| 1.1 Depression (continuous) Show forest plot | 17 | | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.1.1 Short‐term FU (under 6 months) | 15 | 1247 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.45 [‐0.67, ‐0.22] |
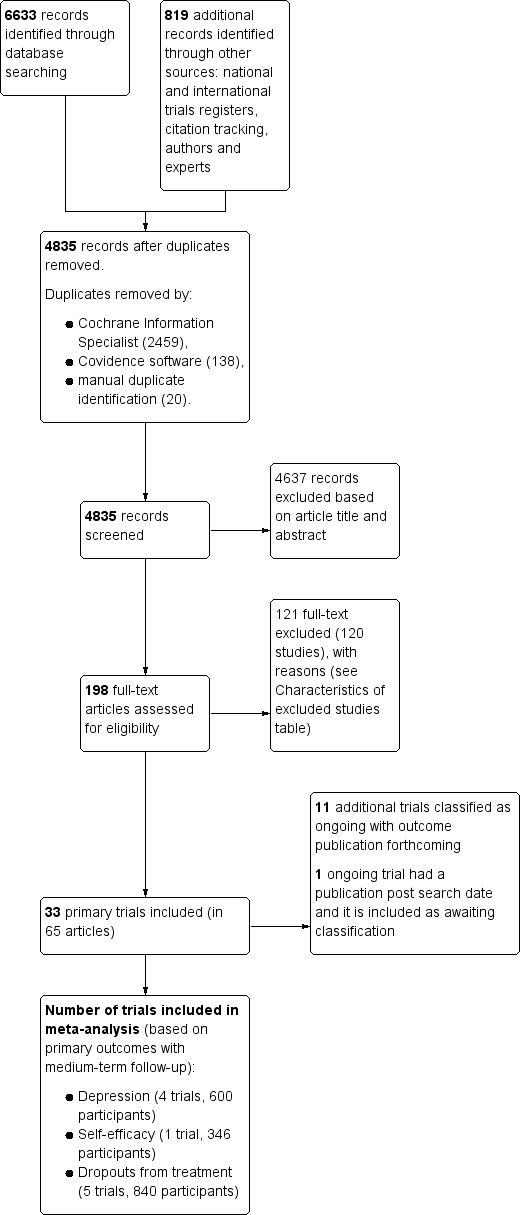
| 1.1.2 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 4 | 600 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.24 [‐0.47, ‐0.01] |
| 1.1.3 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 3 | 503 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.08 [‐0.30, 0.14] |
| 1.2 Depression (categorical) Show forest plot | 2 | | Odds Ratio (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.2.1 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 2 | 528 | Odds Ratio (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.68 [0.47, 0.98] |
| 1.2.2 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 1 | 195 | Odds Ratio (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.50 [0.29, 0.89] |
| 1.3 Depression (recruitment setting of participants) Show forest plot | 17 | 1729 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.36 [‐0.55, ‐0.17] |
|
| 1.3.1 Healthcare | 6 | 519 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.18 [‐0.38, 0.01] |
| 1.3.2 Community | 5 | 469 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.24 [‐0.62, 0.15] |
| 1.3.3 Shelter / refuge | 1 | 52 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.55 [‐1.13, 0.02] |
| 1.3.4 Various | 5 | 689 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.55 [‐0.96, ‐0.13] |
| 1.4 Depression (type of intervention) Show forest plot | 16 | 1604 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.24 [‐0.37, ‐0.11] |
|
| 1.4.1 Cognitive behavioral therapy | 4 | 262 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.31 [‐0.55, ‐0.06] |
| 1.4.2 Humanistic therapies | 4 | 161 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.47 [‐0.91, ‐0.03] |
| 1.4.3 Integrative therapies | 6 | 892 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.09 [‐0.23, 0.04] |
| 1.4.4 Other psychologically‐oriented interventions | 2 | 289 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.41 [‐0.99, 0.16] |
| 1.5 Depression (intensity of intervention) Show forest plot | 17 | 1729 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.36 [‐0.55, ‐0.17] |
|
| 1.5.1 Up to four sessions | 5 | 644 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.03 [‐0.18, 0.13] |
| 1.5.2 Five or more sessions | 12 | 1085 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.49 [‐0.73, ‐0.25] |
| 1.6 Depression (person delivering the intervention) Show forest plot | 15 | 1342 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.36 [‐0.57, ‐0.16] |
|
| 1.6.1 healthcare workers | 10 | 649 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.42 [‐0.73, ‐0.11] |
| 1.6.2 non‐healthcare workers | 5 | 693 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.21 [‐0.39, ‐0.03] |
| 1.7 Self‐efficacy Show forest plot | 4 | | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.7.1 Short‐term FU (under 6 months) | 3 | 279 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.20 [‐0.22, 0.63] |
| 1.7.2 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 1 | 346 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.12 [‐0.33, 0.09] |
| 1.7.3 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 1 | 331 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.23 [‐0.45, ‐0.01] |
| 1.8 Dropouts from treatment Show forest plot | 33 | | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.8.1 Short‐term FU (up to 6 months) | 22 | 3022 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.21 [0.98, 1.48] |
| 1.8.2 Medium‐term FU (6 to 12 months) | 5 | 840 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.75, 1.44] |
| 1.8.3 Long‐term FU (greater than 12 months) | 6 | 1655 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.08 [0.85, 1.38] |
| 1.9 Mental health Show forest plot | 4 | | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.9.1 Short‐term FU (under 6 months) | 2 | 353 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.34 [‐0.55, ‐0.13] |
| 1.9.2 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 2 | 219 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.11 [‐0.38, 0.16] |
| 1.9.3 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 2 | 355 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.27 [‐0.48, ‐0.06] |
| 1.10 Anxiety (continuous) Show forest plot | 5 | | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.10.1 Short‐term FU (under 6 months) | 4 | 158 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.96 [‐1.29, ‐0.63] |
| 1.10.2 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 1 | 166 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.20 [‐0.51, 0.10] |
| 1.11 Anxiety (categorical) Show forest plot | 1 | | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.11.1 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 1 | 192 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.45, 1.49] |
| 1.11.2 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 1 | 195 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.48, 1.57] |
| 1.12 Post‐traumatic stress disorder (continuous) Show forest plot | 10 | | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.12.1 Short‐term FU (under 6 months) | 9 | 1150 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.48 [‐0.80, ‐0.16] |
| 1.12.2 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 4 | 484 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.24 [‐0.54, 0.06] |
| 1.12.3 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 1 | 170 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.27 [‐0.57, 0.04] |
| 1.13 Quality of life Show forest plot | 4 | | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.13.1 Short‐term FU (under 6 months) | 2 | 382 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.16 [‐0.04, 0.36] |
| 1.13.2 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 2 | 557 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.10 [‐0.07, 0.27] |
| 1.13.3 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 4 | 699 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.11 [‐0.04, 0.25] |
| 1.14 Re‐exposure to IPV (continuous) Show forest plot | 9 | | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.14.1 Short‐term FU (under 6 months) | 7 | 749 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.00 [‐0.29, 0.29] |
| 1.14.2 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 2 | 547 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.03 [‐0.14, 0.20] |
| 1.14.3 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 4 | 837 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.07 [‐0.20, 0.07] |
| 1.15 Re‐exposure to IPV (categorical) Show forest plot | 7 | | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.15.1 Short‐term FU (under 6 months) | 5 | 797 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.45 [0.21, 0.96] |
| 1.15.2 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 1 | 186 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.55, 3.01] |
| 1.15.3 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 2 | 381 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.28, 2.11] |
| 1.16 Safety planning and/or safety behaviour (continuous) Show forest plot | 1 | | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.16.1 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 1 | 337 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.04 [‐0.18, 0.25] |
| 1.16.2 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 1 | 318 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.00 [‐0.22, 0.22] |
| 1.17 Safety planning and/or safety behaviour (categorical) Show forest plot | 2 | | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.17.1 Short‐term FU (under 6 months) | 1 | 138 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.38 [0.66, 2.89] |
| 1.17.2 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 1 | 191 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.68, 2.27] |
| 1.17.3 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 1 | 192 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 2.14 [1.18, 3.91] |
| 1.18 Use of healthcare and IPV services Show forest plot | 2 | | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.18.1 Short‐term FU (under 6 months) | 1 | 371 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.60 [0.68, 3.76] |
| 1.18.2 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 1 | 364 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.21 [0.44, 3.33] |
| 1.18.3 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 2 | 526 | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.79 [0.21, 2.97] |
| 1.19 Social support (continuous) Show forest plot | 2 | | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only |
|
| 1.19.1 Short‐term FU (under 6 months) | 2 | 245 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.31 [‐0.38, 1.00] |
| 1.19.2 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 2 | 235 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.05 [‐0.21, 0.31] |
| 1.20 Social support (categorical) Show forest plot | 1 | | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
|
| 1.20.1 Short‐term FU (under 6 months) | 1 | | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
| 1.20.2 Medium‐term FU (6 to under 12 months) | 1 | | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
| 1.20.3 Long‐term FU (12 months and above) | 1 | | Odds Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |