test or a series of tests; availability of the intervention Observational prospective study | |
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk | |
| 2. Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Investigators enrolling participants could not foresee assignment because one of the following methods was used to conceal allocation: central allocation (including telephone, web‐based, and pharmacy‐controlled, randomisation); sequentially numbered drug containers of identical appearance; sequentially numbered, opaque, sealed envelopes. |
| High risk | Investigators enrolling participants could possibly foresee assignments because one of the following methods was used: open random allocation schedule (e.g. a list of random numbers); assignment envelopes without appropriate safeguards (e.g. if envelopes were unsealed or nonopaque or not sequentially numbered); alternation or rotation; date of birth; case record number; any other explicitly unconcealed procedure Observational prospective study | |
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk. This is usually the case if the method of concealment is not described or not described in sufficient detail to allow a definite judgement | |
| 3. Blinding of participants and providers (performance bias) ‐ Objective outcomes | Low risk | No blinding or incomplete blinding, but the review authors judge that the outcome is not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding Blinding of participants and key study personnel ensured, and unlikely that the blinding could have been broken |
| 4. Blinding of participants and providers (performance bias) ‐ Subjective outcomes | Low risk | Blinding of participants and providers and unlikely that the blinding could have been broken |
| High risk | No blinding or incomplete blinding, and the outcome is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding Blinding of participants and key study personnel attempted, but likely that the blinding could have been broken, and the outcome is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding | |
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk | |
| 5. Blinding of outcome assessor (detection bias) ‐ Objective outcomes | Low risk | No blinding of outcome assessment, but the review authors judge that the outcome measurement is not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding Blinding of outcome assessment ensured, and unlikely that the blinding could have been broken Record linkage |
| 6. Blinding of outcome assessor (detection bias) ‐ Subjective outcomes | Low risk | No blinding of outcome assessment, but the review authors judge that the outcome measurement is not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding Blinding of outcome assessment ensured, and unlikely that the blinding could have been broken |
| High risk | No blinding of outcome assessment, and the outcome measurement is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding Blinding of outcome assessment, but likely that the blinding could have been broken, and the outcome measurement is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding | |
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk | |
| 7. Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) For all outcomes except retention in treatment or dropout | Low risk | No missing outcome data Reasons for missing outcome data unlikely to be related to true outcome (for survival data, censoring unlikely to be introducing bias) Missing outcome data balanced in numbers across intervention groups, with similar reasons for missing data across groups For dichotomous outcome data, the proportion of missing outcomes compared with observed event risk not enough to have a clinically relevant impact on the intervention effect estimate For continuous outcome data, plausible effect size (difference in means or standardized difference in means) among missing outcomes not enough to have a clinically relevant impact on observed effect size Missing data have been imputed using appropriate methods All randomised participants are reported/analysed in the group they were allocated to by randomisation irrespective of non‐adherence and co‐interventions (intention‐to‐treat) |
| High risk | Reason for missing outcome data likely to be related to true outcome, with either imbalance in numbers or reasons for missing data across intervention groups For dichotomous outcome data, the proportion of missing outcomes compared with observed event risk enough to induce clinically relevant bias in intervention effect estimate For continuous outcome data, plausible effect size (difference in means or standardised difference in means) among missing outcomes enough to induce clinically relevant bias in observed effect size 'As‐treated' analysis done with substantial departure of the intervention received from that assigned at randomisation | |
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk (e.g. number randomised not stated, no reasons for missing data provided; number of dropouts not reported for each group) | |
| 8. Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The study protocol is available and all of the study's pre‐specified (primary and secondary) outcomes that are of interest in the review have been reported in the pre‐specified way The study protocol is not available but it is clear that the published reports include all expected outcomes, including those that were pre‐specified (convincing text of this nature may be uncommon) |
| High risk | Not all of the study's pre‐specified primary outcomes have been reported. One or more primary outcomes is reported using measurements, analysis methods or subsets of the data (e.g. subscales) that were not pre‐specified One or more reported primary outcomes were not pre‐specified (unless clear justification for their reporting is provided, such as an unexpected adverse effect) One or more outcomes of interest in the review are reported incompletely so that they cannot be entered in a meta‐analysis The study report fails to include results for a key outcome that would be expected to have been reported for such a study | |
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk | |
| 9. Other bias: comparability of cohorts for baseline characteristics and outcome measures on the basis of the design or analysis | Low risk | Exposed and non‐exposed individuals are matched in the design for most important confounding factors Authors demonstrated balance between groups for the confounders Analyses are adjusted for most important confounding factors and imbalance Randomised controlled trial |
| High risk | No matching or no adjustment for most important confounding factors | |
| Unclear risk | No information about comparability of cohorts | |
| 10. Other bias: selection of the non‐exposed (control) cohort | Low risk | The sample has been drawn from the same community as the exposed cohort |
| High risk | The sample has been drawn from a different source | |
| Unclear risk | No description of the derivation of the non‐exposed cohort | |
| 11. Other bias: protection against contamination | Low risk | Allocation was by community, institution or practice and it is unlikely that the control group received the intervention |
| High risk | It is likely that the control group received the intervention | |
| Unclear | It is possible that communication between intervention and control groups could have occurred |

Flow diagram of literature search

Methodological quality graph: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item presented as percentages across all included studies.
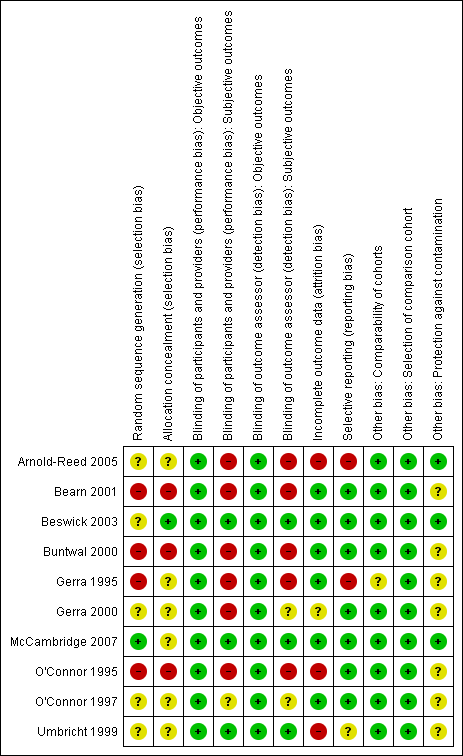
Methodological quality summary: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item for each included study.

Comparison 1 Antagonist‐adrenergic combination versus adrenergic agonist, Outcome 1 Peak withdrawal severity.

Comparison 1 Antagonist‐adrenergic combination versus adrenergic agonist, Outcome 2 Overall withdrawal severity.

Comparison 1 Antagonist‐adrenergic combination versus adrenergic agonist, Outcome 3 Completion rate.
| Antagonist‐adrenergic combination compared to adrenergic agonist for opioid withdrawal | |||
| Patient or population: opioid dependent adults | |||
| Outcomes | Impact | № of participants | Quality of the evidence |
| Peak withdrawal severity ‐ Naltrexone | In 1 study peak withdrawal severity was similar for the 2 types of intervention. In the other study peak withdrawal was more severe in the group receiving antagonist‐adrenergic combination. | 184 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ |
| Peak withdrawal severity ‐ Naloxone | This comparison reported by only 1 study, which found more severe withdrawal with naloxone‐clonidine combination. | 91 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ |
| Overall withdrawal severity ‐ Naltrexone | No difference in overall withdrawal severity for 2 studies; in 1 study overall severity significantly less for antagonist‐adrenergic combination. | 256 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ |
| Overall withdrawal severity ‐ Naloxone | This comparison reported by only 1 study, which found less severe overall withdrawal with naloxone‐lofexidine combination. | 49 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ |
| Completion rate ‐ Naltrexone | Completion rate with adrenergic agonist only ranged from 42% to 94%. Completion rate with antagonist‐adrenergic agonist combination ranged from 73% to 95% | 330 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ |
| Completion rate ‐ Naloxone | Completion rate with adrenergic agonist only ranged from 28% to 94%. Completion rate with antagonist‐adrenergic agonist combination ranged from 73% to 98% | 463 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | |||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | |||
| aOne study at high risk of bias. | |||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Peak withdrawal severity Show forest plot | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 Naltrexone | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 Naloxone | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Overall withdrawal severity Show forest plot | 4 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 Naltrexone | 3 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 Naloxone | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Completion rate Show forest plot | 9 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 Naltrexone | 4 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 Naloxone | 6 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |

