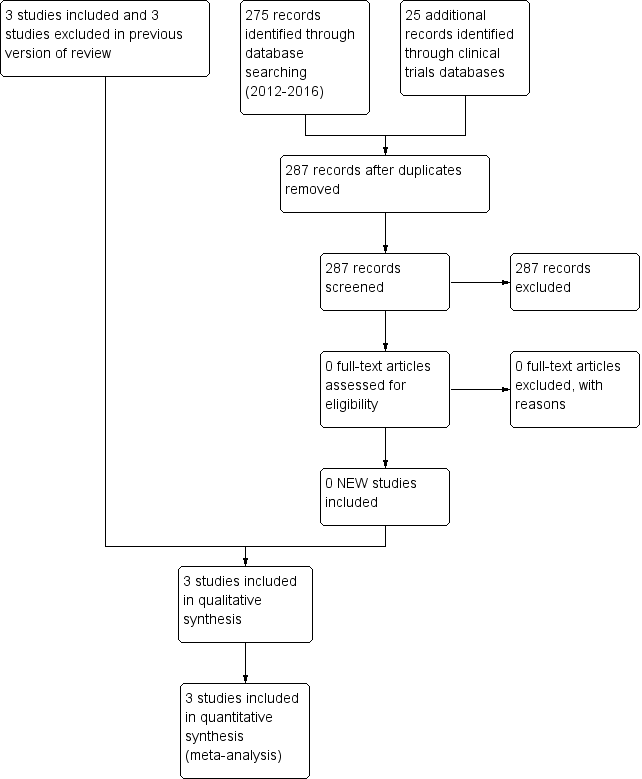
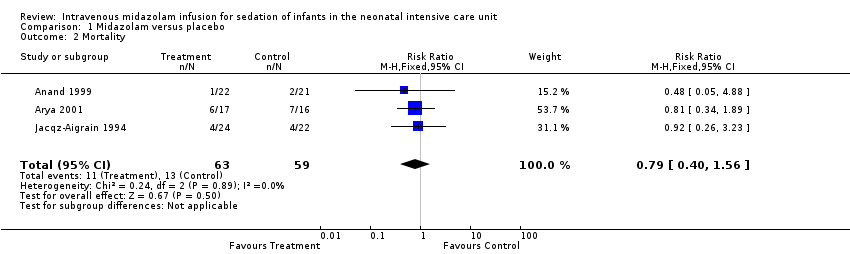
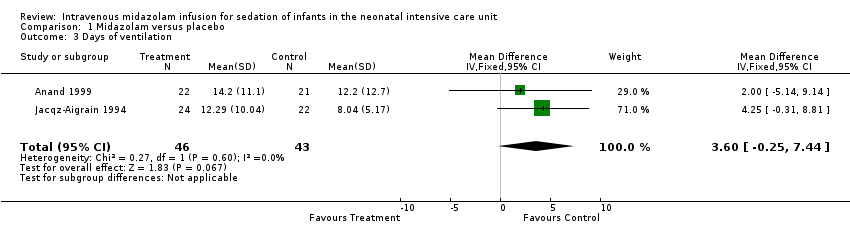
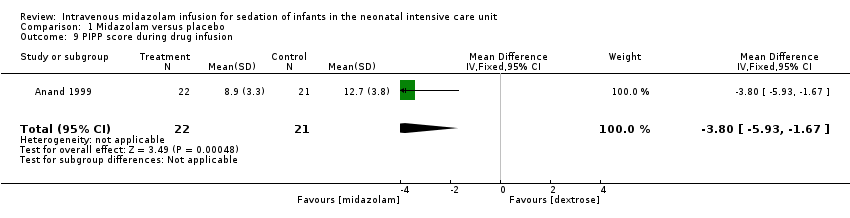
Related content
Related reviews and protocols
Abdulraoof Almadhoob, Arne Ohlssona | 27 January 2020
Olga Romantsik, Maria Grazia Calevo, Elisabeth Norman, Matteo Bruschettini | 10 May 2017
A. Semih Görk, Richard A Ehrenkranz, Michael B Bracken | 23 January 2008
Amy K Keir, Dominic Wilkinson, Chad Andersen, Michael J Stark | 20 January 2016
Chang Gao, Jacqueline Miller, Carmel T Collins, Alice R Rumbold | 20 November 2020
Kwi Moon, Gayatri K Athalye‐Jape, Uday Rao, Shripada C Rao | 8 April 2020
Adrienne Pahl, Leslie Young, Madge E Buus-Frank, Lenora Marcellus, Roger Soll | 21 December 2020
John C Sinclair, Marcela Bottino, Richard M Cowett | 5 October 2011
Marcela Bottino, Richard M Cowett, John C Sinclair | 5 October 2011
Iris Morag, Arne Ohlssona | 10 August 2016